COVID-19 Vaccinations: A Quick Guide
By Richa Arora +2 more

Get,

to manage your symptom
Get your,


4 Cr+ families
benefitted

OTP sent to 9988776655



You’ve successfully subscribed to receive
doctor-approved tips on
Whatsapp

Get ready to feel your best.

Hi There,



Register to Avail the Offer
Send OTPBy continuing, you agree with our Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions

Hi There,

Trusted by 4 crore+ families

OTP sent to 9988776655



You have unlocked 25% off on medicines




Code: NU25

By Richa Arora +2 more
Table of Contents
COVID-19 is a viral infection caused by a family of viruses called the Coronaviruses, resulting in specific flu-like symptoms such as common cold and fever. These viruses have also been the causative agents, earlier for the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) and severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), which had plagued certain parts of the world not many years ago.
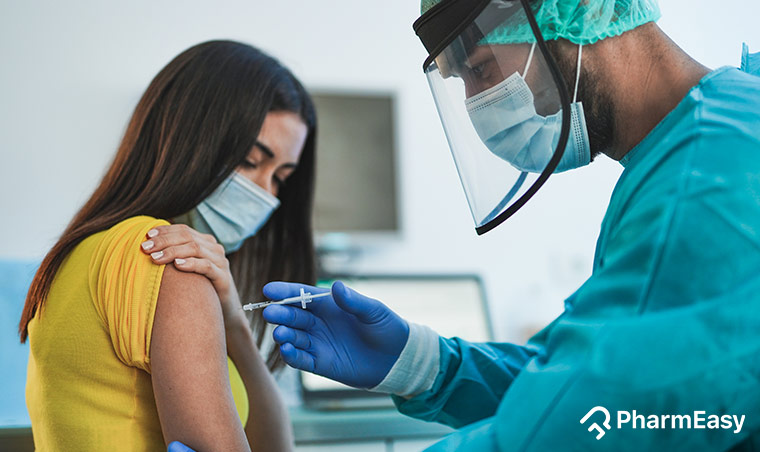
COVID -19, the new coronavirus strain, was identified in China and spread from being an epidemic to a pandemic of enormous proportions. The viral strain is now known as Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and due to its origin in 2019, was named COVID-19. The full form of COVID-19 is Coronavirus disease 2019.
The symptoms and signs of COVID-19 would generally appear within the first two weeks of contact and infection with the virus. The common symptoms of the viral infection are:
You may also experience other symptoms such as:
You can prevent getting infected by the SARS-CoV-2 virus by following these instructions:
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Pfizer and Moderna, among a few other vaccines for immediate administration in the United States of America. Similarly, in India too vaccines such as Covishield and Covaxin have been approved for administration.
Each vaccine is different in terms of offering protection and immunity to the body. The body is triggered to generate a ”memory” B and T-lymphocytes expected to offer lasting immunity.
Hence, the body takes a few weeks to produce the B and T-lymphocytes. In some cases, the vaccinated individual may also experience fever and body pain in developing immunity. Rest assured, these signs are entirely normal.
Immunity can be triggered to generate these specific cell types by vaccinating. In this regard, several vaccine types have been developed. Presently, there are three main types of COVID-19 vaccines recommended. These are:
mRNA is the coding genetic material of the body that is directly transcribed into proteins. Therefore, the mRNA vaccines contain the virus’s genetic material that carries instructions to transcribe a harmless unique protein.
When recognised by the body’s defence mechanism, this protein is destroyed, followed by the generation of the protein in the body to destroy viral protein The cells develop a memory to identify it in the event of an infection.
Vector vaccines are a modified version of another virus that closely resembles SARS-Cov-2. The genetic material inside the shell of the modified virus contains a segment of SARS-CoV-2 and is hence called a viral vector. When injected, the genetic material is transcribed into a protein. The body’s immune system eliminates the foreign protein and generates the memory of B and T-lymphocytes for any infection in the future.
As the name suggests, the protein subunit vaccines are harmless segments of the viral protein instead of the whole viral protein injected into the body. The immune system recognises the foreign protein and builds the memory repertoire for any future infections.
The COVID-19 vaccine builds immunity post-vaccination. Despite the apparent benefits, you may experience some side effects post-vaccination, which are entirely normal. These side effects last only a couple of days and may mildly affect your daily activities. These side effects are:
The arrival of new forms of vaccines has been accompanied by many common myths that have prevented many people from getting vaccinated. Some of the myth busters are outlined here. These are:
Some vaccines that have been manufactured require more than one shot to develop adequate immunity in the body. These are:
The bottom line is that out of all the precautions, vaccinations are considered a step closer to protection than the other preventative measures. It is vital for people who are ill or have comorbidities and can significantly reduce mortality.
Therefore, post-vaccination, you may be able to perform a lot more activities than you could before vaccination. This, however, does not rule out the fact that you must not let your guard down. You must continue to observe all measures, not just for yourselves but also for the people around you.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.

Leave your comment...
Comments