Potential Benefits of Beta Alanine: Understanding Its Role in Performance Enhancement
By Dr. Shubham Pandey +2 more

Get,

to manage your symptom
Get your,


4 Cr+ families
benefitted

OTP sent to 9988776655



You’ve successfully subscribed to receive
doctor-approved tips on
Whatsapp

Get ready to feel your best.

Hi There,



Register to Avail the Offer
Send OTPBy continuing, you agree with our Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions

Hi There,

Trusted by 4 crore+ families

OTP sent to 9988776655



You have unlocked 25% off on medicines




Code: NU25

By Dr. Shubham Pandey +2 more
Table of Contents
To boost your athletic abilities there are loads of athletic enhancers out there. Today, we’re focusing on one that’s grown popular over time. That’s beta-alanine. Numerous athletes and fitness enthusiasts believe it may help them perform better. It’s particularly handy for high-intensity, short-term workouts. But that’s not all. It has potential benefits related to the body shape, brain function, and blood sugar. In this article, we will be discussing beta-alanine in detail. Lastly, we will answer some frequently asked questions regarding this topic.
Did you know?
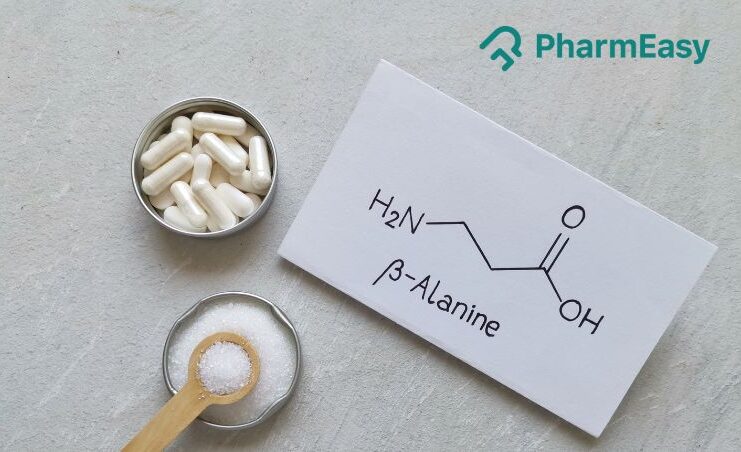
Beta-alanine is a non-essential amino acid, which means the body makes it naturally, so it’s not essential to your diet. It is necessary to help make something called carnosine. That’s a molecule that gives your physical output a boost.
Beta-alanine has an interesting structure. It’s made up of an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxylic acid group (-COOH). Its special status as a beta-amino acid comes from where its amino group sits. It sets it apart from the other alpha-amino acids in proteins.
Beta-alanine helps make carnosine in your body when paired with another amino acid, histidine. This combination then gets stored in the muscles and brain. In simple terms, it helps manage muscle acidity during brief, high-intensity workouts.
As we already mentioned, beta-alanine helps make carnosine with histidine. This lets the body store carnosine in the muscles. The amount of beta-alanine in the muscles often limits carnosine production. You can raise muscle carnosine up to 80% by taking beta-alanine.
When you do high-intensity workouts, your muscles produce hydrogen ions. This makes them more acidic. Acidic muscles make it harder for you to work out. They often lead to a feeling of tiredness. Carnosine acts as a buffer against this acidity. It helps you feel less tired and perform at peak levels for longer periods.
If you take beta-alanine, your muscle carnosine is said to get a boost. This helps your muscles resist the effects of acidity during tough workouts. As a result, you may be able to push yourself harder for longer and get better results.
Beta-alanine may be a game-changer. It is proposed to help boost muscle growth and output during resistance training.
Research suggests that taking beta-alanine might lead to increased lean muscle mass. By boosting the volume of exercise and reducing tiredness, which stimulates the muscles to grow.
Beta-alanine is supposed to provide better results in resistance training. This includes strength, training volume, and time to exhaustion.
Beta-alanine is not just for high-intensity, short workouts. It’s proposed to also be useful for endurance training.
Carnosine, made from beta-alanine, improves nitric oxide production. Nitric oxide improves blood flow and oxygen delivery to muscles. This may enhance your heart health during long workouts.
Taking beta-alanine has been linked to more time before fatigue during endurance exercises, like running, cycling, and rowing. That means you might be able to work out for longer periods before feeling tired.
Beta-alanine comes into its own during high-intensity, short-duration exercises. Especially when muscle acidosis is stopping you perform at your best.
Some studies have found that beta-alanine may improve performance and staying power during HIIT sessions. This is probably because it helps buffer muscle acidity during hard workouts.
It is proposed that both trained and untrained people can sprint better after taking beta-alanine. The increased buffer capacity it offers may help maintain peak sprinting speed before getting tired.
Beta-alanine isn’t just for athletes. It may also offer some benefits when it comes to general health and wellbeing.
As we’ve seen before, taking beta-alanine may increase lean muscle mass. That may also improve body shape.
The effects of beta-alanine on fat loss are a little vague. Some studies found no big changes in body shape after taking it. We need more studies to see if beta-alanine impacts fat loss.
Taking beta-alanine may indirectly lead to increased lean muscle mass. This is probably due to better performance and endurance in those taking beta-alanine.
Carnosine, made by pairing beta-alanine with histidine, may help control blood sugar.
Carnosine may boost insulin sensitivity. This is proposed to lead to better blood sugar control and a lower risk of type 2 diabetes. However, we need more studies to look at beta-alanine and its impact on insulin sensitivity.
Carnosine might also play a part in improving glucose uptake in muscle cells. This helps regulate blood sugar levels during and post workouts. We need more research to assess the role of beta-alanine in glucose uptake and confirm these findings.
Carnosine may have some properties that protect nerve cells.
Animal tests have found that carnosine might improve cognitive function. Memory and learning abilities, in particular. However, we need more studies on humans.
Carnosine has antioxidant properties. That might help protect nerve cells (or neurons) from damage. By fighting oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, carnosine might help keep cognitive function in check. It may also help avoid decline tied to aging.
Your body naturally makes beta-alanine. But you can also get it from certain foods and pills.
Animal-based foods are a good source of beta-alanine. Especially ones rich in carnosine.
If you don’t eat meat or want more beta-alanine, supplements are a good option.
To get the most from your beta-alanine, consider the proper dosage and timing.
The current evidence suggests you should aim for a daily intake of 2–5 grams. This is the ideal daily amount to enhance your performance and stamina.
Looking to get the max from your beta-alanine for your workout? Try taking it 30 minutes to an hour before your high-intensity, short-term exercises.
Are you new to beta-alanine? It might be good to start with a “loading phase”. High daily amounts for several weeks. After that, switch to a “maintenance phase”. A lower daily amount to keep a high level of carnosine in your muscles.
Alongside smart dosage and timing, add beta-alanine to a balanced training program. Cover your bases with proper methods, solid nutrition, and ample recovery time.
It is to be noted that if you are planning on taking beta-alanine supplements for any of the above-mentioned potential health benefits, do so after consulting your healthcare professional. Never self-administrate.
Beta-alanine isn’t without its drawbacks. As with any supplement, it’s crucial to consider the possible risks and side effects tied to its use.
Some people may feel tingling or flushed after taking beta-alanine supplements. Larger doses tend to cause this more often.
Paraesthesia, or tingling sensation, is a common side effect of taking beta-alanine. This tends to happen to the face, neck, and back of the hands. You can manage it by adjusting your dosage and how often you take it.
Reducing side effects is as simple as altering the dosage and how often you take it. Begin with smaller doses and slowly build up as you get used to it.
Despite its potential benefits, it’s always important to play it safe. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen especially if you’re on medication, pregnant, breastfeeding, or have a pre-existing condition. Never self-administrate.
At the moment, the long-term implications of beta-alanine are a question mark. It’s seen as safe for short-term use based on current evidence. However, further research is needed to confirm its safety for long-term use.
Beta-alanine needs more safety data for specific groups. For now, it’s not recommended for children, pregnant or breastfeeding individuals, or those with pre-existing medical conditions. Always ask a healthcare professional first.
Beta-alanine may be mixed with other sports supplements like sodium bicarbonate and creatine to increase its benefits.
Like beta-alanine, sodium bicarbonate helps beat down acid build-up in muscles during high-intensity exercise. Research shows that teaming these two may boost workout performance even more. Especially when muscle acidosis is affecting performance.
Creatine helps increase energy in muscles and improve exercise performance. When combined with beta-alanine, these two is said to work together to boost performance, strength, and lean muscle mass.
Beta-alanine and BCAAs have different roles in the body — with beta-alanine focusing on muscle carnosine levels and BCAAs promoting muscle repair and growth — but combining them may optimise overall athletic performance and recovery.
Again, always run it with your doctor before combing or trying out any new supplements and never self-administrate.
Beta-alanine is a supplement that holds a promise of potential benefits. These benefits are particularly pronounced in athletic performance and high-intensity exercise. Carnosine synthesis from beta-alanine may improve muscle buffering capacity. This leads to improved performance, increased endurance, and reduced muscle fatigue.
However, keep in mind that any form of supplementation should be done with care and under the advice of a healthcare professional. Maximising the benefits while minimising potential risks requires good knowledge of correct dosages, timing, and integration with other training practices.
In the end, beta-alanine has great potential for those looking to raise their game in athletics or fitness. Always keep your healthcare professionals in the loop before incorporating any supplement into your daily routine.
While it’s generally safe for healthy people, certain people are advised against taking beta-alanine. These include children, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and those with pre-existing health conditions. A healthcare professional should always be consulted first.
The time it takes to see improvements varies based on the person and the nature of the exercise. As a general rule, it’s suggested to supplement with beta-alanine for at least two weeks before expecting improvements in athletic performance.
You can combine beta-alanine safely with sodium bicarbonate, creatine, or BCAAs as part of a well-rounded athletic performance and recovery plan. Just remember to consult with a healthcare professional before adding any new supplements to your regime. Never self-administrate.
Yes, you can naturally increase your beta-alanine levels by eating foods high in carnosine like poultry and meat. However, to significantly bring up the levels of carnosine in muscles and maximise athletic performance, taking supplements might be necessary. Always consult your doctor before taking a supplement.
While beta-alanine doesn’t directly result in muscle growth like creatine does, it does increase workout performance, endurance, and delayed muscle fatigue. This indirect boost may potentially lead to increased muscle mass and strength, thanks to consistent training.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.

Leave your comment...
Comments