“Kacchi kairi” or raw mango is reminiscent of our childhood days for many of us. The name itself is sufficient to stimulate our taste buds. The scientific name of mango is “Mangifera indica”, and it belongs to the family Anacardiaceae. Be it the tangy kacchi kairi (raw mango) or the sweet ripened fruit, mangoes are one of the most relished fruits in India.
There are over 30 different species of mango, each with a unique taste, colour, size, and shape. Every part of the mango tree has some medicinal properties. For example:
Various parts of the tree have also been used as antiseptic, dentifrice (tooth powders and toothpaste), diaphoretic (to increase perspiration), and vermifuge (anti-helminthic).
The taste and numerous health benefits justify why mango is called the “King of Fruits.” Let’s find out more about this nutrient-rich fruit.
Raw mango is a great source of nutrients, rich in vitamins, minerals, dietary fiber, and carotenoids. Here are the nutritional components of raw mango per 100 grams2:
Did you know?
Research has found that the consumption of raw mangoes may show the following properties:
Some of the potential benefits of raw mango are described as follows:
Raw mango is high in fiber and low in calorie content and can help manage weight. Yanni et al. conducted a study5 in 2022 to assess the effect of mango consumption on weight-related health outcomes. It was found that the male adults who consumed raw mangoes showed a lower Body Mass Index (BMI), waist circumference and body weight compared to the non-consumers. This may indicate that the consumption of raw mangoes may help in weight management. However, more studies to support these claims are needed3,4.
Raw mango is rich in antioxidants like polyphenols and mangiferin. A review6 conducted in 2017 stated that mangiferin helps inhibit cell proliferation and apoptosis (cell death). It is known to interfere with cell cycle regulation and thus, the carcinogenic pathway. This may indicate that raw mangoes can help in managing cancers. However, human studies are required to ascertain these claims.
Raw mangoes may help in avoiding liver problems by stimulating bile production. Bile is a juice produced by the liver that helps break down fats and aids digestion. It helps in the removal of drugs and toxins from the body. Additionally, mangiferin, an antioxidant in raw mangoes, has a hepatoprotective function. This may indicate that consuming raw mangoes may help improve the liver’s health. However, no human studies have been conducted so far to support these claims3,5.
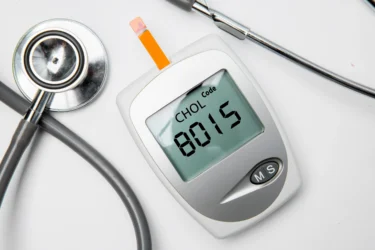
Raw mangoes contain a unique antioxidant, mangiferin, which helps balance triglycerides, cholesterol, and fatty acids. Additionally, the fibre, potassium, and vitamin content in mangoes may help reduce the risk of cardiac diseases. Therefore, there is a possibility that the consumption of mangoes can help promote a healthy heart, but we need more human studies to support these claims3.
Due to the presence of nutrients like Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin E, proteins, iron, zinc, etc., raw mangoes are a good option for nourished hair and healthy skin. Furthermore, vitamin C is important for forming collagen, which strengthens the hair and skin. In addition, raw mangoes may help improve hair growth and produce sebum, which is known to moisturise the scalp and keep the hair healthy. This indicates that the consumption of raw mangoes may exert a beneficial effect on hair and skin. However, there needs to be more studies to support these claims in humans3.
Raw mangoes are rich in Vitamin C, which may help reduce the risk of various blood disorders like haemophilia, anaemia, and blood clot formation. Additionally, raw mangoes may help increase the elasticity of blood vessels and aid the hematopoiesis process (formation of new blood cells). This indicates that consuming raw mangoes may help manage blood disorders. However, as the scientific evidence supporting these claims is limited, it is best to seek a professional opinion if you might be suffering from a blood disease3.
Though there are studies that show the benefits of raw mangoes in various conditions, these are insufficient and there is a need for further studies to establish the true extent of the benefits of raw mangoes on human health.
Did you know that one cup (165-gram) of sliced, raw mango contains approximately 100 calories? Mangoes are not only delicious but also provide a satisfying and nutrient-rich snack option5.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Raw mangoes can be used in the following ways:
You must consult a qualified doctor before taking any herbal supplements. Do not discontinue or replace an ongoing treatment of modern medicine with an ayurvedic/herbal preparation without consulting a qualified doctor.
Individuals with a latex allergy should exercise caution when consuming mangoes, as they may experience a cross-reaction. This means that the proteins in mangoes can trigger an allergic response in those who are sensitive to latex7.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
A few side effects related to the consumption of raw mango include:
However, if you experience any adverse reactions to raw mango, discontinue its intake and immediately contact a doctor or your Ayurvedic physician who has prescribed it to you. They will be able to guide you appropriately for your symptoms.
Also Read: Red Rice: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects & More
Eating raw mango is okay if it is taken in moderate amounts. However, general precautions must be followed while consuming raw mango. The majority of the precautions are:
Also Read: Bakuchi: Uses, Benefits, Dosage & Side Effects
Raw mangoes inhibit the cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are known to metabolise certain drugs like warfarin, propranolol, theophylline, etc. Inhibition of these enzymes can alter the blood concentration of drugs metabolised by this pathway. Therefore, you must always seek the advice of your doctor about the possible interaction of raw mangoes with other drugs, and follow the prescription thoroughly, as they will know your health condition and other medications you are taking.
Also Read: Peanuts: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects and More
The scientific name of mango is “Mangifera indica”, and it belongs to the family Anacardiaceae1.
Mango is known as the king of fruits1.
Raw mangoes contain a high level of carotenoids, which may help improve eyesight. However, there are no human studies which have proven these claims. So, it is advised to consult a doctor for proper treatment.
Consumption of raw mangoes in excess can result in stomach pain and diarrhoea. Some people may experience allergies or throat pain after consumption of certain raw mango varieties.
Since raw mangoes can inhibit the cytochrome P450 enzymes, medicines which are metabolised by this pathway may show an unwanted reaction. So, it is advised to consult a doctor for proper advice.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Due to prolonged sitting habits throughout the day, we experience limited flexibility in the hip muscles. Since these muscles lose flexibility, they can be painful and the movements get restricted. These changes in the movements impact the other regions of our body and ultimately affect the way we move. Yoga poses might help address flexibility issues of the major muscle groups1.
Bhadrasana, is one such yogasana. It is a sitting posture. Let us read further to know more about bhadrasana benefits2.
Bhadrasana is a combination of two words, Bhadra and asana. Bhadra means firm or auspicious; thus, bhadrasana is also called the firm or auspicious posture. It is an excellent meditation pose. This asana helps to increase blood flow in the pelvic (region between abdomen and thighs) part2,3.
Did You Know?
To perform the bhadrasana yoga pose, we must sit with our neck, head and back straight with your legs stretched in the front. Let the hips and palms rest on the floor comfortably. Then follow the following steps to get into the bhadrasana posture:
If you cannot touch your thighs to the floor or cannot even reach them somewhat close to the floor, you may place a soft cushion underneath the knees for support.
Practising bhadrasana might increase the flexibility of your legs, and improve strength in the thighs, hips, backbone, and buttocks. Additionally, it may also relieve varicose veins in people who regularly practice it9.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Yogasanas have benefitted humankind for ages; bhadrasana is another beneficial yoga pose which helps in several ways, as follows:

According to the American Heart Association6, eating healthy, exercising and meditation might be good preferences to benefit for heart disease. Cardiovascular diseases (a group of disorders of the heart and blood vessels) may be caused due to high cholesterol levels and increased blood pressure. Appropriate yoga practices are of high importance to help in these two conditions and help reduce mental stress. In the study by Karunaratne HK, Hatha Yoga Pradipika-based literature survey was conducted to investigate the yoga practices suitable for cardiovascular health. The study found that Hatha Yoga, which was correlated with asanas and Yogic exercises, including muscular stretch, might benefit cardiovascular diseases. Bhadrasana, one such practice, might have similar special effects and thus can help maintain cardiovascular health.

In the study7 conducted in 2017, Chauhan et al. found that the body mass index or BMI (a person’s weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters) of the study participants doing bhadrasana was reduced within a month; this effect might be the asana that might help to decrease the fat deposited within the adipose tissue. Their findings also indicated that yoga therapy, which includes several yoga asanas including bhadrasana could possibly reduce obesity-related complications.

Bhadrasana can help to keep the body firm and stabilise the mind2. According to the 2017 study7 done by Chauhan et al. The asanas such as bhadrasana might relax and calm the mind. It might balance and regularize the stress-controlling centre in our nervous system.
The upright position of the spine in these asanas, such as bhadrasana, allows slowing down of heart rate. This effect reduces load on the heart to pump blood to the brain against gravity. Thus, the heart rate and the cardiac output simultaneously slow down, and BP is controlled7.

Thakre and Bhati, in a study8 in 2018, conducted a clinical trial to study the effectiveness of bhadrasana, along with other asanas, on Stress Urinary Incontinence (SUI) patients. According to the Yogic literature, bhadrasana might help strengthen pelvic floor muscles (muscles between the thighs containing the urinary region, genitals, rectum, bottom, and vagina). They further found that regular practice bhadrasana and other such asanas might strengthen abdominal muscles and the pelvic floor and reduce the SUI symptoms.
Yoga practice may help develop the mind and body; however, it is still not an alternative to modern medicine. You must not rely on yoga alone to treat any condition. Please consult a qualified doctor who will be able to assess your condition correctly and advise accordingly. Moreover, it is necessary to practice and learn yoga under the supervision of a trained yoga teacher to avoid any injuries.
As we all know, any yoga asana works around some chakras in the body. Bhadrasana is associated with one of the chakras, the root chakra. The root chakra is associated with the Earth element. Practising bhadrasana may open this root chakra which can result in activating a sense of security in the mind9.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Any asana should be essentially performed correctly under the guidance of an expert yoga trainer or instructor. While performing bhadrasana following risk factors must be kept in mind:
Also Read: Benefits of Virasana (Hero Pose Yoga) and How to Do it By Dr. Ankit Sankhe
Bhadrasana is a sitting posture that is helpful to keep the body upright and calm the mind. Archaeologists have found evidence of the existence of this asana in ancient times. We must perform this bhadrasana yoga pose under expert guidance to achieve maximum benefits for conditions like cardiovascular disorders, Stress Urinary Incontinence, blood pressure and obesity. Thus, it can be a way to achieve good health and relief from stress through regular practice.
Also Read: Benefits of Kapotasana (Pigeon Pose) and How to Do it By Dr. Himani Bisht
Since “Bhadra” means firm or auspicious thus, other names of bhadrasana can be firm posture or auspicious posture2.
No, since the asana might put some pressure on the knees as it requires folding of legs. It is advised that this asana may be avoided by patients who have arthritis2.
Studies have shown that bhadrasana, along with other yoga poses, might help reduce body mass index or BMI (a person’s weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters) and it might help decrease the fat deposited within the adipose tissue. Thus, yoga practices, including bhadrasana, can help us in weight management7.
Bhadrasana might be beneficial for women’s problems, such as relief of abdominal pain often experienced during menstruation and issues related to pregnancy. This effect strengthens pelvic floor muscles (muscles in the areas between the thighs containing the urinary region, genitals, rectum, bottom, and vagina). Bhadrasana, along with other such asanas, can also reduce the SUI symptoms in women2,8.
Also Read: Benefits of Konasana (Angle Pose) and How to Do it By Dr. Ankit Sankhe
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Goji berries are orange-red berries with a sweet-tangy flavour. Goji berry is also called Chinese wolfberry, possibly because the Chinese observed the wolves eating goji berries. It is known as a ‘super fruit’ because of its wide range of medicinal properties. The scientific name of the goji berry is Lycium barbarum, belonging to the family Solanaceae. Goji berries are widely grown in China, Japan, Taiwan, Korea and Mongolia. China is the leading producer of goji berries and is often grown in Gansu, Shaanxi, Xinjiang and Hebei regions1. Traditional Chinese medicine has used goji berry for over 2000 years due to its nutritional benefits. Let us look at some of the benefits of eating goji berries.
Goji berries may contain several bioactive compounds like dipalmitin zeaxanthin carotenoids, betaine, polysaccharides, cryptoxanthin, neoxanthin, β-carotene, fatty acids, organic acids, phenylpropanoids, flavonoids and many more. Additionally, goji berries may contain the following nutrients1:
Several studies have shown that goji berries may have the following properties1:
Did you know Goji berry may act as an anti-ageing agent? Goji berries have proven anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that may help rejuvenate skin cells by reducing oxidative stress and free radical damage to the cells10.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Some of the potential uses of goji berries are:

Hsu et al., published in 2019, that a study2 conducted on humans showed that goji berry might improve the immune system. The mechanism was by increasing the number of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and immunoglobulin G (a type of antibody). However, large-scale studies are required to check this claim. You must keep a healthy lifestyle and take steps to boost your immune system on a daily basis. Feel free to consult a healthcare provider for tips on boosting your immunity.

A study3 by Wawruszak et al. in 2016 showed that goji berry extract might be beneficial for breast cancer as it can cause the death of cancer cells (apoptosis). Additionally, a bioactive compound, betaine, in goji berry may reduce the risk of colorectal cancer. However, more studies are required to check the anti-cancer effect of goji berries. Cancer is a dangerous disease; therefore, you must take proper treatment instead of self-medicating. Please do not rely on goji berries alone for managing your condition.
A study by Silva et al. in 2017 showed that goji berry might lower blood glucose levels; therefore, it may be beneficial for diabetes mellitus4. In addition, bioactive polysaccharide-protein complex in goji berries may improve insulin resistance due to a bioactive polysaccharide-protein complex. Insulin is a hormone that may control the amount of sugar in the blood. With insulin resistance, the glucose might not enter the body cells and is built up in the blood. This may lead to high blood glucose levels. However, these studies were conducted on animals, and further studies on humans are yet to be done. Therefore, you must check your sugar levels regularly and consult your doctor if you have abnormal sugar levels.

A study1 by Pint et al. In 2010 showed that polysaccharides in goji berries might protect the heart. Goji berries may regulate blood pressure and reduce bad cholesterol levels, thereby protecting the heart. However, more studies are yet to be done to check if goji berries may be beneficial to protect the heart. Therefore, you must consult your doctor if you have any symptoms of heart disease.
A study5 by Azami et al. in 2019 showed that goji berries might contain a bioactive compound, zeaxanthin dipalmitate, which may protect the liver. Goji berries may inhibit scarring and thickening of liver tissue and reduce collagen (a protein that provides structure to the tissues) levels, which may harm the liver when in excess. Additionally, zeaxanthin dipalmitate in goji berry may lower the levels of liver enzymes like ALT (alanine transaminase) and AST (aspartate aminotransferase). High levels of these liver enzymes may indicate some liver disease. However, more studies on humans are yet to be done to check if goji berries may be beneficial for liver diseases. Therefore, you must consult your doctor if you experience any symptoms of liver disease.

Goji berries may contain carotenoids, zeaxanthin and lutein, which are also present in the retina of human eyes6. These bioactive compounds may protect the retina from harmful free radicals, blue light damage and dry-eye disease (condition where tears are insufficient in lubrication of the eye). Zeaxanthin in goji berries may be beneficial for eye diseases like cataracts, glaucoma and retinitis pigmentosa (a genetic disorder that may cause loss of vision). Goji berries may inhibit macular degeneration (part of the retina at the back of the eye). However, more studies are required to check if goji berries may be beneficial for eye diseases. However, you must consult your doctor if you feel any discomfort in your eyes.

In a study7 by Reeve et al. in 2009, vitamin C, lycopene, lutein, nicotinic acid and polyphenol compounds in goji berry may protect the skin from harmful UV rays. These compounds may also reduce inflammation caused by sunburns and reduce the risk of skin cancer. However, more studies are yet to be done to check whether goji berries may benefit the skin. Therefore, you must consult your doctor if you see any abnormality on your skin.

A study by Liao et al. in 2017 suggested that adding goji berries to yoghurt or Sichuan pickle may maintain the viability of lactic acid bacteria (gut bacteria)8. More studies are yet to be done to check the effect of goji berry as a prebiotic. Therefore, consult a doctor to know more about taking care of your gut health and avoid self-medicating.
Though studies show the benefits of goji berry in various conditions, these are insufficient, and there is a need for further studies to establish the true extent of the benefits of goji berry on human health.
Researchers believe that regular consumption of Goji berry juice may result in increased vitality, focus, physical performance, mental clarity, and emotions of peace and satisfaction. Goji berries are well known for their antioxidant property which is believed to reduce oxidative stress and potentially improve the state of mind9.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Goji berries can be consumed in the following way:
You must consult a qualified doctor before taking goji berries in large quantities or any herbal supplements. Do not discontinue or replace an ongoing treatment of modern medicine with an ayurvedic/herbal preparation without consulting a qualified doctor.
Side effects of goji berry may be seen if you eat it in excess or are allergic to it. One article suggests that goji berries may cause the following side effects:
You must consult your doctor if you have any side effects after consuming goji berries.
Also Read: Acai Berry: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects and More By Dr. Smita Barode
The following precautions must be taken before consuming goji berries:
It is advised to consult your doctor before consuming goji berries if you have any pre-existing diseases like diabetes and high blood pressure and you are taking medicines for the same.
Also Read: Tofu: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects By Dr. Smita Barode
Goji berries may interact with the following drugs:
You must consult a doctor before consuming goji berries if you are undergoing any medical treatment.
Also Read: Spinach (Palak) Juice: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects By Dr. Smita Barode
There are several goji benefits. Goji berries may be beneficial for diseases like cancer and diabetes. It may boost the immune system and protect the heart and the liver. It may also be used as a prebiotic. Additionally, it may be beneficial for the skin and eyes. However, you must consult your doctor instead of self-medicating if you have symptoms of any diseases.
According to the findings of one article, goji berry may cause urticaria (rashes and swelling on the skin) on the hand, palms and lips, oedema (swelling caused by trapped fluid), rhinitis (runny nose), dyspnea (shortness of breath), pruritis (itching on the skin) and dysphagia (difficulty in swallowing). Side effects of goji berry may be seen if you eat it in excess or are allergic to it. You must consult your doctor if you have any side effects after consuming goji berries.
Goji berries may protect the skin from harmful UV rays. Goji berries may also reduce inflammation caused by sunburns and reduce the risk of skin cancer. You must consult your doctor if you see any abnormality on your skin.
Goji berries may contain several bioactive compounds like dipalmitin zeaxanthin carotenoids, betaine, polysaccharides, cryptoxanthin, neoxanthin, β-carotene, fatty acids, organic acids, phenylpropanoids, flavonoids and many more. Goji berry may contain fats, proteins, fibres, carbohydrates and sugars. It may contain minerals like iron, sodium and calcium. Goji berry vitamins include vitamins A and C. Additionally, it may contain amino acids like lycine, threonine, valine, cysteine and many more.
1. Vidović BB, Milinčić DD, Marčetić MD, Djuriš JD, Ilić TD, Kostić AŽ, Pešić MB. Health Benefits and Applications of Goji Berries in Functional Food Products Development: A Review. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jan 27;11(2):248. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020248. PMID: 35204130; PMCID: PMC8868247. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8868247/
2. Zhang T, Alexa EA, Liu G, Berisha A, Walsh R, Kelleher R. Lycium barbarum for health and longevity: a review of its biological significance. Obesities. 2025;5(2):35. doi:10.3390/obesities5020035 [cited 2026 Jan 6]. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2673-4168/5/2/35
3. Miranda MR, Vestuto V, Amodio G, Manfra M, Pepe G, Campiglia P. Antitumor Mechanisms of Lycium barbarum Fruit: An Overview of In Vitro and In Vivo Potential. Life (Basel). 2024 Mar 21;14(3):420. doi: 10.3390/life14030420. PMID: 38541744; PMCID: PMC10971595. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10971595/
4. Silva CS, Alves BCA, Azzalis LA, Junqueira VBC, Fonseca R, Fonseca ALA, Fonseca FLA. Goji Berry (Lycium barbarum) in the treatment of diabetes melitus: a systematic review. Food Research. 2017;1(6):221-224. doi:10.26656/fr.2017.6.102 [cited 2026 Jan 6]. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319200037_Goji_Berry_Lycium_Barbarum_in_the_treatment_of_diabetes_melitus_a_systematic_review
5. Bahaji Azami NL, Sun M. Zeaxanthin Dipalmitate in the Treatment of Liver Disease. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Aug 21;2019:1475163. doi: 10.1155/2019/1475163. PMID: 31531108; PMCID: PMC6721266. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6721266/
6. Li X, Holt RR, Keen CL, Morse LS, Yiu G, Hackman RM. Goji Berry Intake Increases Macular Pigment Optical Density in Healthy Adults: A Randomized Pilot Trial. Nutrients. 2021 Dec 9;13(12):4409. doi: 10.3390/nu13124409. PMID: 34959963; PMCID: PMC8708314. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8708314/
7. Reeve VE, Allanson M, Arun SJ, Domanski D, Painter N. Mice drinking goji berry juice (Lycium barbarum) are protected from UV radiation-induced skin damage via antioxidant pathways. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2010 Apr;9(4):601-7. doi: 10.1039/b9pp00177h. PMID: 20354657. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20354657/
8. Skenderidis P, Mitsagga C, Lampakis D, Petrotos K, Giavasis I. The Effect of Encapsulated Powder of Goji Berry (Lycium barbarum) on Growth and Survival of Probiotic Bacteria. Microorganisms. 2019 Dec 28;8(1):57. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8010057. PMID: 31905688; PMCID: PMC7022968. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7022968/
9. Amagase H, Nance DM. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical study of the general effects of a standardized Lycium barbarum (Goji) Juice, GoChi. J Altern Complement Med. 2008 May;14(4):403-12. doi: 10.1089/acm 2008.0004. PMID: 18447631.Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18447631/
10. Skenderidis P, Leontopoulos S, Lampakis D. Goji berry: health promoting properties. J. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021;2(1):3. doi:10.3390/jfct2010003 [cited 2026 Jan 6]. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/1661-3821/2/1/3
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Have you relished avocado toast or guacamole at a brunch party? Isn’t it amusing that oil extracted from the flesh of avocado fruit may have several benefits for health? The scientific name of avocado is Persea americana, which belongs to the Lauraceae family. Avocado oil is extracted from avocado fruit by the cold-press method. Even 16th-century literature has reported use of avocado oil. Avocado oil is highly popular in the cosmetic industry due to the presence of high levels of vitamin E. Avocado oil is usually extracted from the Hass type of avocado which is grown in several countries like the United States, Chile, Mexico, Spain, New Zealand, etc1,2. Let us look at some avocado oil health benefits.
Avocado oil may contain several bioactive compounds like fatty acids, sterols, tocopherols, tocotrienols, phenolics, carotenoids, and chlorophylls1. Additionally, avocado oil may contain the following components:
From my knowledge, lutein and vitamin E, essential for healthy eyes and skin, are found in avocado oil. Researchers believe that particularly lutein is believed to guard against age-related macular degeneration, that may cause vision loss and even blindness11.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Some avocado oil properties are given below:
Some of the possible uses of avocado oil are:
A study14 by Hernandez et al. In 2016 showed that avocado oil might be beneficial in reducing bad cholesterol levels- LDL (low-density lipoproteins) and total cholesterol. Avocados may possess cholesterol-lowering activities due to mono-unsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) and phytosterols2. However, further studies are required to check if avocado oil may help to reduce cholesterol levels. Therefore, you must check your doctor in case of high cholesterol levels.

A study13 by Furlan et al. in 2017 showed that a diet including avocado oil might help to reduce the levels of triglycerides (harmful fats), which may help to lower the risk of obesity. Excessive fat accumulation in the body may lead to diseases like diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and heart disease; therefore, it is vital to maintain a healthy weight2. However, further studies are yet to be done to check if avocado oil may help manage weight. Therefore, you must consult your dietician before making any changes in your diet.

In study4 conducted on rats showed that avocado oil might reduce blood pressure. This may be due to bioactive compounds like oleic acid, which may get incorporated into the cell wall and may control blood pressure2,4. However, more studies on humans are required to confirm if avocado oil may be used to regulate blood pressure. Therefore, you must check your blood pressure regularly and consult your doctor in case of high blood pressure.

A study5 by Avila et al. in 2015 showed that avocado oil might help normalize total cholesterol and triglyceride levels (harmful fats) caused due to diabetes2,5. Another study by Equihua et al. in 2016 showed that avocado oil might reduce insulin resistance Insulin is a hormone that may control the amount of sugar in the blood. With insulin resistance, the glucose might not enter the body cells and is built up in the blood. This may lead to high blood glucose levels. Additionally, oleic acid in avocado oil may help the secretion of specific proteins that can produce insulin2. However, more studies on humans are required to confirm if avocado oil can be used in diabetes. Therefore, you must check your blood sugar levels regularly and consult your doctor in case of high blood sugar levels.

A study6 by Pepa et al. in 2017 showed that fatty acids like mono-unsaturated fatty acids might help to protect the liver. Another study by Sato et al. in 2015 showed that tocopherols in avocado oil might help reduce oxidative stress on the liver2,6. However, more studies are required in humans. Therefore, you must consult your doctor if you have any symptoms of liver disease.

A study7 by Santos et al. in 2018 showed that avocado oil might act against gram-negative bacteria by penetrating through the cell walls of the bacteria. The anti-microbial property of avocado oil may be due to bioactive compounds like tocopherols, carotenoids, β-sitosterol, and terpenoids2,7. However, large-scale studies are yet to be done. Therefore, you must consult your doctor if you suspect any bacterial infection.

One of the features of psoriasis is the development of an itchy rash on the skin. A study8 by Stucker et al. in 2001 showed that topical application of a cream containing vitamin B12, and avocado oil might be beneficial for psoriasis. However, more research is required to check if avocado oil may be used for psoriasis. Therefore, you must consult your doctor and not self-medicate if you have psoriasis.
Though studies show the benefits of avocado oil in various conditions, these are insufficient, and there is a need for further studies to establish the true extent of the benefits of avocado oil on human health.
In my experience, ASU (Avocado Soy Unsaponifiables) may be a wonder ingredient to their food for people with osteoarthritis. Researchers believe that ASU, produced by mixing soybean and avocado oil may be used as an alternate anti-inflammatory therapy to cope with osteoarthritis12.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Avocado oil can be included in the diet in the following way:
You must consult a qualified doctor before taking avocado oil in large quantities or any herbal supplements. Do not discontinue or replace an ongoing treatment of modern medicine with an ayurvedic/herbal preparation without consulting a qualified doctor.
Also Read: Maple Syrup: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects By Dr. Smita Barode
Some clinical trials have shown that the following side effects may occasionally be associated with avocado oil:
You must immediately consult your doctor if you experience any side effects after consuming avocado oil.
Also Read: Coconut Oil: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects By Dr. Rajeev Singh
Avocado oil, being a natural substance is relatively safe to consume. However, as with all other substances, pregnant and lactating mothers shall be cautious before using avocado oil in any form. It is best to consult your doctor before doing so.
Avocado oil may interact with warfarin, a drug that prevents abnormal blood clotting10. You must consult your doctor before consuming avocado oil if you are undergoing any medical treatment.
Also Read: Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil: Health Benefits, Nutrition, and Best Uses
Avocado oil may lower cholesterol, manage weight, regulate blood pressure, and protect the liver. It may act against diabetes, microbial infection, and psoriasis. However, you must consult your doctor if you have any disease instead of self-medicating2,4,8.
Avocado oil may contain bioactive compounds like oleic acid, linoleic acid, and palmitic acid which may help to keep the skin moisturized. It may also contain vitamin E, lecithin, and potassium, which may nourish and detoxify the skin. Phytosterols present in avocado oil may help to rejuvenate stressed skin8.
Avocado oil may contain fatty acids, choline, and vitamins E, carotenoids, sterols and many more1,3.
Avocados may lower bad cholesterol levels due to mono-unsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) and phytosterols like β-sitosterols. You must check your cholesterol levels regularly and consult your doctor in case of high cholesterol levels2.
Avocado oil may interact with warfarin, a drug that prevents blood clots10. You must consult your doctor before consuming avocado oil if you are undergoing medical treatment for prevention of blood clots.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability, or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation of the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Bright red cranberries are not just a delight to the eyes but are packed with goodness. Dried fruits serve as a healthy snack throughout the world. They are concentrated forms of fresh fruits. This reduces service sizes with the same nutritional value. Cranberries with scientific name Vaccinium macrocarpon, has several benefits for human health. It may be consumed as juices, sweetened dried cranberries, etc. Fruit concentrates or sugar is infused into cranberries before drying to get sweetened dried cranberries1,2. Read along to learn more about the potential dried cranberry benefits and side effects.
Dried cranberries are rich in phytochemicals such as total phenolics, flavonoids and flavanols. The percentage nutritional value and nutritional content of dried cranberries is as follows1,3:
It also comprises some amounts of Vitamins such as: Vitamin B6, Vitamin E, Vitamin K. Moreover, each 160gm serve of dried cranberries contains 493 calories and it comprises of a high sugar content of about 116.10 gm.
Due to rich phytochemical compositions, dried cranberries might have potential health-promoting properties such as:
I may say that by including dried cranberries in your diet, you might support the growth of good bacteria in your digestive system. The unique compounds found in cranberries might help reduce the presence of harmful microbes in the colon, creating a more favourable environment for beneficial bacteria13.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Clinical studies and observations have demonstrated potential health benefits of dried cranberries, some of which are as following:

Dried cranberries were reviewed by Howell9 et al., 2005; Jepson & Craig10, 2007; Howell9 2007; Vasileiou12 et. al, 2013; for their ability to effectively reduce severity of urinary tract Infections (UTI) and its reoccurrence. Micali et al. (2014), evaluated11 the efficacy of dried cranberry that may potentially be beneficial in UTI for young and middle-aged women. However, more evidence for its use for humans and its clinical use needs further investigation1. Cranberries might be effective against UTI as it may help reduce the ability of bacteria to adhere to the bladder wall, thus, they might not grow and trigger infection4.

Ruel6 et. al 2006 and Lee7 et. al in 2008, suggested that supplementing a group of patients with bioactive compounds found in cranberry extract might help to manage proteins responsible in an increase in HDL-C (high-density lipoprotein concentration) also known as good cholesterol concentration and improves removal of excess bad cholesterol from the body. Thus, the dried cranberries might have some effect on cardiovascular (heart and blood vessels) health. Further studies would be required to estimate the effect of dried cranberries on cardiovascular health in humans4.
A variety of other mechanisms might account for a favourable effect of cranberry consumption on cardiovascular disease. These are described below:

As per studies conducted on animal models, cranberry juice might be capable of managing platelet aggregation (platelets clump together to form blood clots). Dried cranberries can have some beneficiary effect on platelet aggregation and thrombosis (blood clots that block your blood vessels). Thus, dried cranberries might help in management of in vascular diseases. This effect seems to be not proven and needs to be studied further4.
Dohadwala et al. 2011 in their studies8 have shown that consumption of cranberry juice might have some effect in providing relief from stiffness in central aorta (the main blood vessel through which oxygen and nutrients travel from the heart to all organs). Similar effects might be observed with dried cranberries as they help with stiffness of central aorta and help in circulation of oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. Since any issue with central blood flow is associated with higher risk of cardiovascular disease outcomes dried cranberries might in turn provide benefits for cardiovascular diseases4.

Cranberry extract was studied on animals for its effect on an increase in blood pressure. An in-vitro study suggested that cranberry extracts inhibit angiotensin (a protein-based hormone that causes blood vessels to become narrower) formation. Therefore, it might have some effect in lowering blood pressure4. More studies providing evidence-based support to this claim are needed.
Animal studies have also determined that flavonoids derived from cranberry may have some effect on lowering blood glucose directly. Indirectly, it may reduce blood glucose level by an improved insulin sensitivity as per some animal models having diabetes mellitus4. However, effect of dried cranberries on diabetes in humans is barely explored. We need further studies to validate the dried cranberry benefits for diabetes.
Various in-vitro studies indicate that the bioactive compounds found in cranberry might suppress the activation of immune reaction that may cause inflammation. Several human studies have also provided evidence for anti-inflammatory effect of cranberries. However, these do not provide sufficient evidence for the exact effect on humans thus, further studies are required to clarify these conclusions4.
Though there are studies that show several dried cranberry benefits in various conditions, but these are insufficient and there is a need of further studies to establish the true extent of benefits of dried cranberries on human health.
I may suggest including dried cranberries in your diet if you want to support your oral health naturally. Cranberries contain compounds that may ward off bacteria in the mouth, possibly reducing the risk of cavities, gum disease, tooth decay, and even oral cancer13.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Sweetened dried cranberries can be had as a suitable snacking option2.
You must consult a qualified doctor before taking any herbal supplements. Do not discontinue or replace an ongoing treatment of modern medicine with an ayurvedic/herbal preparation without consulting a qualified doctor.
Cranberries might generally regarded be as safe, but consuming them in larger amount can cause diarrhoea and upset stomach in young children5. Dried cranberries side effects may be similar. Thus, they must be eaten in regulated amounts as per the guidance of our Ayurvedic physician.
Also Read: Persimmon (Amlok) Fruit: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects By Dr. Rajeev Singh
Some studies have shown that cranberry might interacts with the anticoagulant (blood thinner) such as warfarin. Thus, you must discuss your ongoing medications and inform your doctor if you are already on blood thinners like warfarin before consuming dried cranberries.
Also Read: Dronapushpi (Leucas aspera): Uses, Benefits and Side Effects By Dr. Rajeev Singh
Dried cranberries may have several benefits for overall health they might have potential benefits for urinary tract infections, cardiovascular health, blood pressure, diabetes etc. Thus, eating dried cranberries as a snack can be a suitable option and they might be good for our health as well if taken in moderation under guidance of an Ayurvedic physician1,4.
Dried cranberries are good source of Vitamin B6, Vitamin K and Vitamin E and thus they may help with the benefits of these vitamins3.
Cranberries might generally be regarded as safe, but there is insufficient evidence to validate safety of dried cranberry for women during pregnancy or while breastfeeding. Thus, they must be taken in moderation and only after consulting with a doctor5.
Studies have demonstrated the interaction of cranberry with warfarin an anticoagulant (blood thinner). Thus, before consuming dried cranberries you are advised to discuss your ongoing medications with your doctor5.
Dried cranberries might have some ability to effectively reduce severity of urinary tract Infections (UTI) and its reoccurrence. Researchers have evaluated the efficacy of dried cranberry that may potentially be beneficial in UTI for young and middle-aged women4. However, these do not provide sufficient evidence for the exact effect on humans. You must consult a doctor before using dried cranberries for its benefits.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Homemade food is considered the path to nourishment and holistic health. The key to a healthy home-cooked meal is the right choice of cooking oil. Rice bran oil is a vegetable oil and a by product of rice bran. It has been gaining popularity as a premium edible oil in Asian countries like India, China, Japan, Thailand and Taiwan. This wonder oil might become a boon for better cooking due to its unique properties like prolonged shelf life, high smoke (burning) point, less greasy and less oily, along with enhancing the flavour of food. In Japan, it is called ‘Heart Oil’ whereas, in western countries, it is a ‘Functional Food’ or ‘Health Food’. It contains a heart friendly phytochemical, oryzanol, making it an ideal cooking oil1,2. Let us learn about rice bran oil health benefits, properties, side effects and more.
Did you know?
Rice bran oil is a pale yellow, odourless, nutty flavoured oil with a sweet taste. It is free from trans fat and contains antioxidants like γ-oryzanol, tocotrienols, squalene, tocopherols, etc. The nutrient value of rice bran oil is as follows:
Rice bran oil has gained a status as a ‘heart healthy oil’. It has been categorised as healthy edible oil, possibly due to its following health benefiting properties2.
Rice bran oil has a very well-balanced fatty acid profile that is recommended by prestigious organisations like the World Health Organization, the National Institute of Nutrition, the Indian Council of Medical Research, and the American Heart Association5.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Rice bran oil may have several advantages due to bioactive antioxidants, which may benefit our health2. A few of rice bran oil nutritional benefits are described below:

Rice bran oil may have cholesterol lowering properties due to its unique components, such as γ-oryzanol, tocotrienols, and mono and poly unsaturated fatty acids. These bioactive components may be responsible for reducing bad cholesterol levels by increasing bile excretion. Rice bran oil bioactives may also reduce fats and lipids and increase good cholesterol levels (high density lipoproteins). This may create a balance between good and bad cholesterol, which might be important for good health1,2. However, more studies are needed to suggest the benefits of rice bran oil for human health.

Rice bran oil may have blood sugar lowering properties. Rice bran oil, combined with sesame oil used as cooking oil, might reduce the pre and post meal plasma glucose levels in type 2 diabetic patients. These anti-diabetic properties of rice bran oil might be due to the high amount of γ-oryzanol. It might stimulate insulin production in the body and regulate blood glucose levels by activating liver enzymes, lowering blood glucose levels2,4. However, diabetes is a serious condition therefore, getting a proper diagnosis and treatment is necessary. So, kindly do not rely on rice bran oil for managing your sugar levels.

The skin benefits of rice bran oil may be associated with squalene and tocotrienols. These antioxidants may be similar to the skin’s natural oils, which may be easily absorbed into the skin, retaining its moisture. Rice bran oil may also have anti-inflammatory action, which might help skin repair against the harmful effects of UV rays1,2. Hence, rice bran oil might be used in sunscreens, however, take medical consultations and do not self-medicate.

Rice bran oil may have antioxidant properties due to the phytochemical γ-oryzanol. Antioxidants may help enhance body immunity and combat various diseases. These antioxidants may also fight cancer-causing free radicals in the body, thus, reducing cancer risk. Besides, rice bran oil may be effective for weight loss as it contains oleic acid and linoleic acid, which may help lose weight and manage obesity. In addition, vitamin E of rice bran oil may help enhance brain functioning and balance the endocrine hormones. However, further research is needed to study1,2 the antioxidant nature of rice bran oil.

Though studies show the benefits of rice bran oil in various conditions, these are insufficient, and there is a necessity for further studies to develop the true scope of the benefits of rice bran oil on human health. In addition, each person may respond differently to these herbs. Therefore, it is essential to consult a physician before using rice bran oil for any medical condition.
Did you know that rice bran oil (RBO) is not just delicious but also packed with benefits? One fascinating fact is that RBO contains Vitamin E, which might not only improve neurological functioning but may also help to balance endocrine hormones5.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Food cooked in rice bran oil may be less oily with a better taste and flavour2. You may use rice bran oil:
People should consult a qualified doctor before using rice bran oil in large quantities. Further, we recommend not to replace or discontinue any ongoing treatment of modern medications with any ayurvedic or herbal preparations of rice bran oil without taking the medical advice of a doctor. They will guide you with its form and dosage per your health condition.
Gamma oryzanol, found in rice bran oil, has shown impressive results in reducing thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels in patients with hypothyroidism. Additionally, it has been dicovered that gamma oryzanol might be effective in alleviating women’s menopausal issues5.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
Increasing the amount of rice bran oil in a diet may cause certain side effects1. The side effects of rice bran oil may include:
Therefore, you should not use rice bran oil to self-medicate on your own. It is essential to take a doctor’s advice and have it only if recommended.
Rice bran oil (RBO) has a unique property that sets it apart from other oils. It creates fewer polymers, which means it is less greasy compared to other oils. This not only contributes to a better flavour in your dishes but also makes clean-up easier. Additionally, RBO has the advantage of being absorbed less when used in cooking, and still providing enhanced flavour.
Dr. Anuja Bodhare, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Various toxicological studies found that when used in moderation, rice bran oil might be a safe alternative to edible oil2. However, the following precautions must be considered:
If you’re looking for a natural and easy way to freshen your breath, rice bran oil might be your saviour! In a study, it was found that using rice bran oil for oil pulling could be effective in reducing bad breath, also known as halitosis6.
Dr. Ashok Pal, BAMS
Rice bran oil contains γ-oryzanol, which might positively interact with certain drugs resulting in herb-drug interaction. A study (Devarajan et al., 2016) found that rice bran oil blends might positively support the activity of a blood sugar-lowering drug (Glibenclamide) to reduce blood glucose levels in type 2 diabetic patients4.
However, consult with your doctor before using rice bran oil. They will direct you to the better way to have it. Do not self-medicate.
The usage of rice bran oil may have increased due to its unique properties, like its less greasy and oily nature. The prolonged shelf life and high smoke point might enhance the taste and flavour of food1,2.
Rice bran oil is enriched with γ-oryzanol, tocotrienols and unsaturated fatty acids. Therefore, it may help reduce bad cholesterol, fats and lipids and increase good cholesterol levels. This effect might balance the good-to-bad cholesterol ratio eliminating heart problems1,2. However, take a professional opinion in case of hypercholesterolaemia and do not self-medicate.
The benefits of rice bran oil for the skin might be due to bioactive compounds like squalene and tocotrienols. Rice bran oil may be used in creams and gels due to its anti-inflammatory and skin-conditioning properties. It might make the skin smooth and soft and be used as sunscreen against the harmful effects of UV rays1,2.
When consumed in high amounts, the side effects of rice bran oil might be harmful to health. Rice bran oil contains omega-6-fatty acids that may cause cancer. In addition, it might lower blood calcium levels. It might also cause flatulence, gas, and stomach discomfort1,2. Therefore, to avoid such side effects, take your doctor’s advice and use it only if recommended.
Rice bran oil has vitamins like vitamin E and vitamin K3.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Most of us have relished raspberry ice cream on a hot sunny day. Isn’t it astonishing to know that raspberries have several health benefits? It is believed that the Romans first cultivated raspberries in the fourth century. Raspberries are considered to be the first collected by the people of Troy from the foothills of Mt. Ida. This fruit is native to North Asia and Eastern Europe. Raspberry belongs to the family Rosaceae, and its scientific name is Rubus Idaeus, which means ‘bramble bush of Ida’. It was thought that the Olympic Gods were looking for berries on Mt. Ida1. Raspberry are a host of several nutrients. Let us look at some health benefits of raspberries.
Raspberries may contain bioactive compounds like polyphenols, flavanols, gallotannins, hydroxycinnamic acids and many more1. Additionally, it may also contain the following nutrients:
Nutritional value of raspberry (raw)2
Based on studies I came across, eating raspberries might result in changes in genes and blood substances related to the immune system and metabolism. These findings suggest that regularly consuming raspberries may affect our immune and metabolic pathways that might be beneficial for our health14.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Some of the properties of raspberries are:
Let me tell you an interesting fact about raspberries! They may provide a noteworthy amount of vitamin C, that offers multiple benefits for our health. One notable benefit might be its ability to support healthy gums and better blood formation15.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
There are several raspberry fruit benefits. Some of the potential raspberry fruit uses are:

Raspberries may possess antioxidant activity, which may be beneficial for heart diseases. A study1,3 by Mullen et al. in 2002 showed that raspberries might be an antioxidant because of bioactive compounds like ellagitannins, anthocyanins and vitamin C. Anthocyanins may improve the function of endothelial cells (cells that regulate blood flow in the heart). Additionally, raspberries may also regulate blood pressure. However, more studies are required to check if raspberries may protect the heart. Therefore, you must consult your doctor if you have any symptoms of heart disease.

A study1,4 by Jayaprakasam et al. in 2005 showed that the bioactive compound anthocyanins in raspberries might stimulate insulin secretion and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. Another bioactive compound, cyanidin-3-glucoside, may reduce the blood sugar levels. However, more research is required to check if raspberries may be beneficial for diabetes. You must check your blood sugar levels regularly and consult your doctor in case of abnormal blood sugar levels.

A study1,5 by Park et al. in 2010 showed that ketones in raspberry might benefit weight loss. The ketones may break down the lipids or the fats (lipolysis). It may also cause fatty acid oxidation, which may help with weight loss. It may also regulate the secretion of adiponectin, a hormone that breaks down fatty acids. However, more research is required to check if raspberry may benefit weight management. You must consult your nutritionist before making any changes in your diet.
A study1,6 by Bowen-Forbes et al. in 2010 showed that raspberries might inhibit cancer cell growth due to bioactive compounds like anthocyanins. Polyphenols in raspberries may reduce the risk of colon and intestine cancer. Ellagitannins and anthocyanins may reduce the risk of cancer due to their antioxidant property. They may deactivate the harmful free radicals (molecules that harm the body). However, more research is yet to be done to check if raspberries may be used for cancer. Cancer is a serious disease; therefore, you must take an informed consultation and proper medications as advised instead of self-medicating.
Alzheimer’s disease may be characterised by disturbed insulin functioning and increased oxidative stress and inflammation. Raspberries may contain bioactive compounds like polyphenols which may regulate insulin levels, reduce inflammation and reduce oxidative stress. These three factors may cause Alzheimer’s disease. In addition, raspberry fruit may decrease deposition of amyloid-β protein, which may be beneficial in reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s disease1,7. However, more studies are required to check whether raspberry may benefit Alzheimer’s disease. Therefore, you must consult your doctor if you have any symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease and never self-medicate.

A study8 by Wang et al. in 2018 showed that compounds like cyanidin and ellagic acid might help to protect the skin from UV rays. It may reduce skin cell death, thickening, wrinkles, dryness, tanning and redness of the skin. However, more studies are required to check if there are raspberries benefits for skin. You must consult your doctor if you see any abnormality in your skin.

A study9 by Ash et al. in 2011 showed that α-linoleic acid in raspberry might be beneficial to lower triglyceride levels in the body. A condition called dyslipidemia is an excess of triglycerides, which are harmful fats present in the body. Therefore, raspberries may also be beneficial for dyslipidemia. However, more studies are required to check if raspberries can reduce the levels of triglycerides in the body.

A study10 by Harada et al. in 2007 showed that raspberry ketones might be beneficial for hair growth in alopecia patients. The raspberry ketones may increase blood flow in the scalp and help in hair growth. However, more studies are yet to be done to check the raspberries benefits for hair Therefore, you must get proper treatment if you have conditions that cause hair loss like alopecia instead of self-medicating.
Though studies show the benefits of raspberries in various conditions, these are insufficient, and there is a need for further studies to establish the true extent of the benefits of raspberries on human health.
In light of what I have observed, raspberries are a great source of dietary fibre. This might play a crucial role in promoting healthy digestion and managing constipation15.
Dr. Smita Barode, BAMS, M.S.
Raspberry can be consumed in the following ways:
You must consult a qualified doctor before taking raspberries in large quantities or any herbal supplements. Do not discontinue or replace an ongoing treatment of modern medicine with an ayurvedic/herbal preparation without consulting a qualified doctor.
Side effects of raspberry consumption may be seen if you eat in excess or are allergic to it. An article with a case report of 52-year-old woman suggested that consumption of raspberry may cause the following side effects:
You must immediately consult your doctor if you experience any side effects after consuming raspberries.
Also Read: Brahmi Grita: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects, and more!
The following precautions must be taken before consuming raspberries:
It is advised to consult your doctor before consuming raspberries if you have any pre-existing diseases.
Also Read: Passion Fruit (Krishnabija): Uses, Benefits, Side Effects by Dr. Smita Barode
Raspberries may interact with the following drugs:
You must consult your doctor before consuming raspberries if you are undergoing medical treatment.
Also Read: Dried Cranberries: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects By Dr. Rajeev Singh
The benefits of raspberries may be seen in its possible role in several diseases like cancer, diabetes, heart disease and Alzheimer’s disease. It may lower bad cholesterol levels. Raspberry fruit may be used to manage weight. Additionally, it may be beneficial for skin and hair growth3,10. However, you must consult your doctor if you have symptoms of any diseases instead of self-medicating.
Yes, raspberries may be beneficial for weight loss. A bioactive compound, anthocyanin, present in the fruit may be responsible for weight loss1.
It may cause Itching of palms, shortness of breath (dyspnea), intense flushing on the skin (increased blood flow in the skin), and jitters. In addition, it may increase blood pressure and heart rate11,12. Side effects of raspberry may be seen if you eat in excess or are allergic to it. An article with a case report of 52-year-old women suggested that consumption of raspberry may cause these side effects. You must immediately consult your doctor if you experience any side effects after consuming raspberries.
Pregnant and breastfeeding mothers shall be cautious before consuming raspberries12. You must consult your doctor before consuming raspberries.
Raspberries may interact with stimulants like amphetamines. This interaction may increase blood pressure and heart rate. It may also interact with warfarin (a drug used to prevent blood clots). Raspberries may interact with diabetic drugs like glimepiride and metformin12,13. You must consult your doctor before consuming raspberry if you are undergoing medical treatment.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Foods with great nutritional value are in high demand today as people become more health conscious. Flaxseeds is one such crop that has grown both in cultivation and health benefits since civilisation began. Scientifically flaxseed is named Linum usitatissimum L, which literally means very useful. It belongs to the family Linaceae. The fibre present in the plant is one of the oldest fibres existing. Flaxseed oil, also known as flax oil is prepared from ground and pressed flaxseeds to extract their natural oil. Around 3000 B.C., the ancient Egyptians employed flaxseed for nutritional and therapeutic purposes. India, Canada, China, United States and Ethiopia are the major producers of flaxseed. Flaxseeds contain a large number of lignans, fibre, α-linolenic acid and omega-3 fatty acids1,2. Let’s read more about flaxseed oil benefits and properties.
Did you know?
The nutritional value of flaxseed oil per 100g is as follows:
Together with these, flaxseed oil contains omega-3 fatty acids such as alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), oleic, palmitic, linolenic and lignans1.
Flaxseed oil may possess the following properties:

Flaxseed oil contains alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which may control breast cancer growth. It may help to lower the estrogen receptor, which might help stop the growth of cancer cells in the breast. Flaxseed also contains lignans which show antioxidant properties. Due to their estrogen-like activity, lignans resemble the effects of the hormone estrogen. These are helpful in estrogen metabolism, which is related to ovarian cancer and improved health. It may also be helpful in colon and skin cancer1,2. As cancer is a severe condition, kindly consult the doctor for proper treatment. Do not self-medicate.
Generally, a deficiency of essential fatty acids results in poor wound healing. Flaxseed oil is a rich source of essential fatty acids with linoleic acid (omega-6) and α-linolenic acid (omega-3). These components may regulate prostaglandin synthesis, which may fasten wound healing1. Even so, kindly consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment, and do not self-medicate as it may cause pain.

The anti-inflammatory activity and omega-3 fatty acids in flaxseed oil may help hair growth. It may moisturise the damaged hair after application. It may also help increase the volume of hair. In addition, it may help soothe the scalp4. However, more research is needed on the benefits of flaxseed oil for hair. Kindly consult a professional for better results.

Flaxseed oil contains polyunsaturated fatty acids, linolenic acids, gamma-linolenic acid, and alpha-linolenic acid. These molecules are an essential part of our skin but are usually deficient in our diet. A healthy intake of flaxseed oil with a proper consultation from a nutritionist may help you fix these deficiencies. It may be appropriate for all skin types, including oily, dry and normal. Psoriasis and sunburns may also recover faster with flaxseed oil2,4. Even so, you must consult the doctor before using flaxseed oil instead of relying on flaxseed oil for solving your skin problems, as it may cause side effects.

Alpha-linolenic acid present in the flaxseed oil may help reduce triglycerides. It may also lower the very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) or bad cholesterol in the liver. However, more research is needed to demonstrate the effects of flaxseed oil on human cholesterol levels2. So, please consult the doctor for diagnosis and treatment. Do not self-medicate.
Flaxseed oil contains ALA, which may lower the risk of heart disease through various biological pathways. For example, it may help regulate platelet function, blood vessel health, inflammation, and arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat). In addition, a study2 conducted at Boston’s Simmons College shows that flax seed oil protects against heart attacks and circulation issues. Kindly consult the doctor for diagnosis and treatment. Do not attempt to self-medicate since conditions could worsen.

Haemorrhoids are a condition characterized by swollen and inflammatory veins located around the anus or in the lower part of the body. Flaxseed oil may facilitate stool passage in the intestines due to its fibrous structure. It may also be beneficial for constipation2. However, more research is needed to check the effects of flaxseed oil on constipation and haemorrhoids. Kindly consult the doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Flaxseed oil has many health benefits. It is a rich source of fibre. Because of this, it may be extremely useful for various digestive diseases like constipation, diarrhoea, irritable bowel syndrome, etc6.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Gout is a form of arthritis with symptoms such as pain, redness, tenderness and swelling in one or more joints, especially in one or both of the big toes. Alpha-linolenic acid in flaxseed may help reduce inflammation in the joints. It may also reduce the cholesterol level raised by gout. Flaxseed oil in gout may reduce swelling and joint pain2. However, more research is required to study the effects of flaxseed oil on gout. Do not self-medicate, as it may cause serious adverse effects. Kindly consult the doctor for better health results.
Though there are studies that show the benefits of flaxseed oil in various conditions, but these are insufficient and there is a need of further studies to establish the true extent of the benefits of flaxseed oil on human health.
Flaxseed oil can be used as follows:
You must consult a qualified doctor before taking flaxseed oil in large quantities or any herbal supplements. Do not discontinue or replace an ongoing treatment of modern medicine with an ayurvedic/herbal preparation without consulting a qualified doctor.
Flaxseed oil is a rich source of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. According to some results, omega-3 fatty acids can reduce inflammation. Due to these properties, flaxseed oil may have a beneficial effect in correcting dry eyes, especially in Sjogren’s syndrome7.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Avoid flaxseed oil if you are allergic to it. It may show as symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and intestinal or abdominal pain5.
Following are the precautions to take with flaxseed oil:
The interactions of flaxseed oil with some drugs are as follows:
Also Read: Coconut Oil: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects By Dr. Rajeev Singh
No. However, more research is needed to know the effects of flaxseed oil on migraine. Kindly consult a doctor.
No. However, more research is required to determine the impact of flaxseed oil on the eyes.
No. However, more studies are needed to prove the effects of flaxseed oil in leprosy. So, please consult the doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Flaxseed oil may have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-platelet, anti-microbial, anti-fungal, anti-cancer, and cardioprotective properties1,3. However, these effects need to be confirmed by further researches. Kindly consult a doctor for better health results.
No. You must consult a gynaecologist before using flaxseed oil and do not try to self-medicate5.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Have you ever wondered which fruit twins with oranges? It is persimmon! A fibrous, fleshy, deciduous and tropical fruit. The scientific name of persimmon is Diospyros kaki, and it belongs to the family Ebenaceae. Persimmons are commonly cultivated in countries like Japan, China, Korea, Brazil, Italy and Turkey. However, the maximum production of persimmon is from China. There are about 400 species of persimmon, did you know? It is the fifth fastest-developing fruit crop in the world! Persimmons have been gaining popularity due to their hidden health benefits1,2. Let us have a glance at some of them.
Persimmon fruits may contain several bioactive compounds like proanthocyanidins, catechins, triterpenoids, carotenoids, tocopherols, flavonoids, tannins, phenolic acids, polyphenols and many more. Additionally, persimmon fruit may contain the following nutrients:
Several studies have shown that persimmon fruit may have the following properties1:
Persimmon fruit is highly nutritious and packed with vitamins, polyphenols, and dietary fibre. Fermented versions of Persimmon fruit might be associated with helping in around 15% weight reduction and reduced liver and abdominal fat13.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Some of the potential uses of persimmon fruit are:

A study4 by Buelga et al. in 2000 showed that bioactive proanthocyanidins in persimmon fruit might help lower blood pressure. It may also reduce the risk of platelet aggregation and thereby reduce the occurrence of thrombosis. Thrombosis occurs when a blood clot blocks the arteries or veins. Persimmon can also enhance nitric oxide production in the body, which may further relax the blood vessels to improve blood flow. In these ways, persimmon may be beneficial in reducing the risk of heart diseases2,4. However, more studies on humans are yet to be done to check the effect of persimmon fruit for heart conditions. Therefore, you must consult your doctor if you have any symptoms of heart disease and not just rely on persimmons.

A study5 by Gorinstein et al. in 2000 on rats suggested that persimmon fruit may reduce bad cholesterol levels and triglycerides. This may be attributed to its antioxidants like lycopene and epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCG)2,5. However, these are data from animal studies, and further studies on humans are yet to be done. Therefore, you must consult your doctor for abnormal cholesterol levels instead of self-medicating.

There are possible persimmon fruit benefits for the management of diabetes. A study6 by Lee et al. In 2007 showed that proanthocyanidins in persimmon might inhibit the enzymes α-amylase and α-glucosidase. These enzymes may metabolize carbohydrates into glucose which enters the bloodstream. This may delay glucose uptake in the blood, thereby reducing blood glucose levels. Additionally, persimmon fruit may inhibit the rapid absorption of glucose after eating carbohydrate-rich meals, which may inhibit the spike of blood sugar levels2,6,7. However, more studies are required to check if persimmon fruit may be beneficial for the management of diabetes. Therefore, you must check your blood glucose level regularly and consult your doctor in case of a high blood glucose level.

A study8 by Jo et al. in 2011 showed that persimmon fruit might inhibit cancer cell growth. Bioactive compounds like carotenoids and catechins in persimmon fruit may be beneficial for breast, prostate, oral and blood cancer2,8. However, more studies are required to confirm if persimmon fruit can help in cancer. Cancer is a dangerous disease; therefore, you must get proper treatment instead of self-medicating.

A study9 by Jeun An et al. in 2005 showed that persimmon leaf extract might be beneficial for various skin problems like skin eruptions, eczema (inflammation of the skin) and acne. This use may be due to bioactive compounds like flavonoids, catechins, β-carotenes, tannins, organic acids and vitamins B1, B2, C, and K9. However, more studies are required to assess persimmon fruit benefits for skin.

A study10 by Matsumura et al. in 2017 showed that tannins present in persimmon might act against bacteria like those of the Mycobacterium species, which may cause lung infections. Additionally, it may reduce inflammation caused due to bacterial infections10. However, further studies are required to check if persimmon fruit may be used in case of bacterial infections. Therefore, you must consult your doctor if you suspect a bacterial infection.

A study15 by Seddon et al. in 1994 showed that lutein, a bioactive compound in persimmon, may protect the macula part of the eye from damage. The macula is a yellow spot at the back of the retina in the eyes, which is responsible for the central vision. Lutein (a carotenoid) present in persimmon fruit is also found in the macula of the eye2. However, further research is yet to be done to check if persimmon can be used to protect the macula from damage. Therefore, you must consult your doctor if your vision is hampered.
Though studies show the benefits of persimmon fruit in various conditions, these are insufficient, and there is a need for further studies to establish the true extent of the benefits of persimmon fruit on human health.
According to my observations, an increase in free radicals can lead to oxidative stress that results in cell damage. As Persimmon fruit is packed with bioactive compounds such as proanthocyanidins, tannins, carotenoids, etc., it can act as an antioxidant and might aid in coping with cell damage14.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Persimmons can be included in your diet in the following way:
You must consult a qualified doctor before taking persimmon fruit in large quantities or any herbal supplements. Do not discontinue or replace an ongoing treatment of modern medicine with an ayurvedic/herbal preparation without consulting a qualified doctor
A clinical trial has shown that persimmon fruit side effects may be as follows. However, additional large-scale studies are required to confirm the following side effects, as typically, this fruit is not known to produce any serious side effects:
You must consult your doctor if you experience any side effects after consuming persimmon fruit.
Also Read: Praval Pishti: Uses, Benefits and Side effects By Dr. Rajeev Singh
Adequate precautions should be taken before consuming persimmon fruit, like any other medicine. Pregnant women and lactating mothers should be extra cautious. Likewise, before giving persimmon fruit to the elderly or children, precautions should be taken. Therefore, it is suggested to consult a doctor before using persimmon fruit for these individuals in case of any medical conditions.
Also Read: Cantaloupe: Uses, Benefits & Side Effects
There are not enough studies on the interaction of persimmon with other drugs. Further studies on the interaction of persimmon fruit are yet to be done. Therefore, you must consult your doctor if you are on any other medication before consuming persimmon fruits.
Also Read: Elephant Yam (Suran): Uses, Benefits, Side Effects and More!
There are several persimmon health benefits. It may protect the macula, improve heart health and lower cholesterol levels. It may also be used against bacterial infections and diseases like diabetes. In addition, persimmon fruit may benefit the skin. However, you must consult your doctor if you have any diseases instead of self-medicating1,2,4,10.
Persimmon may cause pruritis (itchy skin), urticaria (swelling, redness and itching on the skin), oedema (swelling due to excess fluid trapped), trigger asthma, rhinorrhea, stomach and many more. It may cause nausea and make you feel dizzy11.
You must consult your doctor if you experience any side effects after consuming persimmon fruit.
Persimmon fruits may contain several bioactive compounds like proanthocyanidins, catechins, carotenoids, tocopherols, flavonoids, tannins and many more. Additionally, persimmon fruit may contain water, energy, carbohydrates, fats and proteins. It may contain minerals like phosphorous, sodium, calcium, iron, potassium and many more. It may contain vitamin C and many amino acids1,3.
Oligomers and polymers present in bioactive compound proanthocyanidins in persimmon fruit might inhibit the activity of enzymes α-amylase and α-glucosidase which may delay glucose uptake and reduce blood sugar levels. Additionally, persimmon fruit may inhibit the rapid absorption of glucose in the body after eating carbohydrate-rich meals2,6,7. However, you must check your blood glucose level regularly and consult your doctor in case of a high blood glucose level.
Bioactive proanthocyanidins in persimmon fruit might help to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of platelet aggregation and thereby, reduce the occurrence of thrombosis (blood clot formation). Persimmon can also relax the blood vessels to improve blood flow by enhancing nitric oxide production2,4. However, you must consult your doctor if you have any symptoms of heart disease.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
We often get sugar cravings where most of us reach for high-sugar foods like cookies, candies, a fun-size ice cream, or a chocolate bar despite knowing its bad effects. However, we bring you a nutritious and healthy snack, which might help with your sugar cravings. Raisins are dried grapes and are considered a traditional dried fruit. Raisins are sweet, consisting of sugar, with high fibre and provide satiety. Raisins are made from Vitis vinifera grapes and are largely produced in the United States, followed by Turkey, China, Iran, Chile, Greece, and Australia. Varieties of raisins are available, which include Dark raisins made from Thompson seedless grapes, Golden raisins, Sultanas, and Zante currant raisins processed by sun-drying or dehydrating grapes1,2. Let us discuss the health benefits of eating raisins, their nutritional value and more.
Did you know?
Raisins are rich in sugar, fructose, and glucose. They have an abundance of dietary fibre and bioactive compounds like vitamins, minerals, polyphenols, anthocyanins, and flavonols. One hundred grams of raisins may provide 301 kcal energy, and the water content is 14.9 g1,3. The nutrients of raisins include:
Here’s the information in pointer format:
Raisins may have health-benefitting properties like:
Let me share an interesting fact with you. Raisins, those little dried grapes, are packed with powerful antioxidants like polyphenols, tannins, and phenolic acids. In an animal study, researchers discovered that feeding ageing rats a diet rich in black raisins may lead to higher antioxidant levels in their bodies. The exciting part is that these antioxidants possibly had a positive impact on the rats’ spatial memory, cognitive function, and motor skills7.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Including raisins in a daily diet may provide favorable health benefits. The following may be the potential advantages of raisins:

Bad cholesterol may be a culprit for various heart diseases. Raisins are a good source of dietary fibre (fructans) and phytochemicals, which may have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Studies have found that the benefits of eating raisins with other foods might lower blood lipids (fats) and cholesterol levels in patients suffering from high cholesterol problems. Adding raisins to your diet might provide enough fibre and might reduce the risks of heart disease1,2,4. However, more studies are needed to suggest the advantages of raisins for fighting heart problems.
Raisins contain antioxidants, which might play an antibacterial role against oral bacteria. In addition, raisins may be low in sucrose concentration, limiting the formation of dental plaques. Hence, eating raisins may be beneficial for oral health. The phytochemicals present in raisins may act as antibacterial and may inhibit the growth of oral bacteria that cause dental diseases1. However, if you have a dental problem, visit a dentist and get a clean-up.

High blood pressure may cause hypertension. The benefits of eating raisins daily may provide enough potassium and dietary fibre, which may lower blood pressure. Furthermore, raisins may also contain polyphenols, which might release nitric oxide and may act to control high blood pressure1. However, more clinical studies are required to draw a firm conclusion about using raisins against blood pressure. Till then, take doctor’s consultations and do not use raisins to self-medicate.

Losing weight is challenging, and a fibre-rich diet may facilitate weight loss. Eating raisins may make you feel full and reduce hunger. The gut hormones might be altered, feeling satisfied and reducing energy intake. It might limit the absorption of fat and starch in the bowel. Thus, having raisins may lead to lesser absorption of complex carbohydrates, which might help in maintaining correct body weight and may aid weight loss1,4. So, adding raisins to your weight loss meal might help you lose weight. However, more studies are required to support the true scope of raisins health benefits on humans.

A high-fat diet may disturb the functions of the thyroid gland. An animal study5 (Ayuob et al., 2022) found that raisins may contain fibres, polyphenols, flavonoids, and phenolic acids, which may be powerful antioxidants. These nutrients might help modulate the levels of thyroid hormones. It may increase the production and action of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in the body5. However, this animal study is insufficient; more human studies are required to support the uses of raisins for thyroid imbalance. If you have thyroid problems, consult a doctor, and do not self-medicate.

Though studies show the potential uses of raisins in various conditions, these are insufficient, and there is a necessity for further studies to develop the true scope of the benefits of raisins on human health. In addition, each person may respond differently to these herbs. Additionally, it is essential to consult a doctor before using raisins for any medical condition.
I came across a fascinating study that revealed something truly amazing. Black raisins might just be a natural remedy against anaemia! In a study with rats, researchers found that providing anaemic rats with raisin extract potentially improved their blood count and made their red blood cells appear to be healthy and normal. So, if you’re looking for a delicious and nutritious way to boost your iron levels, adding black raisins to your diet might be a wise choice8.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Grapes were dried for storage and travel in prehistoric times. Since then, raisins have been produced as food. Raisins are cherished because of their sweet flavour and do not require refrigeration2. You may use raisins as
You should consult a qualified doctor before using raisins in large quantities. Do not discontinue or replace an ongoing modern medical treatment with an Ayurvedic/herbal preparation of raisins without consulting an Ayurvedic physician. They will guide you with its form and dosage per your health condition.
Eating raisins (Kishmish) might be safe. However, a few reports suggest raisin allergies in small children. Raisin allergy is rare and uncommon6. The raisins side effects might be observed as follows:
However, if any allergic reactions are encountered, you must immediately rush to the hospital and consult your doctor to get the proper treatment for your allergies.
Also Read: Mango (Aam): Uses, Benefits, Side Effects by Dr. Smita Barode
Eating raisins in small quantities might be safe. However, a few precautions are necessary:
Also Read: Hibiscus: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects and More!
More research and scientific data are needed to state the potential interaction between raisins and other drugs. Therefore, one must take medical consultations with Ayurvedic doctors before using raisins in a regular diet.
Also Read: Gond Katira: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects & More
Raisins are a traditional dried fruit. Raisins are produced from sun-drying or dehydrating Vitis vinifera grapes variety. They are sweet-flavoured and consist of fibre, proteins and other phytochemicals which are beneficial for health1,2.
Different varieties of raisins include Dark raisins made from Thompson seedless grapes, Golden raisins made from Muscat grapes, Sultanas produced from seedless yellow grapes and Zante currants raisins from black Corinth grapes. Today, around 95% of raisins are produced from dried “Thompson seedless” grapes1,2.
Raisins contain antioxidants, which may have antibacterial activity against oral bacteria. They also have a low concentration of sucrose, which limits dental plaque formation. Hence, raisins may benefit oral health1. However, in case of dental issues, take the doctor’s advice and do not self-medicate.
The essential vitamins in raisins include vitamins E, C, K, B9, B6, B3, B2 and B13.
A few disadvantages of eating raisins may include allergic side effects such as nausea and itching of the mouth within a few minutes of having raisins6.
1. Olmo-Cunillera A, Escobar-Avello D, Pérez A, Marhuenda-Muñoz M, Lamuela-Raventós R, Vallverdú-Queralt A. Is Eating Raisins Healthy? Nutrients. 2020;12(54):1–17. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7019280/pdf/nutrients-12-00054.pdf
2. Williamson G, Carughi A. Polyphenol content and health benefits of raisins. Nutri Res. 2010;30(8):511–9. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0271531710001375
3. FoodData Central. Raisins, golden, seedless [Internet]. U.S. Department of Agriculture. 2019 [cited 2022 Oct 6]. Available from: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168164/nutrients
4. Bell S. A Review of Dietary Fiber and Health: Focus on Raisins. J of Med Food. 2011;14(9):877–83. Available from: https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/abs/10.1089/jmf.2010.0215
5. Ayuob N, Shaker S. Raisins preserve the function and structure of the thyroid gland. J of Micro and Ultras. 2022;10(2):55–62. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9272700/pdf/JMAU-10-55.pdf
6. Chibuluzo S, Pitt T. Raisin allergy in an 8-year-old patient. Aller, Asth and Clini Immu. 2014;10((Suppl 2): A6):23–6. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4304147/pdf/1710-1492-10-S2-A6.pdf
7. Ghorbanian D, Gol M, Pourghasem M, Faraji J, Pourghasem K, Soltanpour N. Spatial memory and antioxidant protective effects of raisin (currant) in aged rats. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2018;23(3):196-205. doi:10.3746/pnf.2018.23.3.196. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6195892/
8. Abu Zaid FA, Abduljawad EA, Aljadani HM, Ali NM, Mohammedsaleh ZM, Ibrahim M, Ali SS, Abunasef SK, Ahmed OT, Amin HA, Al Jaouni SK. Black raisins improved experimentally induced iron deficiency anemia: biochemical and histological evidence. J Pharm Res Int. 2021;33(34A):188–201. doi: 10.9734/JPRI/2021/v33i34A31839. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/353005864_Black_Raisins_Improved_Experimentally_Induced_Iron_Deficiency_Anemia_Biochemical_and_Histological_Evidence
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Next Page »« Previous Page