Regonat 40mg Bottle Of 28 Tablets
Description
Regonat tablet is used in the treatment of colon and rectal cancer. It contains regorafenib as its main ingredient. Regonat Tablet should be taken with food, and it is advisable to take it at the same time every day to maximise benefits.
The most common side effects of this medicine include infection, low blood platelet count, anaemia, decreased appetite, hemorrhage, and high blood pressure. If any of these side effects trouble you, inform your doctor.
Regular blood tests are necessary to monitor your blood cells and liver function. Many other medications can interact with this medicine, so be sure to inform your healthcare team about all the medications you are taking.
This medicine is not recommended during pregnancy or while breastfeeding. Effective contraception for both males and females is important during treatment to prevent pregnancy.
Product Summary
| Offer Price | ₹7703.44 |
| You Save | ₹1577.81 (17% on MRP) |
| Contains | Regorafenib(40.0 Mg) |
| Uses | Cancer of colon and rectum |
| Side effects | Low blood platelets, anemia, decreased appetite, hemorrhage, and high blood pressure |
| Therapy | ANTI-NEOPLASTIC |
Uses
Contraindications
Side effects
- Diarrhoea
- Stomatitis
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Thrombocytopenia
- Anaemia
- Decreased appetite and food intake
- Haemorrhage
- Hypertension
- Dysphonia
- Hyperbilirubinaemia
- Increase in transaminases
- Rash
- Weight loss
Precautions and Warnings
Pregnancy
Breast Feeding
Driving
Other General Warnings
- You have liver disease or a history of liver problems.
- You have a history of Gilbert's syndrome.
- You have an active infection or develop signs of an infection that worsen.
- You have a condition that predisposes you to bleeding.
- You are taking blood thinners (anticoagulants) like warfarin or phenprocoumon.
- You have liver cirrhosis.
- You develop severe abdominal pain.
- You have unstable angina, new-onset angina (within the last 3 months), or a recent heart attack (within the last 6 months).
- You have heart failure (NYHA Class 2 or higher).
- You have a history of ischemic heart disease and experience new or worsening chest pain or other signs of reduced blood flow to the heart.
- You experience seizures, severe headaches, altered mental status, vision changes, or cortical blindness, possibly with high blood pressure.
- You have high blood pressure that is not well controlled.
- You have risk factors for aneurysms or artery dissections, such as high blood pressure or a history of aneurysm.
- You develop signs of Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA) such as fatigue, fever, confusion, decreased urination, or bruising easily.
- You are scheduled for major surgery.
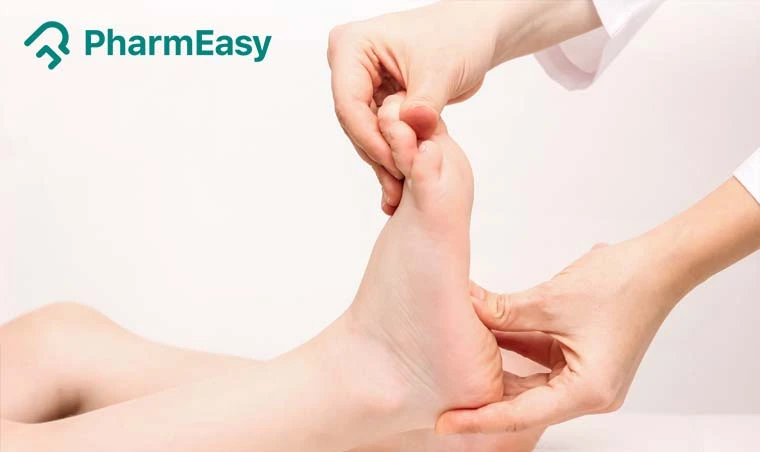
- You develop a severe or persistent skin rash, especially on your hands and feet (Hand-Foot Skin Reaction).
- You experience persistent or recurrent significant changes in your blood electrolyte levels (e.g., low phosphate, calcium, sodium, or potassium).
- You experience persistent or recurrent significant changes in thyroid-stimulating hormone, lipase, or amylase levels.
- You are on a low-sodium diet.
- You have a known allergy to soya or lecithin derived from soya.
Directions for Use
Storage and disposal
Dosage
Overdose
Missed a Dose
Mode of Action
How Does It Work?
Interactions
Interactions with other medicines
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Strong inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, clarithromycin, grapefruit juice) can increase regorafenib exposure and decrease active metabolite exposure. Avoid concomitant use.
- UGT1A9 Inhibitors: Strong inhibitors (e.g., mefenamic acid, diflunisal) should be avoided due to potential unknown effects on regorafenib and metabolite levels.
- CYP3A4 Inducers: Strong inducers (e.g., rifampicin, phenytoin, St. John's Wort) can decrease regorafenib exposure and increase one active metabolite. Avoid or consider alternative medications.
- UGT1A1/9 Substrates: Regorafenib can increase the exposure of drugs metabolized by these enzymes (e.g., irinotecan's active metabolite SN-38).
- BCRP Substrates: Regorafenib can significantly increase the plasma concentrations of BCRP substrates (e.g., rosuvastatin, methotrexate). Monitor for increased side effects.
- P-glycoprotein Substrates: No clinically significant interaction observed with digoxin.
- P-glycoprotein and BCRP Inhibitors/Inducers: May affect the exposure of regorafenib's active metabolites (M-2 and M-5); clinical significance is unknown.
- CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2B6, CYP3A4, CYP2C19 Substrates: No clinically meaningful drug interaction expected.
- Antibiotics (Neomycin): Can significantly decrease the exposure of active metabolites M-2 and M-5, potentially reducing regorafenib efficacy.
- Bile Salt-Sequestering Agents: May decrease regorafenib absorption, potentially reducing efficacy.
Content Details
Ravindra Ghongade
B. Pharm
Dr. Nikita Toshi
BDS (Bachelor of Dental Surgery), WHO FIDES member
Did you find this medicine information helpful?
Please rate your experience