Calorie Deficit Diet: What Is It, How to Follow, Strategies and More!
By Dr. Mrunal Shirodkar +2 more

Get,

to manage your symptom
Get your,


4 Cr+ families
benefitted

OTP sent to 9988776655



You’ve successfully subscribed to receive
doctor-approved tips on
Whatsapp

Get ready to feel your best.

Hi There,
Download the PharmEasy App now!!


Register to Avail the Offer
Send OTPBy continuing, you agree with our Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions

Hi There,
Sign up on PharmEasy now!!
Trusted by 4 crore+ families

OTP sent to 9988776655



You have unlocked 25% off on medicines




Code: NU25
By Dr. Mrunal Shirodkar +2 more
Table of Contents
Weight loss is a goal for many in the modern world; it is not only for a better appearance but also for improved health quality and self-confidence. Physical activity plays a role, but dietary control has to be prioritized for individuals looking forward to managing their weight. One such effective and healthy approach is the calorie deficit diet.
Calories are necessary for health and provide the body with essential energy but consuming too much of calorie leads to weight gain. Did you know? If you could cut down on at least 500 calories per day, you could lose up to 454 grams per week, which means nearly 2 kg in a month1. Isn’t it wonderful!
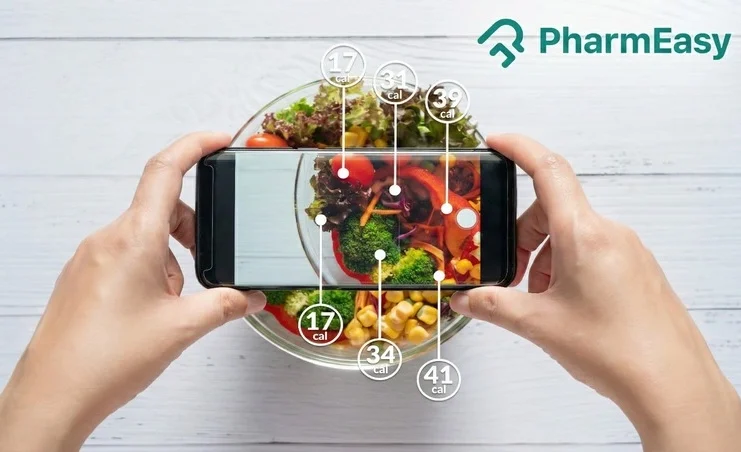

And this is why, despite a variety of specific eating plans like low-carb or keto diets, majority of people adopt a low-calorie diet plan. Studies also confirm that reducing daily calorie intake is the most crucial factor for weight loss and the calorie deficit diet does the same2. Let’s discuss in detail about this diet.
Answer a few quick questions to check eligibility.
Your response has been submitted.
Our team will contact you shortly.
A calorie deficit diet is a diet pattern where you consume fewer calories than your body’s requirement, which results in a shortfall of energy forcing your body to use stored fat for energy, which further leads to weight loss3. There are different terms for this diet pattern for e.g. calorie restricted diet, energy deficit diet, low calorie diet, very low calorie diet etc. While calorie reduction is the goal, an effective way is to ensure your diet is rich in fibre, as fibre-rich foods make you feel full for longer4.
The food we eat gets converted into energy or calories. Our body utilises these calories for normal functions like regulating body temperature, pumping of heart, breathing and also for physical activity. When the calories consumed are in excess to those used, they are stored in the body as fat, which leads to weight gain. With a calorie deficit diet, the intake of calories is lesser than the body’s requirement. Burning more calories than intake creates a negative energy balance, which causes the body to start utilising the stored fat as source of energy, thereby resulting in weight loss3. However, it is important to note that factors like age, sex, body composition and metabolism play an important role in how well calories get utilized by our body and hence they may have an impact on how well these diet’s work.
So basically, despite the confounding factors, to lose weight, the body needs to burn more calories than it consumes. And this can be achieved either by increasing the levels of physical activity (regular exercise) or following a calorie deficit diet or best, a combination of both3.
The most widely accepted healthy weight loss strategy involves maintaining a consistent daily calorie deficit of 500 to 750 calories2. This level of deficit typically leads to a healthy weight loss rate of about 2 kg per month, which is considered safe for most people1. However, this also depends upon personal needs, your metabolism and physical activity levels. As per calorie deficit diets, the daily caloric allowance ranges from about 1200 to 1500 calories for women and 1500 to 1800 calories for men for healthy weight loss5.
High calorie deficit such as more than 800 calories is usually not recommended for long-term as it can result in adverse health effects, including low energy, fatigue, decreased bone density, and nutrient deficiencies6,7.
Note: Before beginning any new diet, you should always consult your healthcare provider or a dietitian to understand the right calorie deficit requirement for you.
Following a calorie deficit diet is the basic step to lose weight. Along with weight loss this diet may offer some other benefits too such as:
A healthy eating pattern should focus on replacing high calorie foods with choices that are lower in calories and fat, but high in fibre and water to keep you full4.

First calculate how much your daily calorie intake should be with this diet. You can calculate this by using an online calculator and get to know the daily caloric requirement for your body to maintain your weight. From this value, you can deduct about 500 calories to achieve a calorie deficit level.
Design a diet plan that is rich in both essential nutrients and fibre. Prioritizing foods that are nutrient dense and high in fibre will help you feel full for longer without adding excess calories. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fat-free or low-fat milk products and lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, eggs, and nuts. Modify recipes to reduce fat and calories. Choose grilled, broiled, or poached chicken or fish instead of fried4.

Include a combination of proteins, good fats and complex carbs in all your meals. Balance your diet by prioritizing nutrient rich foods and minimizing sources of unhealthy fats and sugars. For e.g. Use non-fat milk instead of whole milk, use plain low-fat yogurt or Greek yogurt instead of sour cream in recipes, replace butter with soft margarine that has no trans-fat. Review food content labels or using online resources to check the caloric value of everything you eat1,4.

Portion control means being more conscious on the amount of food you consume. For that skip seconds, that is, fill your plate at once and keep extras in the kitchen. If you still feel hungry, take a second helping of vegetables, fruit, or salad.
Serve one part of anything that you are going to eat in a bowl or a plate to avoid overeating directly from a bag or box1.
Note: This may vary based on individual’s metabolism and specific health conditions. It is always better to consult a nutritionist before starting a diet plan.
An individual on low-calorie diet can consume approximately 1000-1800 kcal per day2,5. The following sample plans can be a good start if you are looking to try out the calorie deficit diet9,10.
| Meal | Menu | Calorie |
| Breakfast | 0.5 cup (45g) cereals + 1 cup low fat milk or 175g yoghurt. | 275 kcal approximately |
| Lunch | 120g legumes + 1 cup rice (100g) + 1 cup mix vegetables, salad (cucumber, radish) | 520 kcal approximately |
| Snacks | 1 cup fruit salad (watermelon, papaya), 150g Greek Yoghurt or 20g roasted almonds/peanuts, 1 cup low sugar tea/coffee (can be divided and taken as morning and evening snacks) | 240 kcal approximately |
| Dinner | Vegetable soup with legumes (beans or peas)/cottage cheese OR vegetables 1 cup (broccoli or spinach) with a slice of wholegrain toast. | 220 kcal approximately |
| Total Calories | 1255 |
| Meal | Menu | Calorie |
| Breakfast | Omelette made of 2 egg whites and vegetables of choice, 50g diced ham + 1 slice toast. | 180 kcal approximately |
| Lunch | 120g lean meat/legumes + 1 cup rice + mixed vegetables bowl | 600 kcal approximately |
| Snacks | 20g snack bag of Popcorn or foxnuts, boiled egg, 1 cup low fat milk/tea/coffee (can be divided and taken as morning and evening snacks) | 210 kcal approximately |
| Dinner | 100g Fish (tuna or salmon) with 1 roti and salad (cucumber, tomato) or on a toast. | 300 kcal approximately |
| Total Calories | 1290 |
| Meal | Menu | Calorie |
| Breakfast | 100g baked beans, 1 slice wholegrain toast | 210 kcal approximately |
| Lunch | 0.5 cup cooked rice or pasta, 100g beans/chickpeas, Garden salad | 500 kcal approximately |
| Snacks | 50g nuts, 1 cup fruit salad, 2 wholegrain snack cracker, 1 cup herbal tea (can be divided and taken as morning and evening snacks) | 300 kcal approximately |
| Dinner | 1 small wholegrain roll, Tofu 80g, 1 cup steamed vegetable (carrot beans) | 220 kcal approximately |
| Total Calories | 1230 |
Please Note: Total calorie values may differ based on cooking methods and recipes.
Make up your mind on what all needs to be followed when you are starting with calorie deficit diet
Eat slowing and chew each bite properly so your brain gets signals of satiety and avoid overeating.
A calorie deficit diet is considered safe, provided it is followed properly and these common mistakes are avoided.
Tracking your weight loss journey will give you motivation to do a little better each day. There are different ways to track your weight loss:
Tracking can help you to evaluate on your progress, where you can see what is working well and which area needs to be a corrected.
Also Read: Thinking About the Pegan Diet? Here’s What You Should Know
The calorie deficit diet is a mostly supported and highly effective method for losing weight. By consistently consuming fewer calories than your body burns and by maintaining a safe deficit of about 500 calories daily, you can promote healthy fat loss, improve metabolic health, and establish better long-term eating habits. You can see a positive result if your diet is balanced, by focusing on nutrient dense foods, practicing strict portion control, staying hydrated, and avoiding common pitfalls like skipping protein or cutting calories too drastically. Combining dietary discipline with light physical activity and consistent tracking ensures both safe and sustainable results. Always consult a healthcare professional or dietitian before starting to ensure the plan is structured to your individual health needs.
Prioritize nutrient-dense foods to maintain a balanced intake of all essential nutrients, even on diet. Make sure to have enough fibre because fibre can make you feel full. You can have fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meat, egg etc. Adopt some fat-free or low-fat cooking techniques like steaming veggies instead of stir fry, all these changes will help you to maintain a healthy calorie deficit diet4,19.
Once you have established your target calorie deficit (typically 500 -750 calories), the next step is to create a detailed daily meal plan encompassing breakfast, lunch, snacks, and dinner. You must consistently track your daily calorie intake to ensure you stay within your established limits. Throughout the day, remember to practice portion control and mindful eating to support your deficit goal1.
To determine your appropriate daily calorie intake, you must first figure out how many calories you need to maintain your current weight. For that multiply your current weight (in pounds) by 15 (this roughly translates to the number of calories per pound of body mass) e.g. your weight is 155 pounds, 155 multiply by 15 is 2325, this should be you daily calorie intake to maintain your current weight. To achieve the safe weight loss rate of 1 to 2 pounds per week, you should consume at least 500 calories fewer than your total weight maintenance calories daily. For instance, if you require 2,325 calories to maintain your weight, your new daily calorie target should be between 1,325 and 1,825. Online calculators are also available for this calculation20.
Yes, you can continue with light workout along with your diet. For best results with your calorie deficit diet, incorporating mild exercise, such as a brisk walk for 30 to 40 minutes, is highly beneficial1.
Yes, calorie deficit diet is considered to be safe if properly managed, specifically by prioritizing nutrient-rich foods to meet your body’s nutritional needs. Avoid the temptation to cut too many calories too quickly in an effort to lose weight rapidly. If you have any underlying health issues, make sure to consult your doctor before starting your diet plan1,4.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Comments

Leave your comment...
You may also like
Comments