Pumpkin, harvested in the fall, is used to scare evil spirits. Carved pumpkin, known as jack-o’-lantern, is used to decorate spooky Halloween parties. It is often used to make thanksgiving pies and seasonal lattes. The scientific name of the pumpkin is Cucurbita moschata, belonging to the family Cucurbitaceae. Pumpkin is cultivated globally at high altitudes and sea levels from Northern Mexico to Argentina and Chile. It has spread to Europe (France and Portugal), Asia (India and China) and Western America.
A pumpkin is a trailing plant or an annual vine. The unripe fruit is often cooked as a vegetable, whereas ripe fruit is used in various beverages and confectionery. Pumpkin fruit contains constituents like β-carotene, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals1. Let us look at some of the potential pumpkin benefits.
The nutritional components of pumpkin are:
All the parts namely, seeds, flesh, and peel of indigenous as well as hybrid pumpkins are nutrient-dense, providing many essential nutrients like carbohydrates, fibres, fats, sodium, potassium, iron, vitamin C, calcium, copper, phosphorus, isoleucine, serine, and tyrosine6.
Dr. Smita Barode, BAMS
Various studies have shown that pumpkin may possess the following properties:
Pumpkin seeds too have a high nutritional quotient. Two tablespoons of shelled and roasted pumpkin seeds provide 163 calories and four grams of carbohydrates, eight grams of protein and eight per cent of your daily iron needs5.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Some of the potential health benefits of pumpkin are given below.
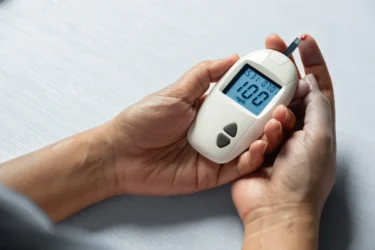
Pumpkin may be used for the management of diabetes. Reports of studies done on rabbits suggest that pumpkins may have properties to keep excess sugar levels in check. The phenolic compounds present in pumpkin may be responsible for the anti-diabetic activity. However, these studies were conducted on animals therefore, more studies are required on humans to claim these findings. You must check your sugar levels regularly and seek medical advice in case of high sugar levels1.

Hypotension occurs due to low blood pressure in the arteries. Studies on rats showed that pumpkin seed oil might relieve hypotension. It may protect against heart attacks due to its high magnesium content. Further studies are required to confirm the effects of pumpkin against hypotension. However, you must check your blood pressure regularly and consult your doctor in case of abnormal blood pressure3.

Pumpkins may protect the liver against fatty liver progression. Bioactive compounds in pumpkin, like phenolic compounds and β-carotene, may be responsible for liver protection. Unsaturated fatty acids may lower blood cholesterol levels and increase cholesterol breakdown in the liver. More studies are needed to claim the role of pumpkins in protecting the liver. You must consult your doctor in case of abnormal cholesterol levels3.

Pumpkins may be used to reduce the risk of certain types of cancers. This is due to the antioxidant activity of polyphenolic compounds present in pumpkins. Pumpkin extract may inhibit the growth of tumour cells and reduce the risk of gastric, breast, lung, colorectal and prostate cancer. A study3 suggested that proteins in pumpkin may inhibit the growth of skin cancer cells. Additionally, polysaccharides (a type of complex carbohydrates) present in pumpkins may show their anti-cancer activity by removing harmful toxins from the body. Further studies are required on the human body to confirm the anti-cancer action of pumpkins. Cancer is a serious disease; therefore, you must consult your doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Researchers have found promising effects of pumpkin seed oil in the prevention of ailments like prostrate diseases, cancers, diabetes, and even anxiety disorders7.
Dr. Anuja Bodhare, BAMS, MD (Ayu)

Pumpkins may possess anti-microbial properties because of their protein content. The oil-soluble components of pumpkins may fight against disease-causing microbes like Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Candida albicans, Klebsiella pneumonia, Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. However, more research is required to confirm the anti-microbial activity of pumpkins3.
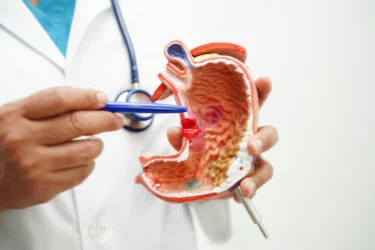
Pumpkins (Kaddu) may be used for ulcers. Studies conducted on albino rats suggested pumpkins may increase the activity of an enzyme, alkaline phosphatase and the mucosal thickness (inner stomach lining) to protect against duodenal ulcers. They are also known to decrease the ulcers as measured by Ulcer index (a scale used to measure the severity of ulcers). However, further studies are needed on humans to check the anti-ulcer activity of pumpkins. You must consult your doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment of ulcers instead of self-medicating3.

Pumpkins may be to help manage arthritis. Certain bioactive compounds in pumpkins may help in the case of arthritis due to their anti-inflammatory activity. A study3 conducted on rats suggested that pumpkin seed oil may act against rheumatoid arthritis due to their antioxidant activity. However, more studies are required to confirm the effect of pumpkins on arthritis therefore, you must not self-medicate and consult your doctor if you experience severe joint pain.
Pumpkin flowers are also edible and healthy. They are loaded with vitamin A which promotes healthy eyes, Vitamin B6 which boosts fertility, vitamin C which gives protection against flu, and phosphorus which helps in bone formation5.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)

Pumpkins may be used to manage depression. This is due to the presence of L-tryptophan, which raises the levels of happy hormones, serotonin. More research is required to confirm the activity of pumpkins for depression. However, if you are suffering from any symptoms of depression, you must visit a psychiatrist1.
Though there are studies that show the benefits of pumpkins in various conditions, these are insufficient and there is a need for further studies to establish the true extent of the benefits of pumpkins on human health.
Animal studies on pumpkin seed oil have revealed its positive effects on hair growth. Researchers believe it could be probably due to phytochemicals and vitamin E present in the pumpkin seed oil8.
Dr. Ashok Pal, BAMS
Pumpkins may be included in the diet in the following ways:
You must consult a qualified doctor before taking any herbal supplements. Do not discontinue or replace an ongoing treatment of modern medicine with an ayurvedic/herbal preparation without consulting a qualified doctor.
Pumpkin, a natural product, has no specific side effects. However, if any reaction is noticed on using it, seek immediate medical attention. Consult your ayurvedic physician who has prescribed it to you they will be able to identify the cause and treat it effectively.
General precautions should be taken while having pumpkins as in any other general medicine. Pregnant women and lactating mothers should take special care. You must consult your doctor before having pumpkins. Precaution should be taken before giving it to the elderly or children. In such cases, you must have pumpkin only if your doctor prescribes it.
Also Read: Kohlrabi: Uses, Benefits and Side Effects by Dr. Rajeev Singh
There is not enough evidence on the interaction of pumpkins with other drugs. Further studies on the interaction of pumpkins are required. Therefore, you must consult your doctor if you are on any other medication before consuming pumpkins.
Also Read: Oolong Tea: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects By Dr. Rajeev Singh
Pumpkins may be used in case of diabetes, hypotension, cancer, ulcers, depression and arthritis. It may protect the liver. It may also fight against bacteria, viruses and fungi. However, the effect of pumpkins for these diseases needs to be confirmed by more research. You must consult your doctor instead of self-medicating if you suspect any diseases1,3.
The nutrients present in pumpkins are proteins, fats, carbohydrates, fiber, sugar and vitamin C. It also contains minerals like calcium, potassium, phosphorus, iron, magnesium and many more2.
Pregnant women and lactating mothers should take special care while eating pumpkin. You must consult your doctor before having pumpkins. Precaution should be taken before giving it to the elderly or children. Apart from this, all general precautions that are taken with other foods should be taken.
Yes, several studies have shown that pumpkin might be good for our health due to its antioxidant, anti-cancer, antimicrobial and many such properties1,3.
Yes, pumpkin may help for weight management due to its low-calorie count and high nutritional value4.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Do you have a habit of munching raw onions in a restaurant while waiting for food to arrive? or fill your pani puri with more pyaaz (onion)? Well, raw onions may or may not be your preference, but in the cooked form they surely can make mouths water. In India, onions are regularly used in our meals and difficult for us to imagine our meals without them. The scientific name of the White onion is Allium cepa L. and belongs to the family Amaryllidaceae. This white onion is one of the most grown and oldest crops in the world which originated in West Asia, Turkistan, and Afghanistan. China is the largest producer of onions and India is the second largest.
Onions have low perishability, i.e., it does not get spoilt so easily1. Different variety of onions like yellow, purple, white, and red are available which are slightly different from each other. In white onions, quercetin (a bioactive compound) is less than in red onions and they contain other compounds called ceposides A, B and C in them2. Let us discuss the health benefits of White onion.
White onion contains 36 kcal of energy in 100gm. The following are the nutrients present in 100g of white onion:
From my knowledge, several compounds in white onions may aid in the fight against cancer. One of the most abundant food sources of a substance known as quercetin, which is believed to stop the activity or production of substances thought to cause cancer. A decreased chance of getting lung cancer has been linked to a diet high in quercetin9.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
White onion might possess the following properties:
Organic sulphur compounds are found in white onions. These substances are to blame for their acrid, overpowering taste and odour. Your risk of heart disease and stroke may be decreased because organic sulphur compounds may assist in lowering the level of cholesterol in your body and may also help dissolve blood clots. I suggest acquiring the most sulphur compounds from onions and consuming them raw as opposed to cooked9.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
There are various active components in white onion that might be helpful against certain diseases. Some of the potential uses of white onion are as follows:

The activity of the alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase play a role in the progression of diabetes. It was seen in studies that white onion might have the capacity to reduce the activity of these compounds and may help in lowering blood glucose levels. This might be due to the presence of the various phytochemicals present in it. Therefore, white onion might be helpful for diabetes. However, ensure that you consult a doctor for the proper diagnosis and treatment of diabetes and refrain from self-medication6.
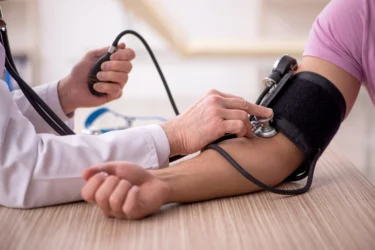
It was seen in studies that white onion might interfere with the activity of an enzyme Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) which alters the blood pressure. Many drugs which are prescribed by doctors for high blood pressure also target this enzyme to lower the blood pressure. Therefore, white onions might also reduce blood pressure. However, kindly consult a doctor and do not self medicate for your health conditions. Do not self medicate6.

Studies have shown that white onions contain many phytochemicals like quercetin and kaempferol which exhibit antioxidant properties. This antioxidant property of white onions might help in reducing oxidative stress by neutralizing free radicals. Thereby, white onion may help against cell damage and chronic diseases caused by oxidative stress7.

White onions contain ceposides in them and these ceposides are saponins that might be responsible for the antifungal activity. In a study4, the ceposides isolated from white onions were evaluated for their antifungal activity against different fungi. Therefore, white onions might be effective against certain fungi and fungal infections. However, more studies are required to prove these possible effects. If you have any fungal infections consult the doctor and do not self-medicate.

Onions might exhibit many beneficial properties as a nutraceutical vegetable and may help in reducing the risk of heart diseases. It may act as an antioxidant, regulate blood lipids, and improve the function of blood vessel cells. Therefore, by decreasing the risk of heart disease, onions might help in the maintenance of heart health. Heart diseases are serious, and you must consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment of suspected heart diseases5. Do not self-medicate.

A study5 was conducted to check the effect of onion on weight. They were given onion peel extracts containing quercetin. It was noted that over a period there may be a decline in the body fat mass and the body-mass index (ratio of fat to muscle calculated according to individual height and weight). Therefore, quercetin present in white onions might be helpful for weight management. However, more large scale studies are required. If you want to manage weight consult a proper nutritionist and do not self medicate.
Though there are studies that show the potential uses of white onion in various conditions, these are insufficient and there is a need for further studies to establish the true extent of the benefits of white onion on human health.
The bulbs of white onion can be used for cooking. It is used in the preparation of different kinds of dishes in various cuisines around the world. It has a pungent flavour and can be used in the following ways:
You must consult a qualified doctor before taking onion in large quantities or any herbal supplements. Do not discontinue or replace an ongoing treatment of modern medicine with an ayurvedic/herbal preparation without consulting a qualified doctor.
Your body odour may be the only drawback to eating white onions that you will likely notice. The sulphur compounds in onions that are broken down by your body may react with perspiration on your skin to produce what is typically thought of as an unpleasant body odour. White onions may worsen gas and bloating in people with irritable bowel syndrome. If so, I suggest limiting their usage is advised9.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
Consumption of white onion might cause heartburn5. There is a requirement for more studies to be performed for the exploration of more side effects of white onion if any. Therefore, ensure that you consult a doctor if you notice any unusual effects after the consumption of white onion.
Also Read: Cabbage (Patta Gobi): Uses, Benefits, Side effects By Dr. Rajeev Singh
White onion is relatively safer when taken in food quantities. There have been no reports regarding the safety of white onion in children and elderly individuals.
There have been no reports of the effects of white onion on pregnant women. Therefore, it is advised to consult and discuss with a doctor before use.
Also Read: Onion (Pyaaz): Uses, Benefits, Side Effects and More!
Studies have shown that eating cooked onions might have the potential to increase warfarin (a drug which is helpful against blood clots) activity8. Therefore, kindly consult a doctor and confirm whether it is safe for you to consume onions, especially if you are undergoing any treatment and are on medication for the same. There is a need for more research to establish the effects of onion on other drugs.
Also Read: Gulvel: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects, Precautions & More!
White onions might be against diabetes, blood pressure, oxidative stress and for fungal infections. However, more research is required to prove the possible benefits of white onion. Therefore, kindly consult a doctor for the stated conditions and do not self-medicate1,4,6,7.
Yes, you can use dried white onion for cooking. You can use it in soups, salads, and dishes1.
There are no reports regarding the potential uses of white onion for hair. Therefore, there is a requirement for more research on this subject.
Sometimes, cooked white onion might cause heartburn. Kindly consult a doctor and discuss whether it is safe for you to consume onions5.
Yes, white onions might help in lowering blood pressure by possibly interfering with the activity of ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) which is responsible for the abnormal rise of blood pressure. However, ensure that you consult a doctor for elevated blood pressure and do not self-medicate6.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Arrowroot powder is a gluten-free product, and the scientific name is Maranta arundinaceae which belongs to the Marantaceae family. In India, arrowroot flour is called ‘aru’ or ‘aru-aru,’ and in Portuguese, it is called ‘araruta.’ This plant is derived from the tropical areas of South America and it appears in the Southeast region of Brazil to till the Guianas. It is termed an ‘arrowroot’ maybe because it resembles the shape of a rhizome or because it is used as a neutralizer to wound dressing. This plant is widely cultivated in Brazil and is the most common ingredient in home preparations for food1. Let us discuss some more health benefits of the arrowroot.
Did you know?
The arrowroot powder contains the following nutrients:
Nutrients present in 100 g of arrowroot powder2.
Studies7 have shown that the consumption of Arrowroot powder may relieve Urinary Tract Infections. Arrowroot powder is known for its anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial properties that may aid in infections.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
The arrowroot powder may have the following properties:
Fun fact: I recently read in a study4 that due to the presence of high fibre content and amylose, Arrowroot may be used as an alternative to regular flour for chapatis. Arrowroot is known for its use in homoeopathy for numerous ailments and this added fact makes it a potential superfood.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Arrowroot powder contains several nutrients that may have potential uses for the human body. Some of the potential uses are as follows:
Arrowroot may contain bioactive compounds like flavonoids that may help in boosting immunity. It may also increase the level of antioxidants (Killing free radicals) and may help in fighting against diseases3.
As per the study4 by Harmayani et. al. arrowroot powder might be a possible source of prebiotics. Prebiotics may help in the maintenance of good bacteria in the gut and may be helpful in digestion. It has also been studied in the research that it might have antidiarrheal activity. As arrowroot may have prebiotic activity, it may help in absorbing nutrients and improve the stomach’s microbiological properties. However, more research is required on prebiotics.
Studies6 reported that arrowroot may be useful for relieving oral pain such as gingivitis (gum inflammation). Arrowroot may have anti-inflammatory properties that might be useful for inflammatory diseases of the mouth. It may also have antibacterial and antifungal properties. These properties of arrowroot powder may help in healing mouth-related conditions. However, do not self-medicate and consult a dentist if you have any dental-related issues.
Arrowroot might be good for the heart and studies3 showed that it may improve the heart rate and may boost immunity. Arrowroot may improve blood circulation and prevent heart diseases such as congestive heart failure. If you have any heart condition, please do consult your doctor, and do not self-medicate.
Some people are intolerant to gluten-containing food and get allergies when they consume gluten-related foods. The only choice is the total removal of gluten from the diet. Arrowroot may help in the preparation of gluten-free products as it might have a lower content of phenylalanine (protein) in it. Several gluten-free products, such as ice cream stabilizers, bread, and infant formulas, are made from arrowroot. However, more studies are required1.
Though there are studies that show the benefits of arrowroot powder in various conditions, these are insufficient and there is a need for further studies to establish the true extent of the benefits of arrowroot powder on human health.
Other than uses medicinal benefits, Arrowroot powder has a potential role in cosmetics as well. Studies8 say that Arrowroot has the capability of absorbing extra oil from the skin which in turn enhances skin rejuvenation. Hence, it may be used in cosmetic products as well.
Dr. Smita barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
Arrowroot powder may be used to make:
You must consult a qualified doctor before taking arrowroot in large quantities or any herbal supplements. Do not discontinue or replace an ongoing treatment of modern medicine with an ayurvedic/herbal preparation without consulting a qualified doctor.
It is believed that Arrowroot powder may be safe and nutritious for expecting mothers. Arrowroot powder has proven rich source of Vitamin B9 and Iron, which is believed to help babies grow healthy. Though, I would suggest that expecting mothers still consult their doctors before consuming the powder and avoid self-medication.
Dr. Anuja Bodhare, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Arrowroot powder is considered safe; however, there is no sufficient information on its consumption in large quantities. In addition, individuals who are allergic to arrowroot may cause stomach discomfort4. Arrowroot powder might have other side effects; however, there is not enough information on the side effects of arrowroot powder. Contact your doctor if you notice any side effects after consuming arrowroot powder.
Also Read: Red Rice: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects & More
Allergy due to arrowroot powder is rare, but there are chances that you might be allergic to it6.
Do not self-medicate. Always talk to your doctor before consuming arrowroot powder.
Also Read: Bhumi Amla: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects & More!
There is no sufficient information related to the interaction of arrowroot powder with medicines. However, if you notice any signs and symptoms, you must report them to your physician.
Also Read: Amchur Powder (Dry Mango Powder): Uses, Benefits and Side Effects by Dr. Rajeev Singh
Arrowroot powder may help against digestive problems such as diarrhoea and dysentery. It may help in relieving pain and may help the heart from the risk3,4. However, it is essential that you meet your doctor before taking arrowroot powder.
Arrowroot contains saponins that might help in weight management. However, do not self-medicate and talk to your doctor if you can consume arrowroot for weight management3.
A few people who are allergic to arrowroot might have stomach discomfort. For this reason, it is important to seek expert advice4.
Arrowroot powder might be good for teeth. It may whiten the teeth and help in reducing mouth sores and gingivitis. However, it is better to consult a dentist and not self-medicate.
Arrowroot powder might be good for the heart. It may improve the circulation of blood and may help against heart-related diseases. However, please consult your doctor before taking arrowroot powder4.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
You might have heard about almonds, cashews, pistachio and peanuts, but have you heard about the pecan nut? Don’t worry if you haven’t, we’ve got all the information that you need to know about this pecan nut. The pecan fruits are dark brown with black spots on them. Their shells are elliptic in shape, having a bulged-out (convex) exterior layer and a bulged (concave) inner layer. These fruits come under the category of drupes which grow in bunches and might contain three to eight nuts in them1.
The scientific name of the pecan tree is Carya illinoinensis, which is an important fruit plant in temperate regions like the Northern Hemisphere. It is an indigenous plant of the United States and Mexico but had spread to the regions of South America, Uruguay, Argentina, Peru, Brazil, and Chile. In recent times, pecan’s popularity has spiked, and it is now being cultivated in regions of China, Australia, and South Africa too. Pecans contain many nutrients which might be beneficial for human health. Some of its potential uses are stated in the following sections1.
Pecan nut contains a total of 691kcal of energy in 100gm and the nutrients present and their content in 100g of pecan nut are:
Vitamins present in pecan are:
Pecan oil is derived from pecan nuts. This edible pressed oil is a good source of protein, unsaturated fatty acids, vitamins, and other minerals. Pecan oil is widely used to improve nerve cell function, strengthen cell activity, and eliminate free radicals. Generally speaking, It also might be useful in keeping cancer, reducing coronary heart diseases and heavy metal toxicity, and may have anti-ageing effects6.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Pecans might possess the following properties:
Pecans contain several bioactive compounds which might be beneficial to health and some of the potential uses are as follows.

Studies have shown that eating pecans regularly might improve insulin resistance, fasting insulin, and the functioning of the cells producing insulin (beta cells of the pancreas). This may help pecans help in lowering their blood glucose levels and it might be helpful against diabetes. However, kindly ensure that you consult a doctor for a serious condition such as diabetes and do not self-medicate3.

Pecans may reduce the risk factors that are related to the heart. Pecans have different bioactive compounds that may help in reducing clinically relevant markers like glucose metabolism and blood lipid levels. The reduction in the clinically relevant markers may help in protecting the heart from cardiometabolic diseases. But there is a requirement for more research to prove the potential effects that pecans on the heart. Therefore, ensure that you consult a doctor if you have heart problems that may be serious3. Do not self-medicate.
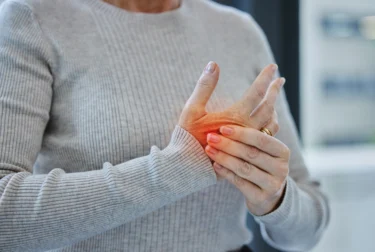
Pecans contain phytochemicals like tannins, ellagic acids and urolithins which might help reduce inflammation. These compounds might have the potential to alter the expression of genes that are responsible for chronic inflammation. This might further be helpful against chronic metabolic diseases caused due to inflammation. However, these effects need to be confirmed by more extensive research3.
Rajaram et al. in their study noticed that the consumption of pecans might have a cholesterol-lowering effect. Both total cholesterol and LDL (low-density lipoproteins) may reduce when pecans are given regularly to their test subjects. This may help pecan nuts to lower the cholesterol levels in the body. Therefore, further research on this subject might be able to reveal the effects of pecans on cholesterol. If you have high cholesterol levels, consult the doctor and do not self-medicate.

Pecans might have the potential to improve the antioxidant status of the body. This might be due to the presence of gamma-tocopherol and catechins in pecans. However, it is believed that by increasing the antioxidant activity in the body, pecans might help in reducing oxidative stress. This might further help us against the various diseases caused by increased oxidative stress in the body4.

Pecan nuts might be helpful against metabolic diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. However, such claims need to be further researched and backed up scientifically to be proven as facts. Therefore, kindly consult a doctor and do not self-medicate1.
Though there are studies that show the potential uses of pecan in various conditions, these are insufficient and there is a need for further studies to establish the true extent of the benefits of pecan on human health.
Pecans can be eaten simply by roasting the nuts. They are also used in the preparation of bakery products, candies, and dairy products. They can also be used for the preparation of various other dishes5.
You must consult a qualified doctor before taking pecans in large quantities or any herbal supplements. Do not discontinue or replace an ongoing treatment of modern medicine with an ayurvedic/herbal preparation without consulting a qualified doctor.
In elderly patients, as body oestrogen levels decreased, the antioxidant levels also reduced. As an effect, increased levels of free radicals can lead to cell damage and shows sign of ageing. According to some studies, pecan oil exhibits antioxidant effects along with anti-ageing properties. Therefore, consuming pecan oil might be useful for reducing ageing effects in elderly patients6.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Pecan nuts might cause allergies in some individuals. Therefore, one should ensure that they are not allergic to pecan nuts before eating them5.
Also Read: Triphala Ghrita: Uses, Benefits, Side effects & more!
People who are allergic to pecans must be cautious and make sure that they do not consume pecans, food containing pecans or food that has been in contact with pecans5.
There are no reports of the effects of pecan nuts on pregnant women. Therefore, pregnant women should confirm the safety of pecan nuts with their doctor before consuming them.
There are no reports of any special precautions that need to be taken by children or elderly individuals for the consumption of pecans. Therefore, kindly consult with a doctor before giving pecans to children or elderly individuals.
Also Read: Barley: Uses, Benefits & Side Effects
Pecans might react adversely to unknown drugs. However, such potentialities have not been reported. Therefore, there is a need for more research to study the adverse reaction of pecans to specific drugs. Kindly ensure that you consult a doctor and discuss whether it is safe for you to take pecans, especially if you are undergoing any treatment and are on medication.
Also Read: Betel Leaves: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects By Dr. Smita Barode
Pecan nut might be helpful against cardiometabolic diseases, diabetes, degenerative diseases, and oxidative stress. However, more research is required to prove the effectiveness of pecan for the mentioned conditions. Kindly consult a doctor for the conditions and do not self-medicate1,3,4.
There are no beneficial effects of pecan for skin reported yet. There is a requirement for more research on this subject.
Yes, pecan nuts can be used for cooking. They are generally used in the preparation of bakery products and flavouring dairy products5.
Yes. Pecans might help lower the risks of cardiometabolic diseases. Therefore, pecans might be good for the heart3.
Vitamin A, B (B1, B2, B3, B5 and B6), C and K are present in pecans2.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Humans depend on nature for their survival. According to Ayurveda, the human body alone may be made up of five elements. The elements might be water (blood), air (breath), Earth (bones and muscles), fire (heat), and space (emptiness). Yoga is a physical exercise that offers a healthy way of life for all age groups, and it has been recognized as a significant part of current culture. All these elements may be balanced in the human body through yoga. Normally hands and legs are stretched during the asanas and mudras in yoga. Mudras are made with fingers. We perform specific yoga mudras by relocating the fingers depending on the factors and asanas. The fingers of our palm may represent the element of Panchabhutas (Fire, Air, Space, Earth, Water) as follows:
Typically, our bodies have an ideal balance of these elements. But when one of them is out of proportion or any imbalance occurs, it may harm the body. Mudras in yoga may help in the removal of imbalance in the body. One of the best mudras we can follow is the Surya mudra. Surya mudra is associated with the earth and five elements. Let’s read and discuss more Surya mudra1,2.
Surya Mudra is also known as Prithvi Shamak Mudra and Agni Vardhak Mudra3.
‘Surya’ refers to the ‘sun’, and ‘mudra’ refers to a hand gesture. Surya mudra is a finger arrangement which is believed to represent that energy in our bodies is received from sunlight. Surya mudra comes under the ‘curative mudra’ in which we practice the mudra to remove any foreign material from the body. This class of mudra may try to bring balance to all the elements of the body2.
To gain health advantages from the Surya mudra, we must practise it correctly. The steps of Surya mudra or Agni Vardhak mudra are as follows:
Do You Know?
Several mudras may be designed to get different benefits depending on our requirements. Some of the benefits of Surya mudra are as follows:
Yoga mudras may improve pancreatic function. In a study, regularly performing the mudras might increase metabolic rates and may help in weight management. It might help in lowering blood sugar levels, which may reduce type-2 diabetes4. However, more studies may be necessary to determine the exact impact of Surya mudra on diabetes. Before performing the Surya mudra, you should seek medical advice because diabetes is a severe condition. Do not self-medicate and practice the Surya mudra under a proper trainer.
Surya mudra may enhance the functioning of the thyroid gland in the body. Therefore, it might lower the issues such as obesity caused by hypothyroidism.1 Please seek medical advice to avoid any complications. If you have a thyroid problem, consult your doctor. Do not self-medicate and practice the Surya mudra under a proper trainer.
Surya mudra may be one of the mudra or asanas which may act against weight loss5. This mudra may reduce the number of nutrients in the body which may raise the fire element in the body and decrease the Prithvi element. Obesity may affect heart functioning, which may be lowered by Surya mudra.3 If you have obesity, consult your doctor. Do not self-medicate and practice the Surya mudra under a proper trainer.
When we practice Surya mudra along with Surya namaskar, it may regulate the body temperature. Surya mudra may avoid shivering, which may be caused by low and cold temperatures. In addition, in ‘hypohidrosis’ the body may not cool down by sweating, or a person may sweat less than usual. This might be lowered by doing Surya mudra3. However, don’t rely just on the Surya mudra and consult your physician. Do not self-medicate and practice the Surya mudra under a proper trainer.
A mudra is a hand movement that regulates the flow of energy to particular parts of the brain. As the Surya mudra may increase the body temperature it may lead to the release of antioxidants. It may lower stress levels and induce feelings of joy and satisfaction with life by keeping frustration away3. However, don’t rely on the Surya mudra and consult your doctor. Do not self-medicate and practice the Surya mudra under a proper trainer.
Yoga practice may help develop the mind and body; however, it is still not an alternative to modern medicine. You must not rely on yoga alone to treat any condition. Please consult a qualified doctor who will be able to assess your condition correctly and advise accordingly. Moreover, it is necessary to practice and learn yoga under the supervision of a trained yoga teacher to avoid any injuries.
If you’re performing it in the summer, I would suggest it’s best to drink a lot of water to avoid dehydration. Practising Surya mudra during summer may increase the level of the fire component.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Also Read: Benefits of Virabhadrasana (Warrior Pose) and How to Do It By Dr. Himani Bisht
Surya mudra has the following risk factors:
In case of any medical condition, kindly consult the doctor and practice Surya mudra. However, more research is required to state the risk of exercise. Proper guidance of a qualified and experienced yoga teacher/yoga expert, we can assess and analyse the risk factors and continue to practice exercise with precautions.
Also Read: Benefits of Sirsasana (Headstand) and How to Do it By Dr. Ankit Sankhe
Yoga mudras are yoga techniques that restore elemental balance inside the body by regulating the flow of life energy. Surya mudra is one of the techniques that may act against thyroid function, weight loss, and relieving constipation. You may do Surya mudra anywhere in the open or at home in any position. By regulating the heat factor in the body, Surya mudra may treat all the diseases related to it. It may be associated with increasing Agni (fire) element, so it is also known as ‘Agni Vardhak Mudra’. It may decrease the Prithvi (earth) element in the body, so it is also called ‘Prithvi Shamak Mudra’. To avoid complications, you may do Surya mudra frequently by taking the required precautions, possibly under the supervision of a yoga instructor.
Also Read: Benefits of Bhramari Pranayama and How to Do it By Dr. Himani Bisht
Surya mudra may increase the metabolism and energy flow to the body, which may help in absorbing the food. It may also boost the immune system. However, don’t rely just on the Surya mudra and consult your physician. Do not self-medicate and practice the Surya mudra under a proper trainer.
Surya mudra may reduce the risk of heart attack by lowering the levels of cholesterol in the human body. However, don’t rely just on the Surya mudra and consult your physician. Do not self-medicate and practice the Surya mudra under a proper trainer.
Daily practice of Surya mudra might strengthen the eyes and may help to improve vision.
No, however, we must require more research on Surya mudra to determine its effect on the liver.
Surya mudra may help to reduce constipation, acidity, and indigestion which ultimately improves digestion.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
The ancient Indian discipline of yoga has taken the Western world by storm. Modern-day yoga has been excellently reflected in the blogosphere. Famous Hollywood celebrities like Jennifer Aniston, Madonna, Britney Spears, Maria Sharapova, Meghan Markle, Robert Downey Jr., and many more have been practicing the art of yoga for their mental and physical well-being.
The United Nations proclaimed 21st June as the International Day of Yoga to spread awareness about the importance and holistic health benefits of yoga. Yoga is more than just an exercise; it is a way to discover a sense of oneness with yourself, the world, and the nature.
Yoga consists of ancient mudra science, which connects certain energy flows in the mind-body system. For example, five fingers represent five elements: thumb (Fire), index finger (Air), middle finger (Space), ring finger (Earth), and little finger (Water). The yoga mudras aim to bring back the elemental balance by guiding the flow of life energy within the body. Let us look at the health benefits of one of the mudras- prithvi mudra1.
Did you know?
Mudras have been depicted in Buddhist, Hindu and Christian imagery for centuries. Mudra therapy is an age-old effective therapy propounded by ancient sages. Mudra means hand gestures made for the betterment of the physical body. The principle of mudras is that the transfer of energy takes place from a higher to a lower level1,2.
Imbalances in earth elements can cause obesity, weakness in cholesterol, bones or muscular diseases, etc.
In Sanskrit, ‘prithvi’ means earth, and ‘mudra’ means a gesture of the hands. Therefore, Prithvi mudra helps to awaken the element of earth in our body. Prithvi Mudra is also known as the ‘Sign of Benediction or Blessing1,2.
In my experience, Prithvi Mudra might be like a magical hand trick. It may help if someone is losing weight without any explanation or feeling very weak. By practising this gesture, one might feel more balanced and healthy.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
Prithvi mudra is a simple yogic hand gesture. It is performed using the ring finger and thumb in the following way:
Some of the potential benefits of prithvi mudra are:
Prithvi mudra may help in improving stamina. Further research is yet to be done to claim the effect of prithvi mudra on enhancing energy. However, you must consult your doctor and take appropriate medications to improve your stamina instead of solely relying on yoga3.
Prithvi mudra may help to alleviate fatigue which may be caused due to various reasons. Prithvi mudra may help prana to flow better through the spine and the other parts of the body. Prana is the sanskrit word of breath and refers to ‘life force’. This flow of prana ensures energy flow in all parts of the body and may therefore, keep the body energetic and reduce fatigue. More clinical trials are required to check the effect of prithvi mudra to get rid of fatigue. However, you must not rely solely on prithvi mudra to eliminate fatigue1,3.
Osteoarthritis is the wearing off of tissues present at the ends of bones. Prithvi mudra may help in the case of osteoarthritis. Further studies are required to check how beneficial prithvi mudra is for osteoarthritis. Therefore, you must consult your doctor if you experience joint pain3.
Prithvi mudra may help to heal cuts and wounds. It might also help enhance the growth of the tissues. More studies are yet to be done to check if prithvi mudra can help to heal body tissue. However, you must not solely rely on prithvi mudra in case of injury that destroys the body tissues and seek medical help1.
Prithvi mudra may be beneficial for dry and cracked skin. It might help increase the bone density and help in case of bone fractures. Prithvi mudra may also reduce the brittleness of nails. However, more studies are required to check these properties. Therefore, you must consult a specialist for these problems1.
Practising mudras like prithvi mudra on a daily basis may help boost immunity and may therefore, fight against infections like Covid-19. Further investigation is needed to check if prithvi mudra may enhance immunity. You must consult a doctor if you have been diagnosed with infections like covid-193.
A yoga regime consisting of prithvi mudra may be additionally used with ongoing treatment to manage brain tumours. The result of a case study suggested that ayurvedic medication, along with yoga therapy, may be beneficial in managing brain tumours. However, more clinical trials are required to check the effect of the same. You must take proper treatment if diagnosed with a brain tumour4.
Prithvi mudra may have some effect on the cognitive brain. When practiced along with dhyana mudra, it may help to improve concentration and may keep the mind stable. However, more studies are required to check the impact of prithvi mudra on concentration4.
Yoga practice may help develop the mind and body; however, it is still not an alternative to modern medicine. You must not rely on yoga alone to treat any condition. Please consult a qualified doctor who will be able to assess your condition correctly and advise accordingly. Moreover, it is necessary to practice and learn yoga under the supervision of a trained yoga teacher to avoid any injuries.
According to what I have noticed, the regular practice of Prithvi Mudra might help keep your energy levels up. This possibly keeps you from feeling weak or lethargic. So, it’s like having a natural boost to keep you feeling energised throughout the day1.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Also Read: Benefits of Ashwini Mudra and How to Do It By Dr. Ankit Sankhe
There were no associated risks or contraindications that have been investigated or reported as yet. However, it is essential to take necessary precautions before performing prithvi mudra. You must be extra cautious if you have heart disease. Pregnant and lactating mothers should be careful too. It is best to perform prithvi mudra under professional guidance.
Let me tell you a secret. By regularly practising the Prithvi Mudra, you may enhance your self-confidence and might cultivate a strong belief in yourself. This empowering gesture may serve as a reminder of your inner strength, encouraging us to trust in your abilities and embrace your full potential5.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Also Read: Benefits of Ujjayi Pranayama (Ocean Breath) and How to Do it By Dr. Himani Bisht
Mudra therapy is an age-old effective therapy propounded by ancient sages. In Sanskrit, ‘prithvi’ means earth, and ‘mudra’ means a gesture of the hands. Therefore, Prithvi mudra helps to awaken the element of earth in our body. Prithvi mudra may improve stamina, relieve fatigue and boost the growth of tissues. It may be used in the case of osteoarthritis, brain tumour and to heal wounds. In addition, it may prevent covid-19 infections and may improve concentration. It is best to perform prithvi mudra under professional guidance.
Also Read: Benefits Of Paschimottanasana (Seated Forward Bend Pose) and How to Do it
Prithvi mudra may improve stamina, relieve fatigue and boost the growth of tissues and heal wounds. It may be used in the case of osteoarthritis, brain tumour, and to heal wounds. In addition, it may boost immunity and may improve concentration. However, you must not solely rely on prithvi mudra for the treatment of the diseases,4.
First, sit in a relaxed position. Now, bring your ring finger and your thumb closer. Next, place your hands with palms facing upwards on the thighs or above the knees. Slowly fold your ring finger and tap the tip of the ring finger to the tip of the thumb with some pressure. Try to keep the rest of the three fingers extended and straight as much as possible1.
There are no associated risks or contraindications that have been reported as yet. However, it is essential to take necessary precautions before performing prithvi mudra. You must be extra cautious if you have heart ailments. Pregnant and lactating mothers should be careful too. It is best to perform prithvi mudra under professional guidance.
Yes, regular practice of prithvi mudra may boost the body’s immunity. Therefore, it may help to fight against infections like Covid-19 infections3.
Prithvi mudra may have some effect on the cognitive brain. It may help to improve concentration and may keep the mind stable4.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Nowadays the internet is all about fitness goals and workout challenges. Of these fitness goals, one of the major ones is yoga. Famous Bollywood celebrities like Sara Ali Khan, Janhvi Kapoor, and Shilpa Shetty do their yoga practice. Yoga is an art of the old times that involves physical movement. Yoga is among the six systems of Hindu philosophy: Samkhya, Vaisheshika, Yoga, Nyaya, Uttara Mimamsa, and Purva Mimamsa. Pranayama is practiced to control and restrain one’s vital energy in the body. Ujjayi pranayama is one of the techniques practiced in yoga. The most popular type of breath control utilized in yoga is ujjayi breathing. It is a method that concentrates on using your nose to breathe and compressing your throat to produce a sound like a faint snore. Let us look at some of the health benefits of ujjayi pranayama1.
Pranayama is a breathing technique that is embedded in yoga and practiced simultaneously. It can control the energy in one’s body and regulate the breath to the proper channel. Ujjayi pranayama is also known as ocean breathing or victorious breathing. Ujjayi is composed of two words- ‘ud’ which means a sense of superiority or power, and ‘Jaya’ means victory, conquest, or success, giving it the meaning of victorious breathing. It is known as ocean breathing due to its ocean wave-like sound during exhalation and inhalation. The sound is produced due to friction of the throat with the air. Ujjayi pranayama can be practiced alone or with other yogic exercises1,2.
The ujjayi pranayama steps are given below2:
Did You Know?
Ujjayi pranayama is a breathing technique that may help to manage mental, physical, and spiritual health. Some of the potential benefits of ujjayi pranayama are:
Ujjayi pranayama may improve voice quality, giving a soothing and powerful melodic texture. Everyone can practice ujjayi pranayama and majorly this may help the people who use their voice regularly in their profession. Regular practicing of ujjayi pranayama may reduce the risk of voice disorders in teachers, singers, and actors. However, further studies are required to see if Ujjayi pranayama can help to improve the quality of voice1.
Ujjayi pranayama may help in the case of hypothyroidism, which is caused due to limited activity of the thyroid gland. Practising Ujjayi pranayama may help to improve thyroid function. However, more research is yet to be done to check the exact function of Ujjayi pranayama on hypothyroidism. You must consult a doctor instead of self-medicating if you have thyroid disease2.
Ujjayi pranayama may be helpful in the case of asthma. Ujjayi pranayama may be often recommended as a combination therapy along with conventional asthma treatment. More studies are yet to be done to check the effect of Ujjayi pranayama on asthma. If you experience severe asthma attacks, you must immediately consult your doctor3.
Ujjayi pranayama may be beneficial to individuals with high blood pressure. A study conducted on sixty young healthy volunteers suggests that regular practice of Ujjayi pranayama may lower blood pressure. The same study suggested that regular practice of ujjayi pranayama may reduce the pulse rate in the body.4 However, further studies are yet to confirm if Ujjayi pranayama can reduce blood pressure. You must consult your doctor if you have high blood pressure and do not self-medicate4.
I would like to emphasise a gentle caution for those with low blood pressure when it comes to practising Ujjayi Pranayama. This particular breathing technique involves applying pressure to the carotid sinus, which may potentially cause a further decrease in blood pressure. If you have low blood pressure, it is important to consult a doctor before incorporating Ujjayi Pranayama into your practice.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Research conducted to study the immediate effect of ujjayi pranayama on the cognitive abilities of males, it was found that ujjayi pranayama may calm the mind and improve attention and memory. However, more studies are required to check the effect of Ujjayi pranayama on enhancing attention and other cognitive functions5.
Ujjayi pranayama may help to reduce and manage anxiety6. However, further systemic studies are required to evaluate the effect of Ujjayi pranayama on anxiety. Therefore, it is important to consider consulting a therapist or psychiatrist if you feel anxious often.
Ujjayi pranayama may be used to stabilize energy and consciousness. When individuals practice Ujjayi pranayama, they might experience pure consciousness. In a study7, this was reflected in an electroencephalograph, which is an instrument used to measure the electrical activity in the brain. However, further studies are yet to confirm if Ujjayi pranayama can stabilize energy and consciousness.
Yoga practice may develop the mind and body. However, it is still not an alternative to modern medicine. You must not rely on yoga alone to treat any condition. Please consult a qualified doctor who will be able to assess your condition correctly and advise accordingly. Moreover, it is necessary to practice and learn yoga under the supervision of a trained yoga teacher to avoid any injuries.
I may recommend trying Ujjayi Pranayama for those seeking natural ways to manage sleep-related issues. By practising Ujjayi Pranayama, individuals may experience a calming and soothing effect on the mind, promoting more restful and peaceful sleep8.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
The risks associated with Ujjayi pranayama are as follows:
You must practice yoga under the guidance of a trained yoga professional to avoid any injury.
Ujjayi pranayama is a breathing technique known as ocean breathing or victorious breathing. Ujjayi is composed of two words- ‘ud’ which means a sense of superiority or power, and ‘Jaya’ means victory, conquest, or success. Ujjayi pranayama may help to improve the quality of voice. It may act against hypothyroidism, asthma, high pulse rate, and high blood pressure. It may also be used to improve attention, manage anxiety, and stabilize energy in the body. It is advised to perform Ujjayi pranayama under the training of a yoga professional.
Also Read: Benefits of Jalneti and How to Do It By Dr. Ankit Sankhe
First, sit in a yoga pose Padmasana (Lotus pose), and close your eyes with your back straight. Then, take a long, deep breath slowly from both nostrils. While inhaling, try to contract the throat and feel the touch of air in your throat. Be cautious that it does not touch inside the nose. A distinct sound is produced when the air touches the throat. Keep breathing and relax. Slightly contract your throat and make a gentle hissing sound as you inhale. The sound is not forced, but it can be loud enough. Now breathe out by closing your right nostril and exhale from the left nostril. Try to produce the sound ‘HHHHHAAA’ while exhaling2.
Ujjayi pranayama may help in the case of hypothyroidism and may reduce thyroid problems2.
Yes, ujjayi pranayama may help to reduce blood pressure4.
Ujjayi pranayama may help to improve the quality of voice. It may act against hypothyroidism, asthma, high pulse rate, and high blood pressure. It may also be used to improve attention, manage anxiety, and stabilize energy in the body.
Introverted people shall avoid performing Ujjayi pranayama. Individuals suffering from heart disease may be at risk. Therefore, they shall not combine mudras and breath retention with Ujjayi pranayama. Those suffering from a slipped disc of vertebral spondylitis shall be careful of the position. You must not contract the throat strongly while performing Ujjayi pranayama.
Yes, ujjayi pranayama is often considered a heating pranayama because it generates warmth in the body through the regulation of breath and activation of the throat muscles. This can help stimulate circulation and create a sense of internal warmth during practice.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Yoga has been around for ages. It is only in recent years that interest in it has been renewed. The ease of exercise that Yoga offers is the reason for this new-found interest not only because of the holistic benefits of Yoga alone.
Practicing yoga does not require heavy expensive equipment nor does it require a specialized space (like a gym). It can be done at home, in comfortable clothes, with only a mat. What makes yoga even more attractive is the adaptability that it offers to a beginner. Practically, any yoga pose can be modified to suit a beginner.
Matsyasana is one such interesting yoga asana that can be done in the comfort of your home, with only a yoga mat.
Matsyasana is a popular yogic asana. In the word ‘Matsyasana’, Matsya means Fish in Sanskrit. It is named so since the final posture that the body assumes in this asana resembles a fish. Hence Matsyasana is also called a Fish pose1.
Yoga asanas, when done properly using the proper techniques in a systematic matter, not only help in obtaining the maximum health benefit but also help in reducing the incidence of any injury.
The steps to do Matsyasana are as follows:
Matsyasana has an interesting story attached to it, which makes for an enjoyable read.
Based on what I have observed over the years, practising Matsyasana can bring about various physical benefits for your body. This yoga pose involves stretching and opening the rib cage, hips, and abdominal cavity, which might lead to increased flexibility and improved range of motion7.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
The potential benefits of Matsyasana are as follows:

Diabetes is a complex condition mainly presenting as excess glucose in the blood and urine, as the hormone insulin, needed to metabolize sugar is deficient. It needs to be managed with an integrative treatment approach using exercise, medicines and diet. An inverted pose like Matsyasana may help stimulate the pancreas helping in insulin release and eventually in controlling the rising blood and urinary sugar levels. It may also help improve the blood circulation to the pancreas2.

Gynaecomastia is the medical term for the unusual development of one or both breasts in males. Though commonly seen in men who are overweight at puberty, it can also occur in older overweight men. It can be caused due to hormonal changes or the intake of medicines containing estrogen (the female hormone). Matsyasana may help in reducing the amount of fat in the chest region which may make it appear leaner. It may also help reduce cholesterol deposits in the chest region and overall weight loss5.

Dysmenorrhoea means painful periods without any underlying pathological cause. Primary dysmenorrhoea or menstrual cramps begin when the periods start with the pain usually occurring in the lower abdomen and radiating to the upper part of the thighs and the lower back. It may also be associated with loose motions, nausea, headache, and stress. Practising Matsyasana regularly may improve the flexibility and strength of the back and the pelvic muscle floor, thus benefitting the management of primary dysmenorrhoea6.
I have observed that practising Matsyasana might help in coping with stress and anxiety. This yoga pose involves deep breathing and gentle stretching, which can have a calming effect on the mind and body. It is believed that the stretching of the chest and opening of the heart area in Matsyasana stimulates the relaxation response and helps to release tension, promoting a sense of peace and relaxation7.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Obesity means having excess body fat and is not limited to being overweight. The incidence of obesity is rising rapidly due to incorrect dietary habits and lack of exercise. Matsyasana is a pose that may help combat obesity. Practising Matsyasana regularly may help reduce fat deposits in the thighs and belly as it involves stretching of the abdominal and inner thigh muscles.

Though practicing yoga is beneficial for the mind as well as the soul, it should not be resorted to as the sole treatment option for any medical condition. If you are suffering from any health issues, you must consult a qualified medical practitioner who can assess, examine, and treat you appropriately. Also, it is necessary to practice any form of Yoga under the guidance of a trained yoga expert to prevent any sort of injuries.
Also Read: Benefits of Savasana (Corpse Pose) and How to Do it By Dr. Ankit Sankhe
There are some risks related to practising Matsyasana and one must take adequate precautions in certain situations:
Under the supervision of a qualified and experienced yoga teacher, who can understand your risk factors, you may practice Matsyasana with the necessary precautions.
Also Read: Benefits of Mandukasana (Frog Pose) and How to Do it By Dr. Himani Bisht
Matsyasana or fish pose is an asana that has many benefits for the pelvic region, excess body fat, spine, respiratory organs, painful periods, and pancreas. It is also said to bring about a sense of harmony and balance in those who feel out of balance. To avail maximum health benefit of this asana, it is advisable to practice it under the guidance of a trained Yoga teacher who can assess and advise you regarding the proper technique of practicing without any injuries.
Also Read: Benefits of Ardha Matsyendrasana (Half Fish Pose) and How to Do it By Dr. Himani Bisht
While Matsyasana is said to be useful for uterine issues and sexual dysfunctions in females, there is not enough scientific evidence to declare Matsyasana to be safe during pregnancy.
Matsyasana should be practiced under the supervision of a trained and experienced Yoga professional who can guide you regarding the number of times it may be done during the day.
Practicing Matsyasana regularly may help in reducing fatty deposits in the belly as well as the thighs since the final pose stretches the abdominal and inner thigh muscles.
The final pose in Matsyasana is advised to be held for 10-15 seconds2. However, if you are doing Matsyasana for the first time, it is advisable to hold this pose for as long as you are comfortable.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Isn’t it thought provoking that yoga uses the body to heal the body? Yoga relies on your own body for strengthening it. It focuses on steady posture and relaxation of muscles. This is what makes yoga different from other exercises. Other forms of exercise focus primarily on external equipment and inducing stress on the body.
Indian saints developed the traditional methods of yoga to control the mind and bodily activities. Every human wishes to live in harmony with oneself. Physical, mental and spiritual balance is of utmost importance1.
Today, Yoga is globalized and is widely practiced in India and Western countries. People of all age groups, gender,s and nationalities practice yoga in various settings like schools, gyms, yoga studios, parks, homes, and temples. Yoga has become a profitable enterprise as its interest in people keeps increasing. Yogalates and Yogarobics are some of the modernized versions of yoga2.
Yoga often sees the practice of asanas, one of which is padahastana. Let us look at some interesting features and benefits of padahastasana.
Padahastasana is one of the asanas (pose) of surya namaskar. Surya means sun, and namaskar means salutation. Surya Namaskar comprises of breathing techniques (pranayama) and 7 asanas that are performed in cyclic order, thereby creating 12 asanas in total. Surya Namaskara includes 7 asanas like Pranamasana, Hastautthan Asana, Hastapad Asana, Ashwasanchalan Asana, Ashtang Namaskar, Bhujangasana and Parvatasana.
Pada means feet and hasta means hands. Therefore, padahastasana means keeping the palms down towards the feet4. Padahastasana is also called the hand-to-foot pose. It uses the breathing pattern of Ucchavasa, which refers to normal breathing. This means no exhalation or inhalation of breath, rather simple free breathing3.
Did You Know?
Padahastasana must be done properly for maximum health benefits. One may perform padahastasana in the following manner:
Some benefits of hand-to-foot pose are as follows:

Yogic postures like padahastasana may effectively control headaches. Sang in 2015 found that practising padahastasana may reduce headaches and the use of symptomatic medication. A clinical trial was conducted where migraine patients were using yoga conventional care for six weeks. The results suggested that people who practised this pose showed lesser frequency and intensity of headaches. However, if you have a severe headache for an extended period, you must consult your doctor5.

Yoga postures like padahastasana may help to improve concentration and memory. It may be helpful in the case of ADHD symptoms in preschoolers (Samantha et al., 2019). A clinical study5 on 100 students who practised yoga for about three months suggested significant improvement in attention, concentration and memory.

Short wavelengths of artificial blue light emitted by electronic gadgets may delay sleep by suppressing sleep-inducing hormones. A study5 showed that around 80% of participants using an electronic device for more than three hours a day experienced poor sleep quality. By reducing physiological arousal and inducing relaxation and positivity in the body, this asana may help to improve sleep. However, if you experience chronic sleep issues, you must get in touch with the doctor.

The practice of padahastasana may help to manage stress by reducing heartbeat and blood pressure. It may also reduce the body’s oxygen demand, thereby reducing the vulnerability to stress. Fang and Li conducted a clinical trial on a population of 120 nurses. It was divided into two groups. One group attended the Yoga program while the other group did not. After a six-month follow-up, it was found that the ones who participated in the yoga program had reduced stress levels5.

The practice of padahastasana may help to improve heart health and reduce the risk of heart disease. It may control blood pressure. A study5 by Manchanda, S.C. (2014) suggested that Yoga may maintain cholesterol and blood sugar levels. Patel and North conducted a trial of yoga practice in 34 subjects less than 75 years old. The result showed a significant reduction in blood pressure. However, you must consult your doctor in case of abnormal blood pressure.

This posture may help in the case of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). It includes abdominal pain, discomfort and bloating. A yoga module setup in a clinical trial6, comprised various breathing techniques and postures. Padahastasana was one of the postures. The results showed a possible connection between the postures and the IBS symptoms. However, if you experience severe symptoms of IBS, you must immediately consult your doctor.

Padahastasana may enhance the flexibility of hamstring muscles (muscles present at the back of the thighs). A study of 20 subjects suggested that padahastasana may improve hamstring muscle flexibility and reduce muscle tightness. However, further studies are required to confirm these claims7.
Practising a series of postures that include padahastasana may help in the case of type 2 diabetes. The practice of yoga may keep blood glucose levels in control. Nagarathna et al. conducted a study where the subjects performed a variety of asanas. Padhastasana was one of them. The result of the study8 suggested a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes in individuals who practised yoga regularly. However, you must check your sugar levels and consult your doctor in case of abnormal sugar levels.
Yoga practice may help develop the mind and body; however, it is still not an alternative to modern medicine. Therefore, you must not rely on Yoga alone to treat any condition. Instead, please consult a qualified doctor who will be able to assess your condition correctly and advise accordingly. Moreover, it is necessary to practice and learn Yoga under the supervision of a trained yoga teacher to avoid any injuries.
Practising Padahastasana, also known as the Forward Bend Pose, might have positive effects on your body’s flexibility and strength. By bending forward and reaching towards your toes, this yoga pose stretches the muscles in your back, hamstrings, and calves, increasing their flexibility.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Conditions where padahastasana should be done cautiously are:
With the guidance of a qualified and experienced yoga teacher/yoga expert, we can access and analyse the risk factors and continue to practice exercise with precautions.
In my experience, I have learned that Padahastasana might be effective in reducing excess abdominal fat. This yoga pose involves forward bending, which may help to stimulate the abdominal muscles and improve blood circulation in the area. With regular practice, Padahastasana can contribute to a reduction in abdominal fat and improve overall body strength and flexibility.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Padahastasana is one of the 12 poses of surya namaskar. Pada means feet; hasta means hands. Therefore, padahastasana means keeping the palms down towards the feet. It means hand-to-foot pose. Yogic postures like padahastasana may effectively control headaches, improve concentration, control sleep deprivation and manage stress. The practice of padahastasana may improve heart health by keeping blood pressure in control. Additionally, it may relieve the symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). It may also control blood sugar levels and improve the flexibility of hamstring muscles.
Also Read: Benefits of Matsyasana (Fish Pose) and How to Do it By Dr. Ankit Sankhe
Padahastasana is the hand-to-foot pose. Pada means foot, hasta means hand and asana meaning pose. Therefore, padahastasana translates to hand-to-foot pose in English4.
Padahastasana yoga pose may control headaches, improve concentration, control sleep deprivation and manage stress. It may improve the heart health by keeping blood pressure in control. Additionally, it may relieve the symptoms of Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). It may also control blood sugar levels and improve the flexibility of hamstring muscles5,8.
First, stand straight with feet about 2 inches apart. Then inhale slowly and simultaneously raise your arms up. Then, stretch up the body from your waist. Exhale and slowly bend forward until your palms touch the ground. Make your back as straight as possible by stretching it. Maintain this posture for 10-30 seconds. Breathe normally at this time. Now inhale and slowly come up to an upright position and stretch your arms right above your head. Finally, exhale slowly and come back to the starting position. Relax in samasthiti (simple standing position)4.
People having cardiac disorders, vertebral and disc disorders, hernia, glaucoma, abdominal inflammation, ulcers, myopia, vertigo shall be cautious while performing padahastasana4.
Yes, padahastasana is one of the poses of surya namaskar.
1. Yadav SK, Kumar A, Kumar V, Kumar A. Importance of Yoga in daily life. Accessed on January. 2015;30:2019. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/278673574_IMPORTANCE_OF_YOGA_IN_DAILY_LIFE
2. Singleton M, Byrne J, editors. Yoga in the modern world. London: Routledge; 2008. Available from: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/edit/10.4324/9780203894996/yoga-modern-world-mark-singleton-jean-byrne
3. Nikam VM. A Role Of ‘Surya Namaskara’ For Good Health. Available from: https://www.aiirjournal.com/uploads/Articles/2020/03/4434_25.Vd.Manisha%20Nikam.pdf
4. 21 June INTERNATIONAL DAY OF YOGA INTERNATIONAL DAY OF YOGA Common Yoga Protocol, Ministry of Ayurveda, Yoga & Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha and Homoeopathy (AYUSH) [Internet] 4th Revised Edition, May 2019. [Cited: 2022 Sep 10] Available from: https://mea.gov.in/images/pdf/common-yoga-protocol-english.pdf
5. Sharma B, Pant K, Pant B, Sharma P, Thapliyal M, Sinha S, Pandey A, Chaudhary V, Verma D. ELECTRONIC DETOXIFICATION WITH YOGA AND MEDITATION. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/351618249_ELECTRONIC_DETOXIFICATION_WITH_YOGA_AND_MEDITATION
6. Kavuri V, Raghuram N, Malamud A, Selvan SR. Irritable bowel syndrome: Yoga as remedial therapy. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2015 May 6;2015. Available from: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2015/398156/
7. Paul A, Sasidharan AN, Majeedkutty NA. Effect Of Padahastasana In Improving Hamstring Muscle Flexibility Among Young Adults. Available from: https://www.worldwidejournals.com/international-journal-of-scientific-research-(IJSR)/article/effect-of-padahastasana-in-improving-hamstring-muscle-flexibility-among-young-adults/MTczMjI=/?is=1&b1=1&k=1
8. Chattopadhyay K, Mishra P, Manjunath NK, Harris T, Hamer M, Greenfield SM, Wang H, Singh K, Lewis SA, Tandon N, Kinra S. Development of a yoga program for type-2 diabetes prevention (YOGA-DP) among high-risk people in India. Frontiers in public health. 2020 Nov 17;8:548674. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2020.548674/full
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
We drink milk regularly and consume products made from milk to gain nutritional benefits and feel strong and healthy. Buffalo milk is considered richer than cow’s milk, as it has more nutrients. Scientifically buffaloes are called Bubalus bubalis and these buffaloes are highly adaptable. World milk production has grown twice in the last two decades and buffalo milk has shown an annual growth rate of approximately 2.5% higher than cow’s milk.
The largest producers of buffalo milk are China, India, and Pakistan. Additionally, the nutritional uses of buffalo milk make it a potential alternative to cow’s milk, even for people having milk allergies1. Let us look into buffalo milk nutrition, buffalo milk benefits, buffalo milk disadvantages and the precautions needed for taking buffalo milk.
Did you know?
Below are the nutrient values of Buffalo milk per 100 g:
Milk fat globule membrane, a minor milk constituent contains various nutrients and has many health benefits. They might have positive effects on brain development and function along with physical performance in elderly people5.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Buffalo milk might possess the following properties:
Buffalo milk contains several nutrients that may have many health benefits to humans. Some of the potential uses of buffalo milk are as follows:

As seen in studies, fermented buffalo milk may contain bacteria such as Lactis and this bacterium might be helpful for the heart. Its consumption may lower cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and triglyceride levels. Therefore, daily consumption of fermented buffalo milk might be helpful for the heart1. If you have any heart problems, consult the doctor and take proper medication. Do not self medicate.

Although buffalo milk calories are relatively higher when compared to cow’s milk, buffalo milk may contain the bacteria L.paracasei, and these bacteria may show anti obesity effects on body fat. It also contains probiotics that might help in managing body weight. Therefore, buffalo milk might benefit in managing weight1. Do not take anything on your own and consult your doctor, they will accurately diagnose and treat you.

L.plantarum is a bacterium that may increase the quality of dairy products and is present in buffalo milk. This L.plantarum is known to enhance the absorption of minerals, and vitamins and stimulate the generation of proteins. These probiotics may increase protection against pathogens in the gastrointestinal tract and may boost immunity1. The buffalo milk might have a probiotic nature and may help in boosting immunity. If you have any immunity related diseases, consult the doctor and do not self-medicate.

Buffalo milk was tested for anti-diabetic activity in animals, where it showed an anti-diabetic effect. Buffalo milk contains probiotics that might act against diabetes. Therefore, buffalo milk may have the potential to lower diabetes. However, more studies on humans are required to confirm its effectiveness1,3. Diabetes is a serious condition and must be accurately diagnosed and treated by a doctor. Do not self-medicate.

Milk may contain health promoting bacteria known as probiotics. The consumption of probiotic dairy products might be beneficial for health and may help in lowering cholesterol levels, managing weight, reduce heart related diseases and brain stroke1. However, consult your doctor for the stated conditions and do not self medicate.

Buffalo milk and its products are a major source of protein, which may positively regulate human health and may show beneficial effects such as anticancer, antimicrobial (fight bacteria) and antihypertensive (lowers BP)1. Do not self medicate. It is important that you consult your doctor.
Though there are studies that show the benefits of buffalo milk in various conditions, these are insufficient and there is a need for further studies to establish the true extent of the benefits of buffalo milk on human health.
According to some research, whey product, the byproduct of buffalo milk might have anti-cancer properties6.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
You can drink buffalo milk with/without any additives. You can also make your favourite recipes like milkshakes, coffee, tea, and cake with buffalo milk. However, you must seek expert advice before consuming buffalo milk.
You must consult a qualified doctor before taking buffalo milk in large quantities or any herbal supplements. Do not discontinue or replace an ongoing treatment of modern medicine with an ayurvedic/herbal preparation without consulting a qualified doctor.
Some people are allergic to cow’s milk, and there is a possibility that they might be allergic to buffaloe’s milk as well. Allergies due to milk may be due to one or more proteins present in the milk. Milk allergies are common in children and may also grow later in life, and they build a tolerance to milk. In addition, a few individuals are unable to produce enough lactose. So, when they drink milk the bacteria in the large intestine break down the lactose and show some symptoms this is called lactose intolerance. The symptoms include:
Also, avoid using buffalo milk for its properties or against any health conditions without consulting your doctor. If you are allergic to milk consult the doctor and take proper advice.
An individual should take the following precautions:
Before using buffalo milk for any disease condition, make sure you have consulted with your doctor about the possible precautions. It will help you avoid any unwanted effects.
Also Read: Soy Milk: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects By Dr. Rajeev Singh
Buffalo milk might interact with medicines and alter their activity. However, there is not much information available on the interaction of buffalo milk with medicines. More studies and research are needed to check if it affects any medicines. Therefore, if you are taking any medications, it is important that you consult your doctor after knowing it is safer for you to consume buffalo milk.
Buffalo milk might be good for health as it may have several health benefits. It may have various properties such as anti-diabetic, anticancer, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory1. However, more research is required. Do not self-medicate and consult a doctor for stated conditions.
Some people are allergic to buffalo milk, may become lactose intolerant, and show symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating gas, and diarrhoea4.
Buffalo milk might help with weight management. It was tested for anti-obesity activity, which was found to lower body fat and weight. However, more studies are needed to confirm its weight-managing activity1. Do not self-medicate.
It would be best to talk to your doctor before consuming buffalo milk during pregnancy. Do not self-medicate. Consumption of buffalo milk without expert advice can cause side effects, therefore, talk to your doctor.
Buffalo milk contains proteins, fibres, fats and vitamins A, B and C.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Next Page »« Previous Page