What are Thrombosed Haemorrhoids?
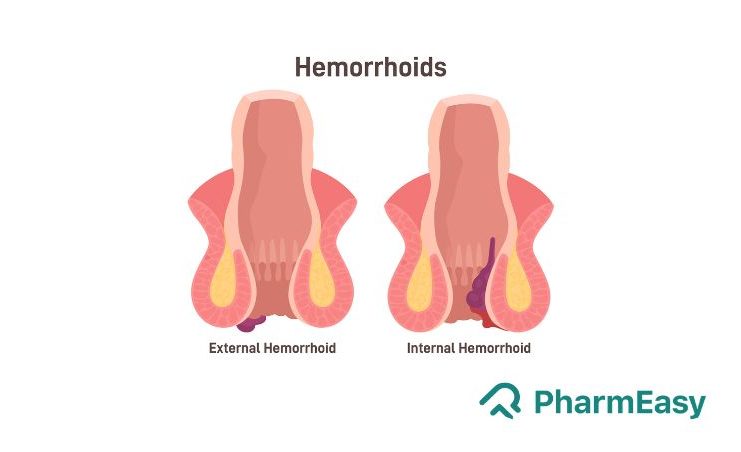
Haemorrhoids usually develop when the tissues supporting the anal opening deteriorate or disintegrate, leading to enlarged or swollen blood vessels in that area. Based on their location, haemorrhoids can be internal, external, or mixed type. Haemorrhoids present inside the anal opening are internal haemorrhoids, and those present under the skin of the anal opening are called external haemorrhoids. Sometimes, there may be a formation of a blood clot inside the haemorrhoid, termed a thrombosed haemorrhoid. They are symptomatic, and their presence is an acute haemorrhoidal disease. Thrombosed haemorrhoids should never be ignored as these can be extremely painful.1-3
Symptoms of Thrombosed Haemorrhoids
Following are the symptoms commonly reported in patients with thrombosed haemorrhoids:4-6
- Pain while sitting, standing, and defecating
- Bleeding associated with bowel movements
- Itching around the anal opening
The signs associated with thrombosed haemorrhoids include:
- Swelling
- Edema
- A dark-bluish lump at the verge of the anal canal, which is tender to touch
- Extreme pain in the perineal region, i.e. between the opening of the anal opening and vagina in women and between the anal opening and scrotum in men
If you notice any of the above symptoms, kindly consult your physician at the earliest.
A thrombosed hemorrhoid occurs when a blood clot forms inside a hemorrhoidal vein, obstructing blood flow and causing a painful swelling of the anal tissues. Thrombosed hemorrhoids are not dangerous, but they can be very painful and cause rectal bleeding if they become ulcerated. Many thrombosed hemorrhoids go away on their own in a few weeks.
Dr. M.G. Kartheeka, MBBS, MD
Causes of Thrombosed Haemorrhoids
The cause of thrombosed haemorrhoids is unknown, but it is hypothesized that it occurs due to the swelling and enlargement of the veins in the anal region. The following are the most commonly reported causes by patients suffering from thrombosed haemorrhoids:3-5
- Straining associated with constipation
- Heavy lifting
- Prolonged sitting
- In pregnancy and during childbirth, because of the pressure exerted by the baby on the veins or due to the force caused by pushing during labour
Risk factors: 1,6
- Constipation
- Prolonged straining on the toilet seat
- A diet low in fibre and high in spices
- Alcohol consumption
- Family history
- Chronic diarrhoea
- Sedentary lifestyle
You may try home remedies and make some diet modifications, but haemorrhoids usually do not go away on their own. Stapled hemorrhoidopexy is associated with less postoperative pain and faster recovery and is an advanced procedure used nowadays surgically.
Dr. Ashish Bajaj, M.B.B.S., M.D
Complications
If not treated on time, a thrombosed haemorrhoid may result in a complication called an ulcerated thrombosed haemorrhoid.
- Ulcerated thrombosed haemorrhoid: It may occur when increased pressure from the thrombosis results in ulceration of the skin or necrosis.4
Diagnosis
Your doctor will take a detailed history and thorough physical examination to confirm thrombosed haemorrhoids. A brief overview of the same is mentioned below:
- History and physical examination: To confirm the presence of a lump or swelling in the perianal (area around the anal opening) region. A thrombosed haemorrhoid may have ulceration with bloody drainage.
- A digital rectal examination: To check the presence of blood in stool and to exclude internal haemorrhoids.
- Imaging tests: If your doctor finds it difficult to make a final diagnosis on the basis of history, physical and a digital rectal examination, the following imaging tests may be needed.
- Anoscope: Used to visualize the lower rectal region.
- Colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy: To rule out the other causes of bleeding, which may be due to cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, etc.5
Treatment
In this section, we will look at the different treatment modalities available for thrombosed haemorrhoids:
1. Dietary and lifestyle modifications:
An increased intake of oral fluids and dietary fibres, mild-moderate intensity exercises, good anal hygiene and refraining from straining may positively impact thrombosed haemorrhoids.
2. Prescribed Medications:
- Stool softeners may help reduce straining associated with constipation.8
- Topical treatment with ointments may help reduce pain and swelling.9
- Painkillers may help relieve pain associated with thrombosed haemorrhoids.5
- Other oral medications may provide symptomatic relief from pain, swelling, bleeding and itching.1,10
- Many Ayurvedic tablets and powders may help in providing relief from anal itching, discomfort, oedema and pain associated with thrombosed haemorrhoids.10-12
3. Surgery:
- In cases of severe and unbearable pain, thrombosed haemorrhoids can be removed surgically by the following methods:
- Surgical excision, which involves surgical removal of the clot.
- Full hemorrhoidectomy, which helps in removing the clot along with the enlarged portion of blood vessels present in the haemorrhoid. There are two types of full hemorrhoidectomy techniques:
- Open Milligan-Morgan hemorrhoidectomy wherein the wound is left open, and on its own, it gets covered with a tissue lining.
- Whereas, in closed Ferguson hemorrhoidectomy, the wound is then closed with a running suture.6
Read more: What is the Cost of Piles Surgery in India?
Points to be kept in mind after full hemorrhoidectomy:
- Avoid taking narcotic pain relievers like codeine as it can cause hard stools and constipation, which may lead to the tearing of tissues in the anal opening after the procedure.
- For the next few weeks, you may experience mild bleeding associated with stools. You can place new gauze over the wound if the older one becomes soiled. In case of heavy bleeding, you should contact your physician.
- With this procedure, infections are rare, but it is advised to apply antibiotic ointments to the site daily for the first week after surgery. In case of surgical-site redness, swelling or foul-smelling drainage, contact your doctor.
- A twenty-minute sitz bath which involves soaking the affected area in a tub of warm water, may aid healing.
- After the surgery is completed, ensure your bowel remains soft. This can be done by increasing the intake of oral fluids and taking a high-fibre diet.
- You should avoid straining after haemorrhoid treatment.
Read more: Patient Experiences Before & After Piles Surgery
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1] What is a thrombosed haemorrhoid?When external haemorrhoids become tender and develop blood clots inside, they are referred to as thrombosed haemorrhoids. They are symptomatic and are also known as acute hemorrhoidal disease.
2] Are thrombosed haemorrhoids dangerous?No, not all thrombosed haemorrhoids are dangerous, but they can be very painful. Thus, they should not be ignored.3
3] What are thrombosed haemorrhoids symptoms?The symptoms of thrombosed haemorrhoids include extreme pain, itching (pruritus) and bleeding associated with bowel movements. These symptoms can affect the patient’s quality of life.6
4] What is an ulcerated thrombosed haemorrhoid?This is a complication of thrombosed haemorrhoids, which occurs when the blood clot in the haemorrhoid exerts pressure and results in ulceration of the skin and necrosis.6
5] What are the risk factors for developing thrombosed haemorrhoids?There are many risk factors which may predispose an individual towards the risk of thrombosed haemorrhoids; these include constipation, prolonged straining, a low-fibre diet, alcohol consumption, consumption of spicy foods, pregnancy, sedentary lifestyle, family history and chronic diarrhoea.1,8
References:
- Lohsiriwat V. Hemorrhoids: from basic pathophysiology to clinical management. World journal of gastroenterology: WJG. 2012 May 5; 18(17):2009. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3342598/
- Sun Z, Migaly J. Review of hemorrhoid disease: presentation and management. Clinics in colon and rectal surgery. 2016 Mar; 29(01):022-9. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4755769/
- Chinnabhovi M. A study on clinical profile of patients with hemorrhoids attending tertiary care hospital. 09(02) 2022; 2515-8260. Available at: https://ejmcm.com/pdf_18980_2cf9de8e7de30fb8ddec4d4db2823970.html
- Zuber TJ. Hemorrhoidectomy for thrombosed external hemorrhoids. American Family Physician. 2002 Apr 15; 65(8):1629. Available at: https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2002/0415/p1641.html
- Rubbini M, Ascanelli S. Classification and guidelines of hemorrhoidal disease: present and future. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2019; 11(3):117-121. doi:10.4240/wjgs.v11.i3.117. available at: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v11/i3/117.htm
- Sanchez C, Chinn BT. Hemorrhoids. Clinics in colon and rectal surgery. 2011 Mar; 24(01):005-13. Available at: https://sci-hub.hkvisa.net/10.1055/s-0031-1272818
- Wronski K. Etiology of thrombosed external hemorrhoids Etiologia zakrzepicy żył okołoodbytowych. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012; 66:41-4. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22371404/
- Lawrence A, McLaren ER. External hemorrhoid. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK500009/
- Perrotti P, Antropoli C, Molino D, De Stefano G, Antropoli M. Conservative treatment of acute thrombosed external hemorrhoids with topical nifedipine. Diseases of the colon & rectum. 2001 Mar; 44:405-9. Available at: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02234741
- Agarwal N, Singh K, Sheikh P, Mittal K, Mathai V, Kumar A. Executive Summary-The Association of Colon & Rectal Surgeons of India (ACRSI) Practice Guidelines for the Management of Haemorrhoids—2016. Indian Journal of Surgery. 2017 Feb; 79:58-61. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5346092/
- Gupta PJ. The efficacy of Euphorbia prostrata in early grades of symptomatic hemorrhoids–a pilot study. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences. 2011 Feb 1; 15(2):199-203. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21434487/
- Hep A, Robek O, Skricka T. Treatment of hemorrhoids from the viewpoint of the gastroenterologist. Personal experience with the Ginkor Fort preparation. Vnitrni Lekarstvi. 2000 May 1; 46(5):282-5. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11227184/









Comments