Telogen Effluvium And Phases Of Hair Growth
By Saksham Bhatia +2 more

Get more insightful and
helpful tips to
treat Diabetes for FREE



Download PharmEasy App




Register to Avail the Offer
Send OTPBy continuing, you agree with our Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions
By Saksham Bhatia +2 more
Have you ever wondered why your hair grows and falls out? Why do people complain of increased hair loss after infections like covid or after being stressed? Well, the answer lies in the fascinating process called the hair growth cycle. Understanding this cycle can provide insights into how to maintain healthy hair and even reduce hair loss. In this article, we will delve into the details of the hair growth cycle, breaking down complex medical information into easy-to-understand sections. So, let’s dive in and explore the different phases of hair growth.
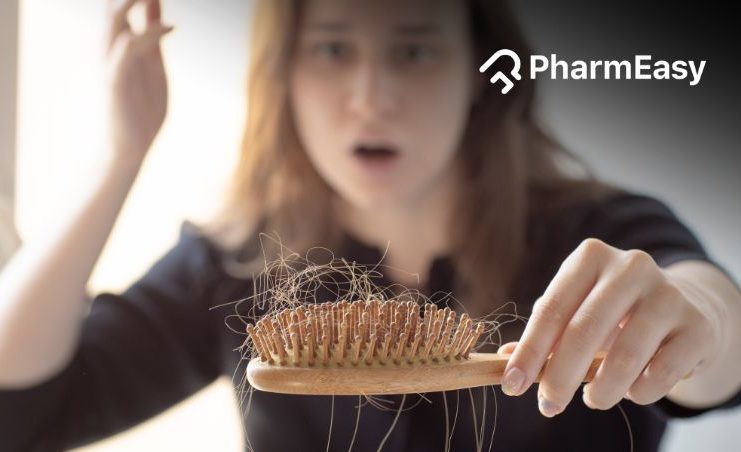
Table of Contents
The anagen phase is the active growth phase of the hair follicles. During this phase, cells in the hair bulb divide rapidly and the hair shaft extends outward. This is the phase where your hair grows around half an inch per month. The duration of the anagen phase varies from person to person and can last between two to six years. The longer the anagen phase, the longer your hair can grow.
After the anagen phase, the hair follicle enters the catagen phase, which is a transitional phase. This phase lasts for a short period of about two weeks. During the catagen phase, the hair follicle shrinks and the lower part of the hair is cut off from its blood supply. As a result, the hair stops growing and becomes club hair, which is a fully formed hair that is no longer attached to its nutrient source.
Following the catagen phase, the hair follicle enters the telogen phase, also known as the resting phase. During this phase, the club hair remains in the follicle while new hair starts growing underneath it. The telogen phase lasts for about three months. On average, about 10-15% of our hair is in the telogen phase at any time. It is normal to shed some hair during this phase as the new hair growth pushes the old hair out.
The final phase of the hair growth cycle is the exogen phase, which involves the shedding of hair. In this phase, the club hair is released from the hair follicle and new hair begins to grow in its place. It is important to note that shedding around 50-100 hairs per day is considered normal. If you notice excessive hair shedding or significant hair loss, it is advisable to consult a trichologist for further evaluation.
Telogen effluvium is a common type of hair loss characterised by excessive shedding or thinning of hair. It occurs when there is a disruption in the hair growth cycle, specifically during the telogen phase. Normally, around 10-15% of our hair is in the telogen or resting phase, but in telogen effluvium, a larger number of hair follicles prematurely enter the telogen phase, leading to increased shedding.
Several factors can trigger telogen effluvium, including:
1. Physical or Emotional Stress
2. Hormonal Changes
3. Nutritional Deficiencies
4. Medications and Medical Conditions
Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, beta-blockers, retinoids and anticoagulants, can cause hair loss as a side effect. Additionally, medical conditions like chronic infections, thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases and scalp infections can trigger telogen effluvium.
Telogen effluvium is characterised by diffuse hair shedding, which means hair loss occurs evenly across the scalp rather than in specific patches. The shedding usually becomes noticeable a few months after the trigger event or underlying condition. Fortunately, telogen effluvium is often temporary and the hair usually regrows once the underlying cause is addressed or resolved.
Treatment for telogen effluvium focuses on addressing the underlying trigger or condition. It is important to be patient, as the regrowth of hair can take several months.
In the meantime, you can take steps to support healthy hair growth and minimise further hair loss.
Now that you have a good understanding of the hair growth cycle and telogen effluvium, let’s explore some practical tips for maintaining healthy hair.
1. Eat a Balanced Diet: Proper nutrition is essential for healthy hair growth. Include a variety of foods rich in vitamins, minerals and proteins, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats and legumes.
2. Avoid Excessive Heat and Chemicals: Frequent use of heat styling tools, such as curling irons and straighteners, as well as chemical treatments like perming or colouring, can damage the hair shaft and affect its growth. Limit the use of these treatments and use heat protectants when styling.
3. Protect Your Hair from the Sun: UV rays from the sun can damage your hair, leading to dryness and breakage. When spending time outdoors, wear a hat or use a hair sunscreen to shield your hair from harmful rays.
4. Practice Gentle Hair Care: Treat your hair with care to avoid unnecessary breakage. Use a wide-toothed comb or a brush with soft bristles to detangle your hair gently. Avoid tight hairstyles that pull on the hair and use hair accessories made of soft materials.
5. Manage Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the hair growth cycle.
Hairfall is a complex issue and treatment of hair fall depends on the underlying causes. While conditions like telogen effluvium can be distressing, it is usually temporary. With proper care and addressing the underlying cause, most people can expect their hair to return to its normal growth cycle and regain its fullness over time.
For healthy hair, follow your dermatologist’s advice, eat healthy, stay physically active, sleep well and learn techniques to manage stress.
Disclaimer: The information included on this site is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional. Because of unique individual needs, the reader should consult their physician to determine the appropriateness of the information for the reader’s situation.
References:

Leave your comment...
Comments