Rotten Teeth: Causes, Consequences, and Research-Based Solutions
By Dr. Aastha Manchanda +2 more

Get,

to manage your symptom
Get your,


4 Cr+ families
benefitted

OTP sent to 9988776655



You’ve successfully subscribed to receive
doctor-approved tips on
Whatsapp

Get ready to feel your best.

Hi There,



Register to Avail the Offer
Send OTPBy continuing, you agree with our Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions

Hi There,

Trusted by 4 crore+ families

OTP sent to 9988776655



You have unlocked 25% off on medicines




Code: NU25

By Dr. Aastha Manchanda +2 more
Table of Contents
Taking care of your teeth is key not only for dental health but also for your total well-being. Gaining insight into the causes and effects of rotten teeth helps prevent it and allows for early treatment.
In this article, we aim to explore the topic of rotten teeth. We’ll delve into what causes it, its symptoms, complications, and possible solutions. Let’s understand together this often-ignored dental issue.
Did you know?
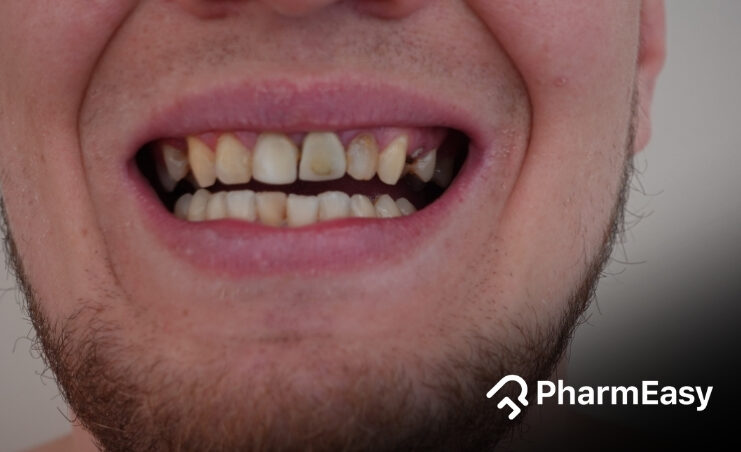
Tooth decay, commonly called as “rotten tooth” or “cavity”, means that areas on your teeth surface are damaged due to buildup of plaque and bacteria. Although this occurs in all ages, certain age groups might be more at risk for rotten teeth.
Let’s transition to a table about age groups and their risks:
| Age Group | Susceptibility to Rotten Teeth |
| Children | High, due to weaker enamel |
| Teenagers | Moderate to low |
| Adults | Moderate to low |
| Seniors | Moderate, depending on dental care |
Cavities are put into three main classes: enamel, dentin, and root cavities. To understand what each type is and how they impact your teeth, let’s dive in deeper.
Enamel cavities impact the outer layer of your teeth – the enamel. This layer is known to be the toughest tissue in the body and serves as a shield for your teeth.
Let’s see how these cavities are formed:
Dentin cavities attack the tissue under the enamel known as dentin. This tissue is softer and more prone to damage than enamel.
The formation process of these are as follows:
Root cavities happen when tooth decay occurs on the tooth root. These can:
Being aware of rotten teeth symptoms steers you towards early dental care, which also keeps further damage away. Common signs of rotten teeth are:
Recognizing factors that lead to tooth decay drops the chances of having rotten teeth. The main factors are not keeping good dental hygiene, a poor diet, dry mouth, having deep dental grooves or uneven surfaces, and lack of fluoride.
Poor dental hygiene has a big role in causing rotten teeth. Certain habits can lead to this:
Some foods raise the chance of getting rotten teeth by creating a good setting for bacteria to grow.
A drop in saliva production, known as dry mouth or xerostomia, makes way for tooth decay to thrive. Less saliva leads to:
Dry mouth may occur as a side effects of drugs, radiation treatment or certain illnesses. These reduce the saliva production and l
ead to dry mouth, increasing the risk of tooth decay.
Deep dental crevices or uneven tooth surfaces make it hard to clean teeth well. This could lead to:
Fluoride is a mineral that strengthens tooth enamel and helps prevent cavities. Lack of fluoride intake can cause tooth decay.
Toothpaste with fluoride are also available that aid in strengthening tooth enamel. However, fluoride should be used in moderation as too much of it can be harmful for teeth and bones.
Your dentist can guide you best about the safe use and concentration of fluoride to help avoid tooth decay.
Kids have a higher risk for rotten teeth because the enamel of their baby teeth is thin and weak. Plus, kids might not be able to maintain adequate oral hygiene by themselves and fight off caregivers trying to clean their teeth. Two things to think about for a child’s dental health include baby bottle rot and early dental care.
Baby bottle decay is a common problem for babies and toddlers who sleep with a milk, juice, or formula bottle.
It’s key to create good mouth cleaning habits to ensure the child’s long-term dental health.
Anybody can develop rotten teeth, but there are certain things that can raise your risk. These risk factors include:
If rotten teeth are not treated, it can lead to many problems that can impact your dental health and total well-being. These complications can be:
As mentioned, a cavity that hasn’t been treated can cause an infection that spreads to the tooth’s pulp. This can lead to a painful tooth abscess.
If tooth decay is not treated or not managed well, it can end in the loss of a tooth or spread of infection to gums and even bone. Severe tooth decay can lead to bacteria forming pockets between the tooth and gums and infecting surrounding bone. This weakens both.
Having bad tooth decay and infection in the mouth can affect the total health. Bacteria from the mouth can spread to other body areas. This could cause more infections or even general diseases.
Early diagnosis of rotten teeth ensures effective dental care. Here are some diagnostics that dentists use:
The treatment for rotten teeth is based on how bad it is and how far it has gone. Some treatment options based on the severity are:
Being proactive in keeping tooth decay away can save you from the discomfort and cost of treating rotten teeth. Here are a few key strategies:
Putting off treatment for rotten teeth can make tooth decay worse. This leads to more serious problems, including higher treatment costs and possibly tooth loss. Identifying and managing tooth decay as early as possible through regular dental visits, proper oral hygiene, and a balanced diet can help keep your dental health well for many years.
Knowing the causes, effects, and solutions about rotten teeth is crucial for optimal dental health. This also helps prevent more serious oral and possibly general health issues. If you practice good oral hygiene, cut down on sugar intake, and seek early intervention from dental professionals, you can keep your teeth and overall well-being in good shape.
In the early stages of tooth decay, enamel damage can be fixed with fluoride treatments your dentist might suggest. But in later stages, the damage cannot be undone and might need treatments like fillings, dental crowns, or root canal treatments.
Signs that you might have a rotten tooth are toothache, sensitivity, dark spots on the tooth, bad breath, and a bad taste in the mouth. Regular dental visits can help spot the start and progress of tooth decay.
How quickly a tooth rots depends on many things like individual dental hygiene habits, diet, and genes. It could take from a few months to a few years. To keep tooth decay at a minimum, brushing, flossing, and regular dental check-ups are required.
Tooth decay is commonly also referred to as cavities. However, in the early stages of decay, you may not actually have a cavity, only deep dental grooves or small pits may be seen. You may prevent the decay process by having regular dental check-ups, getting fluoride application and some minor dental treatment. But if this isn’t treated in time, it will lead to cavities and a need for bigger treatments.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.

Leave your comment...
Comments