Key Highlights:
- Love handles are deposits of fat around the waist, caused by factors such as hormones, stress, lack of sleep, and an unhealthy lifestyle.
- Cutting out added sugar, increasing fiber and protein intake, and staying hydrated may help reducing love handles.
- A mix of cardiovascular exercises, weightlifting, and whole-body workouts may help in shedding love handles.
- Leading an active day-to-day life, including non-exercise activity thermogenesis (NEAT), is crucial for overall weight loss.
- Using a balanced diet and lifestyle habits like moderate alcohol intake, mindful eating, and stress reduction may contribute to losing love handles.
Introduction
Many people have love handles that seem to stick around, no matter how much exercise or diet modification. Love handles often occur due to fat retention in the waist and hip area, creating an unflattering bulge over the waistband of our pants, skirts, and other clothing items. Understanding the causes and adopting lifestyle changes may help in reducing this unwanted body fat.
In this article , we will explore simple and natural ways that may help reduce love handles through a combination of a healthy diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes. We will also address some common questions related to this topic.
Understanding Love Handles
Before learning how to lose love handles, it is essential to understand what they are, why they form, and the potential health risks they may pose.
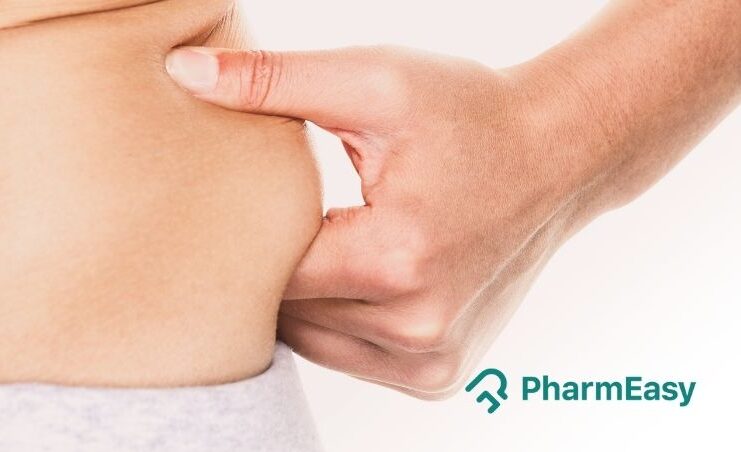
Love handles, also known as muffin tops, refer to excess fat deposits around the waist and hips. This fat can accumulate over time due to various factors, giving an unsightly appearance cascading over the edge of clothing items.
Causes of love handles
Several factors can contribute to the formation of love handles, these are discussed below.
1. Hormones
Hormonal imbalances may lead to fat accumulation, especially around the abdominal area, hips, and lower back. An overproduction or underproduction of certain hormones may affect appetite, metabolism, and body fat distribution. Hormones like insulin, cortisol, etc are responsible.
2. Sleep deprivation and stress
Both sleep deprivation and stress can elevate cortisol levels, also known as the “stress hormone.” High cortisol levels have been linked with weight gain, particularly in the abdominal area.
3. Age
Age is another contributing factor for love handle formation since body composition tends to change as people age. With age, muscle mass decreases, and body fat accumulates more readily resulting in fat accumulation around the hips and waist.
4. Physical inactivity
A sedentary lifestyle may contribute to love handle development. Insufficient physical activity coupled with a high-calorie diet may lead to excess fat accumulation.
5. Medical conditions
Specific medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism, can cause weight gain and contribute to the development of love handles. Addressing the underlying condition through appropriate management may help manage unwanted fat accumulation.
6. Potential health risks
Although love handles themselves are not dangerous, excess fat accumulation could potentially lead to obesity and related health risks. Excess fat in the abdominal area, known as visceral fat, is linked with several health issues, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer.
Researchers have found that the lack of exercise or persistent physical inactivity may affect the development of love handles. An individual may start to gain body fat if they do not burn off more calories than they take in. A diet rich in fats, sweets, and high-calorie foods may also contribute to fat gain in addition to inactivity. I strongly recommend indulging in regular physical activity such as cycling and a proper healthy diet to keep love handles at bay.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Nutrition for Reducing Love Handles
Proper nutrition plays a big part in overall fat loss, including love handles. Here are some diet tips to help you lose those stubborn love handles.
1. Cut out added sugar
One good way that may help manage weight loss and love handle reduction is to remove added sugar from your diet. Foods high in added sugar, like cookies, cakes, and soda, not only contain empty calories but can also lead to weight gain, specifically in the belly area. Instead, go for natural sugars found in whole foods like fruits.
2. Focus on healthy fats
Adding healthy fats like avocados, olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish into your diet may help you stay full longer. This leads to fewer calories eaten throughout the day. These nutrient-rich foods may also help with weight loss, and thus help you get rid of love handles.
3. Fill up on fiber
Foods rich in soluble fiber may help you lose weight. They do this by keeping you full for longer and reducing calorie intake. Some examples of fiber-rich foods are beans, lentils, oats, and fruits like apples and pears.
4. Increase protein intake
Adding high-quality protein sources to your meals is critical for losing fat and keeping a healthy weight. Protein keeps you full for longer and lessens hunger between meals. Lean proteins like chicken, turkey, fish, tofu, and legumes may help you to lose excess fat around the waist, reducing love handles.
5. Drink water to stay hydrated
Staying hydrated is critical for overall health and weight loss. Drinking enough water may keep dehydration at bay and reduce fluid retention, which may make love handles appear worse. Try to drink at least eight glasses of water each day and pick water over sugary drinks like soda and juice.
6. Add in complex carbohydrates
Swap refined carbohydrates like white bread, pasta, and rice for nutrient-rich complex carbohydrates like sweet potatoes, quinoa, beans, oats, and whole-grain products. Complex carbohydrates keep you satisfied and control blood sugar levels, contributing to weight loss and love handle reduction.
7. Eat whole foods
Eating a balanced diet full of whole, unprocessed foods is an excellent way to lose love handles. Include a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your meals. It will provide essential nutrients and may promote weight loss.
Exercise Strategies to Get Rid of Love Handles
Adding regular exercises that focus on whole-body movements and strengthen the core may help reduce love handles. While you cannot spot-target fat reduction, combining cardiovascular exercises and strength training may lead to overall weight loss, and shrinking love handles.
1. Increase cardio workouts
Cardio exercises may burn calories and cut down excess fat. Running, cycling, and swimming are especially good for people looking to trim their waistlines. Try for at least 150 minutes of medium-intensity cardio or 75 minutes of high-intensity cardio each week.
2. Try HIIT workouts
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) involves bouts of intense aerobic exercise followed by a recovery phase. This type of workout may help burning fat, including belly fat. Adding HIIT workouts to your routine may help get rid of love handles faster than usual steady-state cardio.
3. Lift weights
Weight training may build muscle and increase your metabolism. It leads to more calories burned when resting. Combining weightlifting with cardio has been shown to help reduce belly fat. Ultimately, it may help you lose love handles.
Stress coupled with a lack of sleep have a potential impact on cortisol levels. A glucocorticoid called cortisol may impact metabolism, increase appetite, and make the body store extra fat. In my opinion, one should ensure they get enough sleep to keep the cortisol levels in check.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D
4. Add in whole-body moves
Exercises that work the entire body, like burpees or battle rope exercises, may help burn more calories than traditional isolation exercises. Doing whole-body workouts may lead to losing more weight, ultimately slimming down love handles.
5. Engage your core with specific exercises
While you cannot target love handles directly, adding core-strengthening exercises like bicycle crunches, side planks, mountain climbers, and Russian twists may boost muscle tone and help with fat loss overall.
6. Incorporate Pilates and yoga for mind-body connection
Adding pilates and yoga to your workout routine may improve flexibility, posture, and core strength. All are crucial in losing love handles. Pilates and yoga also help reduce stress and enhance mental well-being, supporting weight loss efforts.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Love Handles
In addition to exercise and proper nutrition, making specific lifestyle changes may further help you lose love handles. Here are some tips for making lasting changes.
1. Move throughout the day
Increasing physical activity in your daily life is crucial for weight loss. Take breaks from sitting, walk to nearby locations, and incorporate stretching exercises throughout the day. Staying active may burn more calories and help reduce love handles.
2. Reduce stress through mindfulness and meditation
Stress raises cortisol production that can lead to weight gain, particularly around the waist. Add practices like mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing into your daily routine to lower cortisol and support weight loss.
3. Practice mindful eating
Paying attention to hunger and fullness hints, eating slowly without distractions, and understanding how food impacts your mood and health may aid your weight loss journey. Mindful eating lets you regain control of your eating habits, supporting love handle reduction.
4. Get enough sleep
Lack of enough sleep raises cortisol rates, leading to weight gain. Aim for 7-8 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night to lessen weight gain and promote good health.
5. Seek support from professionals if needed
If you’re finding it hard to lose love handles alone, consider getting help from healthcare professionals, nutritionists, dieticians, or personal trainers. They offer advice, and resources, and hold you accountable, helping you meet your weight loss aims. It is always advised not to starve yourself in the pursuit of trying to get rid of love handles.
The Role of Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT)
What is NEAT?
Non-exercise activity thermogenesis (NEAT) refers to the calories you burn on daily activities that aren’t exercise, such as walking, cleaning, or fidgeting at your desk. Adding more NEAT into your life may make a big impact on your weight loss efforts, thus helping with overall love handle reduction.
Benefits of increasing NEAT
Increasing NEAT may boost your daily calorie burn, leading to better weight management and reduced love handles. It may also help improve your energy levels, mood, and overall health.
Ways to incorporate more NEAT into daily life
- Take regular walking breaks during your workday.
- Use stairs instead of elevators or escalators.
- Stand up while talking on the phone or during meetings.
- Park farther away from your destination to increase walking distance.
- Engage in household chores like cleaning, gardening, or washing dishes.
The Link Between Love Handles and Stress
How stress contributes to love handle formation?
Long-term stress leads to high cortisol levels that can cause weight gain, particularly in the belly region. Excess cortisol may increase appetite, leading to overeating and fat pile-up around the waist, contributing to love handle buildup.
Tips for stress management that may help reduce love handles
- Incorporate mindfulness practices like deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation.
- Exercise regularly, as physical activity can help release endorphins and alleviate stress.
- Connect with friends and family for emotional support.
- Develop healthy coping mechanisms for dealing with stress, such as journaling or engaging in hobbies.
- Prioritize self-care, ensuring you get enough sleep and maintain a healthy diet.
Also Read: How To Get Rid Of A Muffin Top: Effective Strategies Backed By Fitness Experts
Conclusion
In summary, to manage love handles, adopt a mix of a healthy diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle changes. By incorporating whole-body workouts, mindful eating, stress reduction practices, and an active lifestyle, you may effectively get rid of love handles and enjoy a slimmer waistline. If weight loss is not occurring, don’t start starving yourself to lose weight. Contact your doctor who will guide you. Remember that patience and commitment are key to achieving your weight loss goals and maintaining long-term success.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
What causes love handles? Love handles are caused by an accumulation of fat around the waist and hips due to factors like hormonal imbalances, stress, lack of sleep, aging, and an unhealthy lifestyle.
Are love handles genetic? While there may be a genetic predisposition to store fat in certain areas of the body, anyone can develop love handles due to lifestyle factors like poor diet, lack of exercise, and prolonged stress.
Can you get rid of love handles? It is possible to reduce love handles through a combination of a healthy diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle changes.
How long does it take to get rid of love handles? Weight loss varies for each individual, but a consistent and moderate approach to diet and exercise may help you see positive results within a few weeks.
What exercises help in reducing love handles? Exercises like bicycle crunches, side planks, mountain climbers, and Russian twists can target the core area which may help in overall fat reduction.
How can I lose my love handles fast? There is no quick fix for losing love handles. Give thorough attention to consistency, patience, and a combination of a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management for the best result.
How do you get rid of love handles belly fat? Losing love handles and belly fat needs an approach with many fronts, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and good sleep.
Can love handles go away completely? While some people may find it hard to get rid of love handles entirely due to genetic reasons, lifestyle changes may greatly reduce their appearance.
References:
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Added sugar intake and metabolic syndrome in US adolescents: cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005-2012 [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26932353
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Added sugar intake and cardiovascular diseases mortality among US adults [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24493081
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Added fructose: a principal driver of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its consequences [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25639270
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption Is Associated with Abdominal Fat Partitioning in Healthy Adults 1, 2, 3 [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4093984
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Consuming fructose-sweetened, not glucose-sweetened, beverages increases visceral adiposity and lipids and decreases insulin sensitivity in overweight/obese humans [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2673878
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Greater fructose consumption is associated with cardiometabolic risk markers and visceral adiposity in adolescents [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22190023
- The Lancet. Retracted: Effect of a high-fat Mediterranean diet on bodyweight and waist circumference: a prespecified secondary outcomes analysis of the PREDIMED randomised controlled trial [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: http://www.thelancet.com/journals/landia/article/PIIS2213-8587(16)30085-7
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Avocado consumption is associated with better diet quality and nutrient intake, and lower metabolic syndrome risk in US adults: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2001-2008 [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23282226
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Fiber intake predicts ghrelin levels in overweight and obese postmenopausal women [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19369431
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3577372
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Stress and the gut: pathophysiology, clinical consequences, diagnostic approach and treatment options [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22314561
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Migraine: Maladaptive Brain Responses to Stress [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3475609
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Child Anxiety Symptoms Related to Longitudinal Cortisol Trajectories and Acute Stress Responses: Evidence of Developmental Stress Sensitization [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4351756
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Stress and abdominal Fat: Preliminary Evidence of Moderation by the Cortisol awakening Response in Hispanic Peripubertal Girls [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3107005
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Stress, cortisol, and obesity: a role for cortisol responsiveness in identifying individuals prone to obesity [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27345309
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Cortisol, obesity and the metabolic syndrome: A cross-sectional study of obese subjects and review of the literature [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3602916
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Cortisol and antidepressant effects of yoga [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3768222
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Effects of mindfulness meditation on serum cortisol of medical students [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23724462
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). The effect of 12 weeks of aerobic, resistance or combination exercise training on cardiovascular risk factors in the overweight and obese in a randomized trial [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3487794
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Sleep Duration and Five-Year Abdominal Fat Accumulation in a Minority Cohort:The IRAS Family Study [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2831422
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Sleep duration as a risk factor for diabetes incidence in a large U.S. sample [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18246976
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Meta-analysis of short sleep duration and obesity in children and adults [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18517032
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). The effect of abdominal exercise on abdominal fat [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21804427
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Comparison of the acute metabolic responses to traditional resistance, body-weight, and battling rope exercises [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24942174
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). The effects of consuming frequent, higher protein meals on appetite and satiety during weight loss in overweight/obese men [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20847729
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Increased protein intake and meal frequency reduces abdominal fat during energy balance and energy deficit [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23703835
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). High protein diets decrease total and abdominal fat and improve CVD risk profile in overweight and obese men and women with elevated triacylglycerol [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19179060
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Weight loss maintenance in overweight subjects on ad libitum diets with high or low protein content and glycemic index: the DIOGENES trial 12-month results [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24675714
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Aerobic exercise alone results in clinically significant weight loss for men and women: Midwest Exercise Trial-2 [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3630467
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption Is Associated With Change of Visceral Adipose Tissue Over 6 Years of Follow-Up [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26755505
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Sugar-sweetened and diet beverages in relation to visceral adipose tissue [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21901024
- JAMA Network. Sugar-Sweetened Beverages, Weight Gain, and Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in Young and Middle-Aged Women [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/199317
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Effects of dietary pulse consumption on body weight: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27030531
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Short- and Long-Term Effects of Wholegrain Oat Intake on Weight Management and Glucolipid Metabolism in Overweight Type-2 Diabetics: A Randomized Control Trial [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5037534
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Instant Oatmeal Increases Satiety and Reduces Energy Intake Compared to a Ready-to-Eat Oat-Based Breakfast Cereal: A Randomized Crossover Trial [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4674378
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). High intensity training in obesity: a Meta‐analysis [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5598019
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Caloric expenditure of aerobic, resistance, or combined high-intensity interval training using a hydraulic resistance system in healthy men [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25162652
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Mindfulness Intervention for Stress Eating to Reduce Cortisol and Abdominal Fat among Overweight and Obese Women: An Exploratory Randomized Controlled Study [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3184496
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). A randomized trial of an acceptance-based behavioral intervention for weight loss in people with high internal disinhibition [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27804255
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). An acceptance-based behavioral intervention for weight loss: a pilot study [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22440077
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Pilates: how does it work and who needs it? [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3666467
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). The effect of Pilates exercise on body composition in sedentary overweight and obese women [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27607588
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Effects of a mat Pilates programme on body composition in elderly women [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24756739
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Alcohol Consumption and Obesity: An Update [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4338356
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Alcohol consumption and body weight [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19548203
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Ultra-processed foods and added sugars in the US diet: evidence from a nationally representative cross-sectional study [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4785287
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Fried Food Consumption and Cardiovascular Health: A Review of Current Evidence [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4632424
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Consumption of ready-made meals and increased risk of obesity: findings from the Observation of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Luxembourg (ORISCAV-LUX) study [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4302389
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Body Fat Distribution Ratios and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Severity in Youth With Obesity [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5359330
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). High-Intensity Intermittent Exercise and Fat Loss [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2991639
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Healthy Weight [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/managing/healthy-weight.html
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Linea Semilunaris [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555983
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Healthy Eating for a Healthy Weight [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 27]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/healthy_eating/index.html
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.








Comments