What are Piles?
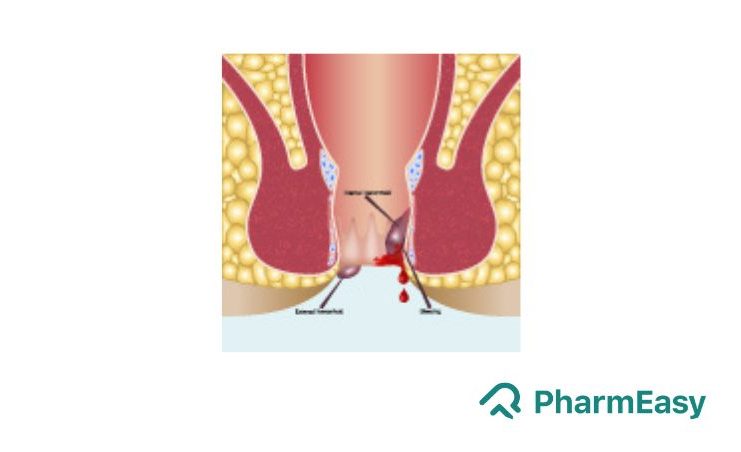
Piles or haemorrhoids are a common condition but can be an embarrassing and unpleasant topic. They are characterised by swollen and enlarged veins present in the anal area causing a great deal of discomfort. In India, piles are known to affect nearly 40 million people but the true incidence is not known due to cultural and socio-economic reasons. Depending upon their location, piles can be internal (found inside the rectal region) or external (found on the skin near the anal region). Depending upon the appearance and whether the haemorrhoids prolapse (bulge out of the rectum) or not, internal haemorrhoids are further classified into four stages. The different stages of piles are described as below:
- First-degree (early stage) haemorrhoids bleed but do not prolapse
- Second-degree haemorrhoids prolapse but return to the original state quickly
- Third-degree where they prolapse but can be reduced by surgeries
- Fourth-degree where they are permanently prolapsed and cannot be reduced1-3
Symptoms1
Following are the symptoms of piles starting stage:
- Pain and bleeding during bowel movements
- Itching, burning, and pain sensations near the rectum and anal region
- Pain in or around the anal region
If you have any of the above complaints, you should seek proper consultation from your doctor or proctologist for proper management of early-stage piles symptoms.
Causes
In the early stages of piles, it is believed that advancing age may cause the supporting tissues in the anal canal to become weak and chronic constipation may exert pressure on the tissues in the anal canal resulting in the piles.2
Also Read: What is a Sitz Bath: Understanding the Benefits and Uses
Risk factors:
1. Diet-related:
- Spicy food
- Low-fibre diet
- Consumption of alcohol
2. Diseases/conditions
- Constipation
- Obesity
- Diarrhoea
Others
Complications4
- Incarcerated prolapsed internal haemorrhoid in which internal haemorrhoids move outside the anus.
- Perianal thrombosis characterised by a clot or a bulge near the edge of anal region which can be extremely painful.
- Recurrence of haemorrhoids2
- Urinary retention3
- Skin tags or skin outgrowths3
Diagnosis3
- Your doctor will take a detailed history and thorough physical examination before confirming piles.
- He may do a digital rectal examination to assess the presence of blood. If still a confirmed diagnosis cannot be made, your doctor or proctologist will use the necessary instruments.
Read More: 8 Best Home Remedies For Piles
Treatment
- Dietary recommendations5
- Add high-fibre foods to your diet like fruits, vegetables, lentils, etc.
- Drink plenty of fluids (4-5 glasses of water or any non-caffeinated or non-sugary drink)
- Reduce the consumption of fatty and fried foods.
- Eat frequently at regular time intervals daily say after every 3-4 hours.
- Lifestyle modifications:6
- Exercise: having a sedentary lifestyle may increase the risk of piles, thus you should do moderate aerobic exercises like brisk walking and swimming for 20-30 minutes a day. Also, you can consult a qualified yoga trainer to learn about yogasanas which may help in improving abdominal and rectal tissue. Avoid sitting immediately after having food.
- Behavioral recommendations:5
- Wash each time after passing stools.
- Avoid sitting for a long duration on the toilet seat.
- Avoid using soaps to wash the anal area
- Make a habit of emptying your bladder completely.
- Do not ignore the urge to pass stool
- Topical relief:6
- Placing an ice pack for a few minutes near the anal region may help reduce swelling and pain
- Sitz bath: after each bowel movement, a 20-minute warm water bath for the hips and buttocks. Dry the anal region afterwards gently.
- Many over-the-counter medications like creams, ointments, wipes and lotions are available which can be topically applied for a soothing effect.
- Non-surgical treatment: 5
- Rubber band ligation
- Sclerotherapy
- Infrared coagulation
- Radiofrequency ablation
If still the symptoms do not resolve, surgical excision of the piles may be needed.
Read More: What is the Cost of Piles Surgery in India?
Conclusion
Piles or hemorrhoids are a common condition characterised by swollen and enlarged veins present in the anal canal. Depending on the location, piles are classified as internal or external haemorrhoids. Internal haemorrhoids depending on their severity are again classified into different stages like I, II, III, and IV. During the early stages of piles (grade I), the management starts with conservative measures that include avoiding constipation by dietary and behavioral recommendations, exercises, topical medications, and oral medications.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1] What is the piles starting stage?The starting stage of piles or Grade I is characterised by piles associated with bleeding which do not prolapse.1
2] What is the piles fourth stage?Piles fourth stage is characterised by permanently prolapsed haemorrhoids which cannot be corrected.1
3] What are the piles initial stages symptoms?
Piles initial stages symptoms may be associated with bleeding stools, itching, and pain, burning sensation in the anal region.1
4] Which is the best homeopathic medicine for stage 3 piles?Although many homeopathic medicines are available in the market for symptomatic relief from piles. It is best to buy a preparation after consulting with your doctor or proctologist.5
5] Can piles be cured at the starting stage?Yes, during the early stages of piles (grade I), appropriate conservative management which includes avoiding constipation by dietary and behavioral recommendations, exercises, topical medications, and oral medications may help. Hence, you should consult a doctor at the earliest stage.
Disclaimer
The information provided at this site is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by any healthcare professional. As per unique individual needs, the reader should consult his/her physician to determine the appropriateness of the information provided for his/her situation.
References:
- Staroselsky A, Nava-Ocampo AA, Vohra S, Koren G. Hemorrhoids in pregnancy. Canadian Family Physician. 2008 Feb 1; 54(2):189-90. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2278306/
- Das KD, Ghosh S, Das AK, Ghosh A, Mondal R, Banerjee T, Ali SS, Ali SS, Koley M, Saha S. Treatment of hemorrhoids with individualized homeopathy: An open observational pilot study. Journal of intercultural ethnopharmacology. 2016 Sep; 5(4):335. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5061475/
- Acheson AG, Scholefield JH. Management of haemorrhoids. Bmj. 2008 Feb 14; 336(7640):380-3. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2244760/
- Slauf P, Antoš F, Marx J. Complications of hemorrhoids. Rozhledy v chirurgii: mesicnik Ceskoslovenske chirurgicke spolecnosti. 2014 Apr 1; 93(4):223-5. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24881480/
- Lohsiriwat V. Hemorrhoids: from basic pathophysiology to clinical management. World journal of gastroenterology: WJG. 2012 May 5; 18(17):2009. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3342598/
- De Marco S, Tiso D. Lifestyle and risk factors in hemorrhoidal disease. Frontiers in Surgery. 2021 Aug 18; 8:729166. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8416428/








Comments