How to Decrease Melanin in Skin
By Dr. Raina N. Nahar +2 more

Get,

to manage your symptom
Get your,


4 Cr+ families
benefitted

OTP sent to 9988776655



You’ve successfully subscribed to receive
doctor-approved tips on
Whatsapp

Get ready to feel your best.

Hi There,
Download the PharmEasy App now!!


Register to Avail the Offer
Send OTPBy continuing, you agree with our Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions

Hi There,
Sign up on PharmEasy now!!
Trusted by 4 crore+ families

OTP sent to 9988776655



You have unlocked 25% off on medicines




Code: NU25
By Dr. Raina N. Nahar +2 more
Table of Contents
All individuals are unique in their appearance, particularly in features such as skin tone, hair colour, etc. Have you ever wondered why this happens? This is because of the variations in a pigment called melanin. Melanin defines the colour of our skin which varies from person to person. The peculiarity of this pigment is that its production increases once the skin is exposed to the sun light1.
The skin pigmentation on sun exposure is actually a defensive mechanism of our body to protect it from harmful UV rays1. But there are conditions where melanin production increases beyond the need and people start feeling low on it. This article may help you understand why this happens and how to reduce melanin in skin to manage this condition.

Melanin is a natural pigment which gives colour to the different parts of our body, such as skin, hair, eyes, etc. There are two types of melanin, eumelanin and pheomelanin1,2.
Melanin is produced by melanocytes, which are the specialised pigment-producing cells found in the epidermis (outermost layer of the skin)1,2. Melanocytes produce melanin from an amino acid called tyrosine, through a multi-step process, by using a key enzyme called tyrosinase. This melanin which is produced is then enclosed in a membrane bound organelle called melanosome. These melanosomes are then actively moved to nearby keratinocytes, which are the main cells of the epidermis2.
As mentioned earlier, melanin normally increases once your body comes in contact with the UV rays. These UV rays penetrate the skin and trigger the melanocytes to produce more melanin, leaving your skin darker or tanned1. Other factors which increase melanin production are discussed in the next section.
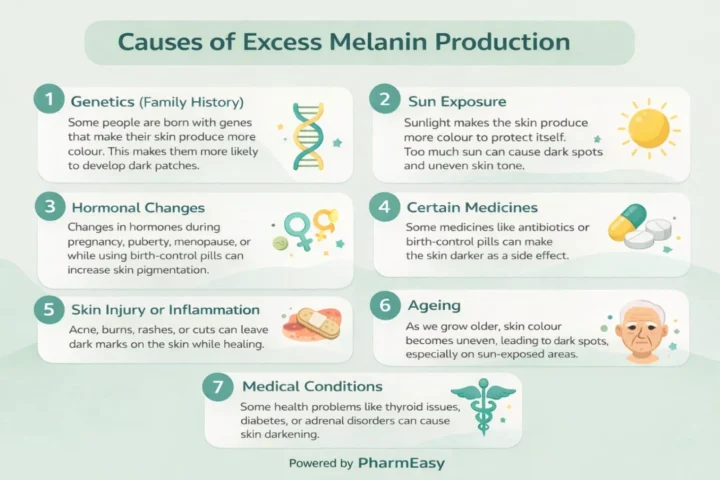
Hyperpigmentation, a result of excess melanin production, can be caused by several factors. Understanding these factors may help you in knowing how to decrease melanin in skin. Following are some common factors among them.
Before seeking medical attention, trying some home care tips may be effective for some common pigmentation issues. Here are some simple home care tips that you can follow for melanin reduction.

Green tea is rich in polyphenols and catechins, which have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. These compounds, particularly polyphenols, have been found to reduce DNA damage, oxidative stress, skin ageing and excess melanin production caused by UV exposure6. Therefore, applying green tea extract or drinking green tea might help calm your skin and reduce melanin production.

Aloe vera is a plant which is extensively adopted in many skincare products and in dermatology. It is well known for its medicinal properties. Its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties might help soothe the skin and reduce inflammation due to skin conditions such as acne, eczema, and rosacea1,7. It also has a compound called aloin, which is said to have skin-lightening properties. Hence, applying aloe vera might help in depigmenting your skin by reducing melanin1.

Turmeric is a traditional plant which is known for its potential uses. It contains curcumin, a compound with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. This compound has been found to lower skin inflammation caused by conditions such as psoriasis and eczema. Another compound called curcuminoid has been found to have exfoliating effects, which helps in removing dead skin cells and reducing hyperpigmentation. Both these compounds work by reducing the formation of the MSH hormone to minimise hyperpigmentation1. Hence, using turmeric might help in lightening your skin by reducing melanin.

Tomato is a vegetable widely used in household kitchens. It has a compound called lycopene, which is a natural antioxidant. It may help protect the skin from sun damage by fighting harmful molecules caused by UV rays. It is also known to reduce skin redness and improve skin appearance by reducing pigmentation and early ageing8. Hence applying tomato might improve your skin by reducing pigmentation.

Argan oil is a natural extract, which is rich in antioxidants and fatty acids. These components in argon oil might help reduce inflammation and promote skin brightening. Its anti-inflammatory property might also be helpful in improving skin conditions such as acne, eczema, and rosacea, by reducing inflammation9. Hence, applying argon oil might help you manage skin darkening and inflammation.

Liquorice root extract is known to have several medicinal properties, especially its benefits for skin health. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties might reduce inflammation and improve skin texture by reducing pigmentation. It’s may also be affective in managing or reducing the severity of skin conditions such as rosacea and acne1. Hence, applying liquorice roots extract might improve your skin from hyperpigmentation’s such as melasma and manage other skin-related diseases.
Although home remedies may be helpful in reducing melanin, consistency is key to see results. When using any new product for the first time, it is always advisable to do a patch test before using to avoid risk of any allergies.
There are several medical options available to decrease melanin in skin and manage hyperpigmentation. Following are some among them:
Topical creams are the most common method for managing hyperpigmentation. These creams contain depigmenting agents like hydroquinone, azelaic acid, kojic acid, niacinamide, or arbutin. Most of these agents work by inhibiting the production of the tyrosinase enzyme, which is essential for producing melanin. Hence, using topical creams which contain these agents might help in lightening your skin by reducing the production of melanin1.
Topical retinoids include retinoic acid, retinol, retinaldehyde, tazarotene, and adapalene. They may help improve the skin by shedding old, damaged, and highly pigmented cells, and by reducing the transfer of melanin. They are mainly applied to manage uneven skin pigmentation caused by sun damage, melasma, and PIH. Combining them with other depigmenting agents like hydroquinone or azelaic acid might give you more effective results11.
Chemical peels involve the application of compounds like salicylic acid, lactic acid, or glycolic acid. They work by exfoliating the top layer of the skin which contains excess melanin1,3. This might diminish the dark patches and promote the growth of new cells. Performing chemical peeling under an expert’s supervision might also help in managing psoriasis, warts, keratoses, and acne, along with reducing hyperpigmentation1.
Laser and light-based therapies are the modern methods for managing or reducing hyper pigmentation. They work by directly targeting the melanin, both over and under the skin surface, without causing any irritation. Hence, you might adopt these therapies to manage age spots and sun damage. Lasers in combination with light energy and intense pulsed light may also be helpful to reduce stubborn pigmentations1.
Oral medications involve compounds such as tranexamic acid. These medicines are known to reduce skin pigmentation by controlling the activity of the enzyme tyrosinase, which plays a key role in melanin production. Hence, taking oral medications under an expert’s supervision maybe helpful in managing skin conditions such as melasma, acne, PIH, and rosacea1,12.
Combination therapy may include topical depigmenting agents, retinoids, chemical peels, and strict sun protection. It is known to improve many pigmentation disorders better than a single approach. This approach enhances effectiveness while lowering the chances of side effects or the pigmentation recurrence13.
Although these medical approaches may be helpful in managing hyperpigmentation, it should only be performed or taken under the guidance of an expert doctor or dermatologist for safety and better results.
Certain foods may help support healthy skin and may reduce excess melanin and pigmentation. Following are some melanin reducing foods that you can go for.

Vitamin C is a strong antioxidant. It reduces the production of tyrosinase enzyme, which is essential for the synthesis of melanin. Hence, consuming Vitamin-C-rich foods might help you in reducing melanin and managing hyperpigmentation. It also promotes collagen synthesis, supporting overall skin health. Examples include citrus fruits such as lemon and orange, kiwi fruit, guava, and strawberries14.

Vitamin E is a vital fat-soluble antioxidant which is produced by plants. It may help reduce pigmentation by protecting melanocytes from damage, increasing glutathione levels, and reducing the activity of the tyrosinase enzyme. Therefore, consuming foods rich in Vitamin E might help your body to reduce melanin production and manage hyperpigmentation. Examples include nuts (almond, hazelnuts, etc), whole grains, spinach, olive oil, and sunflower oil15.

Polyphenol is a compound with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It helps protect skin from DNA damage and oxidative stress and lowers the production of excess melanin due to UV exposure. Hence, taking foods rich in polyphenols might improve your skin by reducing pigmentation and skin damage. Examples include oranges, mangoes, passion fruits, grapes, almonds, green tea, coffee, etc6,16.

Zinc is an essential micronutrient. It may be helpful to manage several dermatological conditions such as infections, inflammatory diseases, etc. It helps manage pigmentation by regulating the melanocyte activity. There, intake of zinc-rich foods might keep your skin healthy and help you in improving hyperpigmentation’s such as melasma. Zinc rich foods are mostly animal-based, such as fish, oysters, eggs, meat, etc17.

Antioxidants are the compounds found in several foods. They combat harmful free radicals in the body. They also lower the melanin level by regulating the tyrosinase enzyme which is important for melanin synthesis. Hence, consuming foods rich in antioxidants might help you in maintaining a lightened skin1. Some antioxidant-rich foods are mangoes, pumpkins, lean meat, grapes, berries, leafy vegetables, potatoes, tomatoes, avocados, etc18.

Vitamin A is an important micronutrient. It plays a key role in skin health by daily replacement of dead skin cells. This might remove the cells which have excess melanin, thereby reducing the chances of hyperpigmentation. Therefore, vitamin-A-rich food intake might help you in managing melanin levels in your body. Here are a few examples of Vitamin-A-rich foods: leafy vegetables (amaranth, spinach, and chard), carrots, pumpkins, eggs, milk, liver, etc19.
While these nutrients have shown depigmentation effect on skin in initial studies, further large-scale human trials are needed for confirmation of these effects of specific food items. It is ideal to discuss with your doctor before incorporating anything new to your routine diet, especially if you have any medical conditions.
As described earlier, melanin is a pigment that gives colour to different parts of the human body and is produced by melanocytes through a process called melanogenesis1,2. As melanin production is mainly determined by genetics1, it is not possible to permanently reduce or eliminate melanin from your skin. We discussed different ways by which melanin production can be reduced or diminished. But all these are meant to give only temporary results. This is because most of these work by inhibiting or reducing tyrosinase enzyme, which is crucial for melanin production1,14. And once you stop these methods, the body starts producing the enzymes and melanocytes depending on the genetic factor. So, the only thing you can do is to manage the level of pigmentation through various safe methods but not permanently reduce it.
Also, it’s important to note that the FDA suggests not to use any over the counter medications for skin lightening, as these may cause permanent damage to skin like ochronosis (skin discolouration)20. This might also interfere with the skin’s natural protective mechanism. Melanin is important for your skin to mask it from harmful UV rays, which can cause several skin disorders1,2. Therefore, stay away from unwanted and unsafe approaches and try natural ways or seek a dermatologist’s help to reduce your pigmentation problems.
Certain changes in your skin might be an indication of any underlying issues. It is important to note such changes and seek medical attention. Following are some warning signs that you must not ignore.
Melanin is a pigment which gives colour to your skin. Excess melanin causes hyperpigmentation issues. To manage it, you may try home care tips, or medical approaches under an expert’s guidance. You can also prioritise foods that help to manage hyperpigmentation. But never ignore if you notice any sudden changes in your skin colour or texture they might be warning signs of any underlying conditions, hence seek immediate medical attention.
Also Read: Is Glycerine Good for Skin?
Yes, Vitamin C, which is a substance naturally found in fruits is known to reduce melanin, by inhibiting the production of the tyrosinase enzyme, which is essential for producing melanin14.
To reduce melanin, the best drinks you may choose are green tea and vitamin C- rich fruit juices6,14 like lemonade, orange juice, strawberry smoothie, although further research is needed to confirm their depigmentation effects.
High melanin levels in the body can result from several factors, including genetics, certain medications, prolonged sun exposure, ageing, hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause, the use of oral contraceptive pills, and underlying health conditions such as Addison’s disease, diabetes, or thyroid1,5.
To reduce hyperpigmentation and improve skin health, it is best to limit excessive sugar, highly processed foods, and foods with a high glycaemic index, as they can worsen inflammation and pigmentation. Also avoid excessive alcohol, baked or junk foods and tobacco24.
The deficiency of vitamin B12 is found to cause the skin darkening. However, it is a reversible type of skin darkening; taking vitamin B12 supplements or eating vitamin B12-rich foods might help reduce or manage this condition25.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Comments

Leave your comment...
You may also like
Comments