Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil: Health Benefits, Nutrition, and Best Uses
By Dr. Malavika Athavale +2 more

Get,

to manage your symptom
Get your,


4 Cr+ families
benefitted

OTP sent to 9988776655



You’ve successfully subscribed to receive
doctor-approved tips on
Whatsapp

Get ready to feel your best.

Hi There,
Download the PharmEasy App now!!


Register to Avail the Offer
Send OTPBy continuing, you agree with our Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions

Hi There,
Sign up on PharmEasy now!!
Trusted by 4 crore+ families

OTP sent to 9988776655



You have unlocked 25% off on medicines




Code: NU25
By Dr. Malavika Athavale +2 more
Table of Contents
Choosing the healthiest cooking oil can be challenging, especially when deciding between avocado oil and olive oil. Understanding their nutritional profiles, potential health benefits, and cooking uses can help you make a more informed choice. This blog will give you a scientific breakdown of these two favoured cooking oils, their extraction steps, nutritional details, and health benefits.
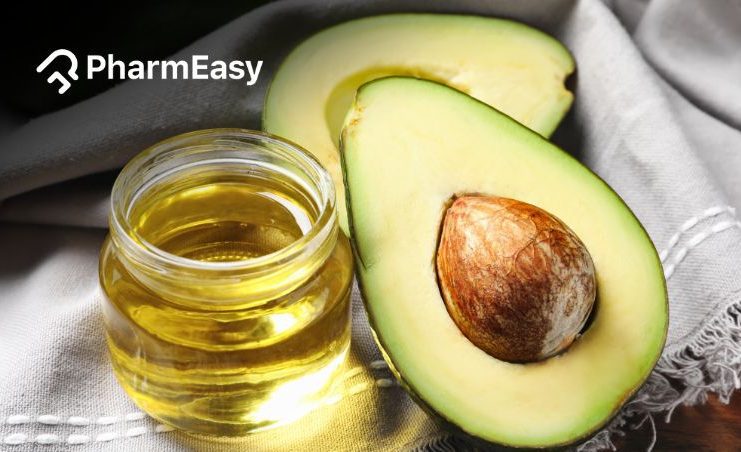

Avocado oil is becoming popular as a healthy and tasty cooking oil. It is derived from the fruit of the avocado tree (Persea Americana), which is native to Central America1.
There are two main ways of extracting avocado oil:
Avocado oil holds many helpful compounds like:
Avocado oil, full of flavour and flexibility, has many uses in the kitchen and cosmetic products. Its mild, butter-like flavour enhances a lot of dishes1. Also, its softening nature makes it a great add-in for skin and hair care items.
From what I have seen, avocado oil might be highly placed for its numerous potential benefits, particularly in the realm of skincare. One notable advantage of avocado oil might be its rapid absorption rate when applied to the skin. This characteristic may allow for quick absorption, delivering its nourishing qualities effectively18.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
A staple in the Mediterranean diet, olive oil is made by pressing olives. There are various kinds of olive oil, each with its unique traits and nutritional properties.
Olive oil is available in different forms, depending on how it is processed3:
Like avocado oil, olive oil is made by either cold-pressing or heat and chemical processing methods4.
Olive oil is made up of a number of good compounds, including:
Olive oil is often used for cooking, dipping, drizzling, and finishing dishes, showing its cooking versatility. Add to this, its moisturising and emollient properties, which make it a go-to ingredient in beauty products. They also form the base of many traditional medicine remedies6.
Based on my observations, I may say that olive oil might serve as a considerably healthier alternative to dietary fats, particularly those derived from animals. When it comes to cooking, olive oil may provide a nutritious substitute for butter, margarine, and various other types of fat. Moreover, a study conducted in this regard demonstrated a remarkable correlation: replacing unhealthy fats with olive oil might be linked to a reduced risk of mortality19.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
To make a smart choice between avocado oil and olive oil, it’s vital to understand their nutritional differences.
Although avocado oil and olive oil are mainly made of monounsaturated fats, their fatty acid profiles differ slightly:
Although both oils have important vitamins and minerals, the quantities can vary.
Calories per tablespoon (15 mL) are similar for both avocado and olive oil. Each provides around 120 calories.
I may attest to the benefits of avocado oil in skincare products. When incorporated into soaps, it might noticeably improve lathering, creating a luxurious and abundant foam. Additionally, when used in creams, it may impart a smoother texture, resulting in a delightful and velvety application18.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
Avocado oil and olive oil provide loads of health benefits, but they differ slightly in the benefits they offer.

The high content of monounsaturated fats and oleic acid in both oils improves cholesterol levels. It also helps regulate blood pressure.

Adding either oil to your diet could help with managing your weight. The unsaturated fats in both oils can curb hunger/help with appetite control. This prevents eating too much and helps with managing meal sizes10.
Oleic acid, polyphenols, carotenoids, and tocopherols add up to the anti-inflammatory properties of avocado oil and olive oil. These compounds work well together to lower inflammation in the body1.
Adding avocado oil or olive oil to your diet could boost digestive health. The monounsaturated fats in these oils reduce inflammation in the gut1. Also, the flavonoids in olive oil are known to have antibacterial effects11. They could protect against harmful gut bugs.
Menopausal women may often face challenges due to hormonal changes, such as emotional fluctuations, hot flashes, depression, anxiety, and vaginal dryness. During these times, I think that olive oil might be a helpful solution. It possesses antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that may help ease symptoms and help cope with menopause20.
Dr. Anuja Bodhare, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)

Antioxidants are needed to fight oxidative stress and they protect body cells.

Avocado oil and olive oil provide soothing and nourishing effects due to their natural ingredients. Therefore, they are popular picks for skin care.
Knowing the value of smoke point in cooking oils is key to retaining their nutritional value. It also keeps the overall quality of the dishes you’re preparing.
The smoke point is the temperature at which an oil starts to break down and release harmful free radicals. Cooking oils at or below their smoke point will maintain both their flavour and their health perks.
Avocado oil’s smoke point is higher than that of olive oil, which means it’s less likely to degrade during high-temperature cooking methods. Avocado oil’s unrefined smoke point is about 480℉ (250℃), while extra virgin olive oil’s smoke point is between 350℉ – 410℉14,15.
Avocado oil is fitting for high-heat cooking techniques, like sautéing, grilling, searing, and baking. This is due to its higher smoke point. On the other hand, olive oil fits best for lower heat methods, like simmering, stewing, and medium-heat sautés.
Both avocado oil and olive oil play a key role in nutrient absorption, especially when consumed with beneficial nutrients in other foods.
Fats, like those found in avocado oil and olive oil, aid in absorbing fat-soluble nutrients, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K. Consuming high-fat foods along with these nutrients improves their availability and uptake by the body.
Both oils help absorb nutrients due to their content of monounsaturated fats. A study found that dressing a salad with avocado oil greatly boosted the absorption of carotenoids from the veggies16. Likewise, adding olive oil to tomato juice was seen to boost the absorption of the carotenoid lycopene17.
Although both avocado oil and olive oil offer countless health benefits like heart health, weight management, anti-inflammatory properties, and skin care, there might be times where one is more beneficial. For example, olive oil might be better for people who put a premium on its higher polyphenol content. Meanwhile, avocado oil might be a better fit for high-heat cooking due to its higher smoke point.
In general, both avocado oil and olive oil add health benefits to your diet. However, do think about personal tastes and specific health needs before buying the oil. This will guide you in choosing the right oil for how you live or as per your lifestyle.
Also Read: Canola Oil: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects by Dr. Smita Barode
Summing it up, avocado oil and olive oil provide a lot of health benefits, flexibility in cooking, and taste. Knowing their nutritional differences and proper uses, you can make an educated choice on the best oil for your diet.
Ultimately, personal taste and individual needs will play a big part in deciding the best oil for you. Grab the chance to test and try out each oil. Then, find your own balance. Logic and some new insights can help you make an educated choice on the best cooking oil.
In many cases, yes. However, remember that their taste profiles and smoke points differ. For high-heat cooking methods, avocado oil might be a better fit. At the same time, olive oil is more suitable for lower-heat applications or as a finishing oil.
Extra virgin olive oil and cold-pressed avocado oil often rank higher in terms of quality and nutritional worth. Yes, they’re pricier. But if your main goal is getting the max health benefits, paying more might be worth it.
Keep both oils in a cool, dark place. Keep them away from heat and direct sunlight. This will extend their shelf life and keep their flavour and nutrients. Also, always seal the container tightly after each use.
As long as they’re part of a balanced diet, there are little risks with avocado oil or olive oil. But it’s important to pick quality products. Also, pay attention to the oils’ smoke points while cooking to avoid harmful free radicals.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Comments

Leave your comment...
You may also like
Comments