Oedema is a common condition that affects many people all over the world. In simple terms, oedema is defined as swelling that occurs due to fluid accumulation in the tissues, and is particularly seen in the hands, feet, ankles, arms, and legs. There are many factors that can lead to oedema, such as heart or kidney diseases, less protein in blood, lung infection and poor blood flow, which requires medical attention when severe1. Additionally, it is necessary to know that even the foods you eat can play a crucial role in avoiding and managing the oedema.
In this article, we will discuss the nature of oedema, types of food that can worsen oedema, explore healthier alternatives, and various lifestyle changes that may help in managing and avoiding this condition. Furthermore, we will also discuss oedema that occurs during pregnancy and answer some frequently asked questions.
Did you know?
Oedema occurs when fluid leaks from small blood vessels into nearby tissues, leading to the following symptoms1.
The types of oedema are based on the area of the oedema and its root cause. Some well-known types of oedema include:
A healthcare provider will examine the affected area, inquire about medical history, any trauma, onset, position change, triggering factors, and may request additional tests to determine the root cause of oedema. Some possible tests include blood tests, ultrasound exams, vein studies, or other necessary diagnostic studies8. Mild oedema usually resolves on its own, but more severe cases may require medication to manage the underlying cause1.
Avoid consuming pickled vegetables if you have edema. These foods are high in sodium due to the pickling process, which involves soaking them in a solution containing salt and vinegar. High sodium intake can worsen fluid retention and exacerbate edema symptoms. Opt for fresh vegetables instead to help manage edema more effectively
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Foods that may worsen oedema include:

High salt intake increases the sodium content in your body, which retains more fluid and worsens oedema3. High sodium is found in unhealthy foods like fast foods, sauces, canned soups, deli meats, and bakery productions.

Processed foods are not only high in fat, they may also cause edema. Examples are chips, crackers, cookies, candy, and ice cream.

Fat-rich foods such as baked goods, meats, and cheese take longer to digest, which may lead to bloating and oedema.

Foods and drinks that cause inflammation may worsen oedema. Common examples include refined sugars, artificial sweeteners, trans fats, and alcohol2.

Lactose, found in dairy products like milk and ice cream, can lead to an upset stomach and bloating in people who are lactose intolerant. Probiotic-rich yogurt or lactose-free alternatives might help in such individuals.

Some foods can trigger stomach upset and add to oedema. These include:
High-processed refined carbohydrates such as pasta may also increase water retention in the body. It is best to avoid these if you have edema and opt for healthier options.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Knowing what to eat and drink plays an important part in dealing with oedema. Making good dietary choices may help keep your health in check.
Pick nutrient-rich, low-inflammation, and low-sodium foods to manage oedema.
Drinking adequate amount of water each day to avoid fluid retention. You may add lemon, mint, or berries to your water for a refreshing twist. Overdrinking water can add to oedema.
Regular breaks throughout the day help avoid long periods of sitting or standing and raising your legs above your heart level helps drain the oedema.
Avoid tight clothes that can limit blood flow and add to oedema symptoms.
Use waist-high compression stockings to avoid fluid build-up in your limbs by promoting better blood flow with gentle pressure.
Regular workouts and a healthy weight boost circulation, and overall health, and help reduce oedema symptoms.
Also Read: What Causes Sulphur Burps and How To Stop Them
Pregnancy brings many changes to your body. One of them could be swelling or oedema. It’s crucial to know what triggers it and how to manage it10.
Swelling in pregnancy usually starts in the second term and may get worse by the third term.
Here are some self-care tips that may help you manage oedema.
Sudden severe swelling or swelling with symptoms like headaches, dizziness, or vision problems need quick medical attention. These symptoms may indicate a serious pregnancy complication like preeclampsia.
Always remember, whether you are pregnant or not, if home remedies do not help, the swelling keeps getting worse, or it is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, you should seek medical care.
Also Read: Why Should You Drink Water in the Morning Before Brushing?
In summary, understanding and managing the impact of oedema on your body is crucial for overall health and well-being. Be aware of the types and causes of oedema and identify the foods and drinks that can aggravate the condition. Focus on healthier alternatives and adopt beneficial lifestyle changes to keep oedema at bay. Moreover, it’s essential to recognise the triggers and warning signs of oedema and know when to seek medical guidance. Stay proactive and make informed decisions to lead a healthy, active life.
Processed, high-salt, high-fat, high-sugar foods and certain dairy products can make oedema worse.
Regular exercise, weight management, and balanced diet can help reduce the oedema9.
Yes, hot and cold compression and massaging can help in reducing oedema.
Avoid high-sodium foods, processed foods, unhealthy fats, and high-sugar beverages if you have fluid retention
Limit high-sodium foods, processed foods, unhealthy fats, and high-sugar beverages that can exacerbate swelling in the feet.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes
Vitamin E is a power-packed nutrient that brings you many potential health benefits. In this article, we will discuss the potential benefits and side effects of vitamin E, and how to use it on the skin safely. We will also answer some commonly asked questions on this topic.
Did you know?
Vitamin E is soluble in fat and rich in antioxidants3. Your body needs these to function well for a strong immune system, healthy blood flow, and cell health4. You’ll find it naturally in nuts, whole grains, some leafy greens, and even some oils3. Vitamin E supplements are available in the form of capsules or drops.
Vitamin E may aid in improving skin health. Its antioxidant powers may help shield your skin from harm caused by pollution and the sun6. It may also protect the cells from damage, calm irritated skin, and fight ageing7.
Below we have described ways to apply vitamin E on your face.
Here are some options.
Here is a list of potential benefits of vitamin E for skin health.

Vitamin E may help reduce the pigmentation caused by UV radiation while vitamin C plays a vital role in depigmentation of the skin. Using a combination of both vitamins may have a greater effect on reducing depigmentation than using just one vitamin8.



While a lot of research has shown that vitamin E has positive effects on the skin, more long-term studies are required to corroborate these benefits.
Studies have found that Vitamin E might have an interaction with warfarin, a blood thinner used by heart patients. I suggest you consult your physician before using Vitamin E capsules and discuss your present medications to avoid any complications15.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Using vitamin E capsules for the face needs a little caution due to the potential side effects and possible interactions with certain medicines.
Also Read: Healthy Skin Tips: Research-Backed Strategies for a Glowing Complexion
You should avoid vitamin E capsules on the face if you have.
In my experience, few people may encounter allergic reactions such as itching, skin rash, hives, and swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat on using vitamin E capsules15.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Before selecting a vitamin E capsule you should:
Also Read: Home Remedies For Tanned Skin
Thanks to its antioxidant powers and potential benefits, vitamin E can help improve your skin health. But remember, do not rush into any new skincare product. Start with a patch test, and if you have any concerns or skin conditions, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional. With proper care, vitamin E may be a simple yet potent addition to your skincare regime.
Also Read: Red Spots on Skin: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and More!
Yes, you can break open a capsule and apply the oil directly to your face or any problem areas, like dark spots. But before doing so, you should always do a patch test in case you may be allergic.
Vitamin E helps most skin types. But super sensitive, very oily, or acne-prone skin might not adjust well with it.
How often you use the vitamin E capsule depends on your specific skincare needs and product type. Usually, using it two to three times a week is safe. However, it is always a good idea to discuss it with your healthcare provider for personalised advice.
Using vitamin E on your face may cause skin reactions and allergic reactions in some people10. Always test a little bit of vitamin E oil on your skin before using it and consult a healthcare professional if you have doubts.
For some individuals, especially those with oily or acne-prone skin, vitamin E might cause breakouts. Always test a small patch of your skin first and keep an eye on how your skin reacts when you start using vitamin E.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Hair, being one of the essential aspects of an individual’s appearance, plays a significant role in boosting one’s self-esteem and confidence. Maintaining the health of our hair is crucial, but daily exposure to environmental stressors, unhealthy lifestyles, and genetic factors can often lead to various hair problems, including hair loss. There are several natural remedies proposed to promote hair growth and improve overall hair health. One such herb is fenugreek which is believed in many cultures as an effective ingredient to deal with hair problems.
This article aims to explore fenugreek benefits on hair growth, supported by scientific studies and traditional applications. We will delve into the nutritional composition of fenugreek and its impact on possibly reducing hair loss and promoting hair regrowth. We will also provide insights on the effective use of fenugreek seeds in hair care routines and potential risks that must be taken into consideration while using them. Lastly, we will guide you through a holistic approach to maintaining the general health of your hair while using fenugreek.
Did you know?
Fenugreek, scientifically known as Trigonella foenum-graecum, is a versatile herb native to the Mediterranean region and South Asia. It has been used for centuries in traditional medicine and culinary practices. Fenugreek seeds are rich in essential nutrients, including proteins, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants8. These seeds also contain compounds such as flavonoids, alkaloids, and saponins, which contribute to their potential benefit to hair health10.
Fenugreek is a herb native to Southern Europe, the Mediterranean, and Western Asia. It looks similar to clover and has seeds that taste and smell like maple syrup. Many cultures use fenugreek in medicine and cooking. In Asian, Southern European, and North African traditions, it’s been used to manage diabetes and help with breastfeeding. In Ayurvedic and Chinese medicine, fenugreek has been used to boost digestion and induce labour. It’s also been used to improve overall health and metabolism.
Today under alternative medical sciences, fenugreek is still used by some as a dietary supplement for menstrual cramps, diabetes3, and promoting milk production for breastfeeding.
The nutritional composition of fenugreek seeds includes the following.
These nutrients provide the foundation for fenugreek’s potential benefits in hair growth and overall health.
Fenugreek has been traditionally used in various hair care applications, which are described below.

Fenugreek seeds are said to stimulate hair growth by nourishing the hair follicles and increasing blood circulation to the scalp9. The proteins present in fenugreek seeds are supposed to strengthen the hair shaft, reducing hair fall and promoting the growth of new, healthy strands.

The proposed mechanism by which it may work is the fact that the various plant compounds in fenugreek may interact with a chemical in the body known as dihydrotestosterone (DHT). If DHT attaches itself to your hair follicles, the result, sooner or later, would be hair loss. Fenugreek may slow down the ability of DHT to attach to your hair follicles9.
A small study13 involving 53 people found that a 300 mg daily oral dose of fenugreek seed extract over six months led to improvements in hair volume and thickness for more than 80% of the participants compared to those given a placebo.

Fenugreek seeds contain hormone-regulating compounds that may help in reducing hair loss caused by hormonal imbalances. Additionally, the seeds have antimicrobial properties that may help protect the scalp from infections, reducing the risk of hair loss due to scalp conditions.

Fenugreek seeds possess conditioning properties that help in reducing dryness and frizz. Regular use of fenugreek seeds as a hair mask or rinse may make your hair soft, smooth, and manageable. They also provide hydration to the scalp, reducing flakiness and itching.

The antifungal and antibacterial properties of fenugreek seeds may be responsible for anti-dandruff effects4. Regular application of fenugreek seed paste or oil may help reduce scalp inflammation, itching, and flaking associated with dandruff5.

Fenugreek’s anti-inflammatory properties may help reduce scalp inflammation and alleviate itchy, red, or irritated skin1. This may aid in improving overall scalp health and promote healthy hair growth.
There are medical conditions also that may affect your hair and scalp, causing scalp issues and hair loss. If you are unsure, it is best to consult a dermatologist before initiating any home remedy.
For most people, fenugreek seeds are safe. However, in my opinion, one should avoid them before the 37th week of pregnancy as they may cause early labour. If you have a peanut or chickpea allergy, you are advised to stay away from fenugreek12.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Fenugreek can be incorporated into your hair care routine in multiple ways, which are described below.

You can use raw fenugreek seeds as a natural hair mask or hair oil. Simply grind the seeds, create a paste, and apply it to your hair and scalp. Leave the paste on for a few minutes before rinsing it off.

Fenugreek powder can be used as a hair mask or mixed with other ingredients, such as yogurt, honey, or oils, to create a nourishing paste. Apply the paste to your scalp and hair, focusing on the roots, and leave it on for about 30 minutes before rinsing thoroughly with lukewarm water.

You can make your own fenugreek oil by heating fenugreek seeds with a carrier oil, such as coconut or olive oil. Let the seeds infuse the oil for a few minutes, then strain the oil and store it in a clean container. Massage the fenugreek seed oil onto your scalp and hair, leave it on for an hour or overnight, and shampoo as usual.

Fenugreek supplements are available in the form of capsules, powders, and extracts, making it easy to incorporate this natural remedy into your daily routine. Consult with your healthcare provider before starting fenugreek supplementation, as it may interact with certain medications.

Fenugreek can be applied topically to your hair and scalp in the form of hair masks, hair rinses, shampoos, and conditioners11.
Fenugreek can be consumed in various forms to incorporate its benefits internally, which are described below.
While fenugreek is generally considered safe for most individuals, there are some possible side effects and risks associated with its use, which are as follows.
Overconsumption of fenugreek may cause the following:
Moderate your fenugreek intake and monitor your body’s reaction to ensure a safe experience.
Like any other herb, people allergic to legumes, peanuts, chickpeas, or related plants might be sensitive to fenugreek, causing inflammation, itchiness, or redness on the skin. If you notice any unusual reactions after consuming or applying fenugreek, discontinue its use and consult your healthcare provider.
Fenugreek might interfere with certain medications, including those used to control diabetes, blood clotting, thyroid disorders, and high cholesterol levels2. Consult with your doctor before taking fenugreek orally if you are on any medication.
When consuming fenugreek, it is crucial to adhere to the recommended dosages. A high dose of fenugreek may cause a sudden drop in blood sugar and may have hepatotoxic effects. Pregnant women should avoid fenugreek supplementation, as it may increase the risk of birth defects.
A holistic approach to hair growth addresses not only the application of topical remedies and supplements for hair health but also considers various factors that can influence hair growth.

Consume a balanced diet rich in hair-friendly nutrients, such as protein, iron, zinc, vitamins, and healthy fats. Ensure that you are getting enough essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals through your diet to support optimal hair growth6. Focus on a variety of whole foods, such as green leafy vegetables, lean protein sources, dairy products, and healthy fats.

Stress is known to affect hair growth negatively. Try incorporating stress management techniques such as breathwork, meditation, yoga, or exercise into your daily routine to help reduce stress and support better hair health7.

Certain lifestyle choices, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor sleep hygiene, can adversely impact hair health. Make a conscious effort to adopt healthier habits and prioritize restorative sleep to support your hair growth journey.

Choose hair care products suited for your hair type and avoid harsh chemicals, sulfates, parabens, and silicones. Adopt a gentle haircare routine, including regular scalp massages to stimulate blood circulation and promote hair growth.

Genetic factors play a significant role in hair loss and hair growth patterns. If you suspect a hereditary pattern of hair loss, consult your healthcare provider to discuss suitable options.
Fenugreek seeds offer remarkable benefits in hair growth and hair health, supported by scientific research and traditional practices. Incorporating fenugreek seeds into your hair care routine may help reduce hair loss, stimulate hair growth, address dandruff, scalp inflammation, and reviving damaged hair.
While using fenugreek may be beneficial, it’s essential to consider possible side effects, allergies, and medication interactions. Utilizing a holistic approach that encompasses proper nutrition, stress management, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate hair care products is crucial for promoting healthy hair growth.
It is not necessary to use fenugreek on your hair every day. Applying it 2-3 times a week as part of a hair mask or oil massage may provide sufficient benefits. Daily use may risk increasing Pitta dosha levels on your scalp.
There is no specific recommended amount of fenugreek for hair growth, as it may vary based on individual experiences and conditions. However, some studies suggest that a daily oral dose of 300 mg of fenugreek seed extract may significantly improve hair growth and thickness. Always consult your doctor before deciding to consume fenugreek.
Typically, you can leave a fenugreek mask on your hair for about 30-45 minutes before rinsing it off with warm water. If you have severely dry hair and dandruff issues, you may leave the mask overnight and wash it off the next morning.
Apart from providing essential nutrients for hair growth, fenugreek water is said to help flush out toxins from your body, improving digestion and bowel movement. As a result, fenugreek contributes to maintaining the harmony of your Ayurvedic doshas in the body, which in turn, is said to promote voluminous hair growth and avoid dryness and dandruff issues5.
Studies suggest that significant improvements in hair growth can be observed after using fenugreek consistently for 3-4 months. However, the duration to achieve desired results may vary among individuals, depending on their unique hair needs and conditions. You may try fenugreek, after using it if you feel there isn’t much improvement then there may be some other reason for hair loss, and it is better to consult a dermatologist. Also, if you want to consume fenugreek then before doing so always discuss it with your doctor first.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
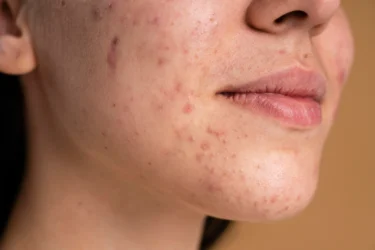
Skin tags, while not dangerous, can still annoy you and affect how you look. They often occur when your skin rubs against skin or clothing1. Even though they are harmless, many people want to remove them for aesthetic reasons or because they can get irritated.
This article will cover all you need to know about skin tags. You’ll learn what they are, why they appear, and the risk factors. We’ll discuss about home remedies and other products you may buy to remove skin tags, coupled with safety measures to follow. You’ll also learn when to reach out to a doctor and explore professional skin tag removal options. Lastly, we’ll go over how to care for your skin after the skin tags have been removed and steps to avoid future formation of skin tags.
Did you know?
Skin tags are harmless growths that usually don’t cause health issues, but can still bother you. Before starting any removal process, it’s key to understand what skin tags are and correctly identify them.
Skin tags, also called acrochordons, are small, soft lumps of skin that arise when skin rubs together. Usually, they are between 2 and 5 millimeters in size but can grow much larger. Skin tags can appear anywhere on the body but are often found near skin folds, like the neck, underarms, torso, eyelids, and inner thighs. They are often the same colour as your skin or darker, and usually don’t hurt unless irritated2.
We don’t know the exact cause of skin tags yet. Still, several known factors can increase your chances of getting these skin growths, which are listed below.
Before taking a swing at home remedies, be sure that it’s a skin tag and not something more serious. Ask a health professional if unsure. We’re about to list a few common home remedies for skin tags, how to use them, and the safety measures to bear in mind.
Safety Considerations: Keep in mind that removing skin tags yourself comes with risks like infection, bleeding, and scarring. If you feel discomfort in any way during or after applying home remedies, get in touch with a healthcare professional immediately. It’s vital to follow all guidelines and to only use clean, sanitized tools when trying these remedies.

This oil is known for its antiviral and antifungal traits and may prove to be a useful home remedy3.
How to apply?
Precautions
Don’t use pure tea tree oil and test it on a small bit of your skin before using it on a skin tag to check for allergies this is known as a patch test. Stay away from the eye area with this oil.

This vinegar is known for its acidic nature, which some say may help skin tags to shrink and drop off4.
How to use?
Risks and precautions
Be careful with apple cider vinegar as it can irritate the skin or cause burns. Be sure not to put it near the eyes and look out for signs of skin reactions while using it.

Some think garlic’s anti-inflammation might make skin tags look better5.
Application and precautions
Note, the strong smell of garlic might put some people off. And be careful if you have sensitive skin, as garlic can cause irritation.

Vitamin E is known for its antioxidant traits, which may fend off wrinkles and keep skin healthy6. Rubbing liquid vitamin E onto a skin tag might make it fall off in a few days.
Usage and benefits
Ensure that you do not have an allergy to vitamin E before using it on your skin. Also, know that using vitamin E near the eyes can be irritating.

Some say banana peels have antioxidant traits, which might help dry out skin tags7.
How to use?
Benefits
Using banana peels to remove skin tags costs little and is not invasive. Still, there isn’t much scientific proof that it works. So, you’ll need a lot of patience with this method, as it may take some time before you see any results.
Recently I came across a study that suggested skin tags can sometimes indicate a higher risk of heart and blood vessel problems. This is because people with skin tags often have other health issues like being overweight, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, insulin resistance, and increased inflammation in their bodies11.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
For those not into home remedies, there are many over-the-counter (OTC) products to help you remove skin tags. Remember though, it’s best to talk to a health professional if you doubt using OTC products.

These creams can be found in loads of stores but may work better for some than others. It’s key to buy a cream that won’t irritate your skin. Be wary of creams holding salicylic acid and tea tree oil, as these might cause your skin to get red.

Such kits, or cryotherapy kits, use deep cold to kill unwanted skin tissue. These kits can be found in most drugstores and need to be used carefully so as not to hurt the surrounding skin. Always keep to the kit’s instructions and watch the skin area where you have applied the kit for bad reactions.

Skin tag removal bands, also known as ligation bands, work by cutting off the blood flow to the skin tag. This method takes time but might cause problems like infection, bleeding, and scarring. On the other hand, skin tag removal patches hold medicines that make the skin tag dry up and fall off. Results vary, and these patches could irritate the skin for some people.
Bands are wrapped around the base of the skin tag. This stops blood flow which kills the cells in the tag. The skin tag then dries up and falls off. Skin tag removal patches usually have medicines that slowly break down the surrounding tissue. This leads to the skin tag falling off.
Removal bands and patches may work, but DIY removal has risks. Be sure to keep everything clean and follow all instructions to lessen the risk of infection, bleeding, and scarring. Also, monitor the affected area for any unusual signs. If you have any bad reactions, talk to a health professional straight away.
To my knowledge, skin tags are way more common than you think. It has an estimated occurrence ranging from 50 to 60% among the general population12.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
While home remedies and OTC products may help some people, there are times when it’s better to get help from a professional. Here are some such situations, described below.
Make sure to see a doctor if the following happens.
It’s crucial for a health professional to check and confirm that your skin growth is a harmless skin tag and not a more serious skin issue.
There are some situations when home remedies and OTC products are a no-go. Ask for professional help to remove a skin tag if:
It’s not widely known that skin tags, typically associated with humans, can also manifest on our furry friends, such as dogs. While common in older canines, these skin tags can present in various forms and are generally harmless. Yet, if you observe any alterations in their size, shape, or color, or if they cause discomfort to your pet, it’s advisable to seek evaluation from a veterinarian promptly.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
If home remedies and OTC products don’t suit you, or if you want a quick fix, professional skin tag removal could be best. Health professionals offer different surgical methods to remove skin tags safely and swiftly.
After removing a skin tag professionally, you need to care for the area well to promote healing and stop infection.
If you understand why skin tags appear, you may try steps to lower their chances of forming.
Skin tags are harmless but sometimes vexing lumps that crop up at several body parts. If you decide that it’s needed, there are many home remedies, OTC products, and professional methods available to remove them. Don’t forget to be careful and follow safety measures when trying home remedies. For the best results and to keep risks low, consider asking a healthcare professional for skin tag removal. Aftercare is crucial to avoid infection and healing well. Knowing potential causes and risk factors for skin tags may help you take steps toward stopping them from forming.
Also Read: Healthy Skin Tips: Research-Backed Strategies for a Glowing Complexion
You may try several methods to remove skin tags at home, like using tea tree oil or apple cider vinegar. But these come with risks, including infection, bleeding, and scarring. It’s safer to consult a healthcare professional for the correct skin tag test and removal.
Keeping a healthy weight, managing diabetes, and sorting any hormonal imbalances may help lower the chance of skin tags forming. But, as things like genetics and infections can also lead to skin tags, completely avoiding them may not be possible.
Home removal methods come with risks like infection, bleeding, and scarring. Poor technique or unclean equipment increases these risks. Seeing a healthcare professional ensures proper removal and lowers these risks.
Once a skin tag is fully removed, it won’t grow back. But new skin tags may arise in the same spot or nearby.
Health insurance plans typically do not cover skin tag removal as it’s often looked at as a beauty-enhancing procedure. However, if a skin tag harms your physical or mental health, your insurance plan may provide coverage.
1. Pandey A, Sonthalia S. Skin Tags. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547724/
2. Healthdirect Australia. Skin tags (acrochordons) [Internet]. Melbourne: Healthdirect Australia; 2025 Mar [cited 2025 Nov 13]. Available from: https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/skin-tags
3. Carson CF, Hammer KA, Riley TV. Melaleuca alternifolia (Tea Tree) oil: a review of antimicrobial and other medicinal properties. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006 Jan;19(1):50-62. doi: 10.1128/CMR.19.1.50-62.2006. PMID: 16418522; PMCID: PMC1360273. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1360273/
4. Luu LA, Flowers RH, Gao Y, Wu M, Gasperino S, Kellams AL, Preston DC, Zlotoff BJ, Wisniewski JA, Zeichner SL. Apple cider vinegar soaks do not alter the skin bacterial microbiome in atopic dermatitis. PLoS One. 2021 Jun 2;16(6):e0252272. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252272. PMID: 34077434; PMCID: PMC8172074. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34077434/
5. Pazyar N, Feily A. Garlic in dermatology. Dermatol Reports. 2011 Apr 28;3(1):e4. doi: 10.4081/dr.2011.e4. PMID: 25386259; PMCID: PMC4211483. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4211483/
6. Keen MA, Hassan I. Vitamin E in dermatology. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016 Jul-Aug;7(4):311-5. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.185494. PMID: 27559512; PMCID: PMC4976416. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4976416/
7. Hikal WM, Said-Al Ahl HAH, Bratovcic A, Tkachenko KG, Sharifi-Rad J, Kačániová M, Elhourri M, Atanassova M. Banana Peels: A Waste Treasure for Human Being. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 May 13;2022:7616452. doi: 10.1155/2022/7616452. PMID: 35600962; PMCID: PMC9122687. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9122687/
8. Tribonias G, Papaefthymiou A, Zormpas P, Seewald S, Zachou M, Barbaro F, Kahaleh M, Andrisani G, Elkholy S, El-Sherbiny M, Komeda Y, Yarlagadda R, Tziatzios G, Essam K, Haggag H, Paspatis G, Mavrogenis G. Endoscopic Local Excision (ELE) with Knife-Assisted Resection (KAR) Techniques Followed by Adjuvant Radiotherapy and/or Chemotherapy for Invasive (T1bsm2,3/T2) Early Rectal Cancer: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort. J Clin Med. 2024 Nov 18;13(22):6951. doi: 10.3390/jcm13226951. PMID: 39598095; PMCID: PMC11594537. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39598095/
9. Dyck PKV, Hockaden N, Nelson EC, Koch AR, Hester KL, Pillai N, Coffing GC, Burns AR, Lafontant PJ. Cauterization as a Simple Method for Regeneration Studies in the Zebrafish Heart. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2020 Oct 3;7(4):41. doi: 10.3390/jcdd7040041. PMID: 33022937; PMCID: PMC7711552. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33022937/
10. Prohaska J, Jan AH. Cryotherapy in Dermatology. [Updated 2023 Sep 15]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482319/
11. Sari R, Akman A, Alpsoy E, Balci MK. The metabolic profile in patients with skin tags. Clin Exp Med. 2010;10:193‑7. doi:10.1007/s10238-009-0086-5. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10238-009-0086-5
12. Pandey A, Sonthalia S. Skin Tags. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547724/
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Feeling a tingle in your hands? It may be more than a minor annoyance and could signal an underlying health issue. That is why it is important to understand the possible causes and known when to see a doctor. In this article, we’ll explore why you experience tingling in the hands and discuss potential management options.
This article highlights the main reasons behind hand tingling, ranging from common causes like diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, and pinched nerves to less-known ones like vasculitis and Guillain-Barré syndrome. We will also discuss the role of autoimmune disorders and infections, along with possible management strategies to guide you.
What does tingling in your hands feel like? Most people describe it as a “pins-and-needles” sensation. It can accompany numb hands, aching pain, or weak muscles. Let’s understand what tingling really is and why it happens.
Tingling is a prickly or itching sensation. It may not always be painful, but it does cause discomfort. It is also important to understand that tingling in your hands and feet now and then can be normal, but if it keeps happening or is always there, it could point to a serious underlying health problem.
Hand tingling is usually perceived as
Tingling of the hands may be caused by many factors. It could be a temporary problem or may point to a bigger underlying problem. Let’s look closer at some likely causes of tingling in the hands.
Diabetic neuropathy is nerve damage caused by high blood sugar levels. It often affects the hands and feet and is characterised by tingling sensations in the extremities4. Therefore, managing diabetes and maintaining normal glucose levels is essential to reduce the risk of developing further complications.
Group B vitamins are key for supporting nerve health. If you’re deficient in these (especially vitamin B12), your peripheral nerves might be affected and cause hand tingling1.
When surrounding tissues put too much pressure on a nerve, it can become pinched, leading to tingling or numbness in the area that nerve serves1. Changing your body position or undergoing physiotherapy may relieve the symptoms.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition, where the median nerve in the wrist is compressed, causing tingling and numbness in the hands and fingers2. To help reduce carpal tunnel symptoms, wear wrist splints and adopt ergonomic practices to keep the wrist straight.
If kidney function is impaired, waste products can build up in the bloodstream and damage the nerves. This nerve damage can result in a tingling sensation in the hands5. Therefore, it is crucial to manage kidney diseases and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Swelling and fluid retention during pregnancy can put pressure on certain nerves, sometimes causing tingling in the hands2. Simple measures such as changing hand positions, gentle stretching, and adequate rest may help ease discomfort.
Some drugs may damage the nerves, which can trigger a tingling sensation in the hands and feet. Consulting a doctor may help determine the most appropriate management plan.
Pain, numbness, or tingling in your thumb, index finger, middle finger, and part of your ring finger may be a sign of carpal tunnel syndrome. If it worsens at night or after a particular activity, it should not be ignored.
Dr. Ashish Bajaj, M.B.B.S., M.D. in Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology
Some autoimmune and infectious diseases may also cause tingling in the hands. In autoimmune conditions, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own cells (including the nerves, leading to a tingling sensation). In infections, the immune system attacks the invading germs, but the resulting inflammation may affect the nerves, causing a tingling sensation1.
Autoimmune disorders may lead to hand tingling if the immune system mistakenly attacks nerves or the tissues that support them. Identifying autoimmune disorders early and managing them well may help lower symptoms. Autoimmune disorders that may be associated with hand tingling include:
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that triggers joint inflammation3. This may lead to hand tingling, especially in the wrists. To manage it, doctors may suggest pain-reducing medicines, anti-inflammatory medications, and physiotherapy.
Multiple sclerosis occurs when your immune system attacks the protective layer of the nerves, which is called myelin. This can cause nerve damage, bringing about tingling and numbness in the limbs, face, and other parts of the body. Detecting and managing this disease early may help to slow it down.
Lupus is an autoimmune disorder that can harm various body parts and cause nerve inflammation, leading to tingling sensation in the hands. Managing it involves taking medications and making lifestyle changes.
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder in which eating gluten damages the small intestine. It may cause hand tingling due to celiac neuropathy, sometimes even without digestive system symptoms. Following a strict gluten-free diet may help manage the condition.
Some individuals may develop a rare disorder called Guillian Barre syndrome after an infection like a stomach infection or the flu. The syndrome first starts as weakness and tingling in the hands and feet and then spreads, causing whole-body paralysis. In this condition, the immune system of the body starts attacking the nerves1.
If the tingling sensation in your hands does not go away in a few minutes or repeatedly appears over a few days, then it could be because of an additional condition or nerve damage. If you have been in an accident or think you have had an injury, seek medical help even if you don’t have any visible injuries.
Dr. M.G. Kartheeka, MBBS, MD(Pediatrics)
Infections can sometimes set off nerve inflammation, resulting in hand tingling. Thus, managing the infection correctly is key to possibly reducing related symptoms. Infections that may be associated with hand tingling include:
Ticks transmit Lyme disease, a bacterial infection. If not managed, it can affect the nervous system and cause hand tingling6. Timely treatment with antibiotics may help control the infection and possibly reduce the tingling sensation.
The varicella-zoster virus can reactivate and trigger shingles6, a painful rash caused by damaged nerve fibres. If it affects the nerves of the hands and arms, you may feel tingling and itchiness. Antiviral medications may help in reducing the rash’s duration and intensity.
Hepatitis B and C are viral infections that mainly affect the liver. If untreated, they can lead to inflammation, cirrhosis, or liver cancer and trigger peripheral neuropathy, resulting in occasional hand tingling. Identifying these conditions and managing them is essential to prevent their progression.
HIV weakens the immune system, increasing the chance of other infections and cancers. If left unchecked, it can worsen and severely damage the immune system6. The virus may also affect the nervous system, causing tingling and numbness. Managing and monitoring HIV in time is of paramount importance to help slow disease progression and help reduce complications like nerve-related tingling.
This bacterial infection affects the skin, nerves, and respiratory tract6. When it affects the nervous system, it can bring about tingling or numbness in the affected body parts, including the hands. Early diagnosis and treatment with appropriate antibiotics is important.
There may be other reasons for experiencing tingling in your hands, as follows:
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland fails to make enough thyroid hormones. In severe cases, it may damage the nerves7, leading to tingling and numbness in the hands and feet. Its management usually includes thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
Some toxins and chemicals act as neurotoxins, harming the nervous system and causing tingling or other symptoms1. Avoiding heavy metals, industrial chemicals, and toxic substances may help reduce the chance of nerve damage.
Fibromyalgia brings about body-wide muscle pain, fatigue, and mood shifts. Some patients with fibromyalgia might feel tingling in their hands. Medications, exercise, stress reduction, and sleep hygiene may ease these symptoms.
Ganglion cysts are liquid-filled bumps that mostly arise around the joints. They can press against nearby nerves, causing tingling in the hand or fingers8. Treatment options include aspiration, immobilisation and, in some cases, surgery.
With age, changes in the cervical (neck region) spine can cause worn-out spinal discs, bone spurs, or arthritis. If these press on the spinal cord, they can lead to worsening neck pain and numbness or tingling in the arms and legs9. Possible management options may be physical therapy, drugs, or surgery.
Raynaud’s phenomenon affects blood flow to the hands and feet. Cold temperatures or stress can cause blood vessels to constrict, reducing blood flow, and leading to numbness or tingling in the fingers and toes. Warming the affected areas, avoiding triggers, and certain medications may help manage the symptoms.
Long-term alcohol use can damage nerves, leading to tingling in the hands and feet10. Cutting down on or quitting alcohol, improving the diet, and seeking medical support may help manage this condition.
Finding the root cause of hand tingling is key to proper management. Always consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and management. They will consider your overall health, medical history, family history, lifestyle, and symptoms to identify possible causes.
Your healthcare provider may use different tools to find the exact cause of hand tingling, as follows:
Once the root cause is identified, your healthcare provider may advise the best way forward, which may include:
Managing stress, regular exercise, a healthy diet, and good sleep hygiene may help keep hand tingling away.
Depending on the cause, prescription drugs, over-the-counter remedies, or vitamin supplements may be advised by your doctor to help manage your symptoms.
Physical therapy, chiropractic care, massage therapy, acupuncture, or other alternative options may be able to offer relief for tingling hands1.
Important: Treatment must always be done as per your healthcare provider’s advice. Self-diagnosis and self-medication must be avoided at all costs.
If you have frequent occurrences of hand tingling, especially with other worrying symptoms, you should consult your doctor as soon as possible.
Watch out for symptoms like swelling in the limb or poor limb strength, numbness, dizziness, or breathing problems, along with hand tingling, as they can indicate serious conditions. In such a case, you need to consult your doctor immediately.
The earlier you find the cause of hand tingling, the better. Timely management may reduce symptoms and stop further issues.
Rarely, hand tingling or numbness might hint at a life-risk event, like a stroke or heart attack. If you experience symptoms like face drooping, slurring of speech, shortness of breath, cold sweats, or discomfort in the chest, neck, jaw, or stomach along with hand numbness11, call an ambulance at once.
Following healthy habits and taking appropriate steps to address the root cause may keep hand tingling at bay.
Adopting simple lifestyle changes can support overall health and may help reduce hand tingling. Some helpful practices include:
A diet with a lot of vitamins and minerals may keep nerves healthy. It may also help reduce vitamin deficiency that often triggers tingling.
Regular workouts and good body posture may help avoid pinched nerves. It may also boost blood flow in the body, reducing the chance of hand tingling.
Lowering your stress levels may reduce the chance of conditions that can trigger hand tingling.
Working with your healthcare provider to manage existing conditions (like diabetes and autoimmune disorders) may help reduce tingling.
Hand tingling may result from temporary issues or more serious underlying causes. Identifying the cause is key to finding the most suitable management options and may also help prevent further health complications. Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, addressing existing conditions, and seeking timely medical advice can support overall well-being and may help reduce tingling in the hands.
Worry about hand tingling when it persists, gets worse, or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, such as swelling, poor limb strength, numbness, dizziness, or severe pain. You should see a healthcare professional for a proper check and management.
Tingling in the hands can be a symptom of carpal tunnel syndrome, which is common during pregnancy due to fluid retention. However, it’s best to consult a doctor to discuss all potential causes2.
Yes, tingling in the hands and feet can be a sign of dehydration. When the body lacks sufficient fluids, electrolyte imbalances can occur, affecting nerve function and causing tingling sensations in the extremities. Rehydration is crucial to alleviate such symptoms.
Yes, tingling in the hands can be a sign of anxiety. During periods of heightened anxiety or panic attacks, the body can experience symptoms like tingling or numbness in the extremities due to increased adrenaline and changes in circulation patterns.
Tingling in the hands in the morning can be due to sleeping positions that compress the nerves, such as sleeping on the arms or hands. The compression can temporarily reduce blood flow and cause tingling sensations.
Tingling in the hands itself is not usually painful; it’s often described as a pins-and-needles sensation or numbness. However, the underlying conditions that causing the tingling, such as nerve compression or neuropathy, can sometimes be associated with pain or discomfort in addition to the tingling sensation.
Vertigo itself typically does not cause tingling in the hands and feet. However, some conditions, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) or vestibular migraines, may cause both vertigo and tingling. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause.
High cholesterol typically does not directly cause tingling in the hands. However, complications related to high cholesterol, such as atherosclerosis (narrowing of arteries due to plaque buildup), may lead to reduced blood flow to the extremities, potentially causing tingling sensations. Managing cholesterol levels through lifestyle changes and medications can help reduce the risk of such complications.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Ever found yourself confused at the grocery store, not sure if you should go for brown or white eggs? No need to feel alone, most people are in the same boat. Some folks think that one kind of egg might be a better pick health-wise or flavour-wise over the other. This article aims to wipe away such confusion by breaking down the facts about brown and white eggs. We will delve into what affects the colour of an eggshell, compare the nutritional values of brown and white eggs, and talk about how they influence taste, cooking and cost. In the end, you will be able to make a wise choice when buying eggs and know what truly sets brown eggs apart from white ones.
Many people believe that the colour of an egg determines its health benefits or nutrients. But the colour of an egg, whether white, brown or even blue, is determined by the chicken breed and its genes. The primary pigment in brown eggshells is something called protoporphyrin IX, and blue eggshells get their colour primarily from the pigment biliverdin1,2. While factors like the chicken’s feed or environment might bring in shade variations, they don’t change the eggshell’s main colour.
Did you know?
Several myths about egg colour have been circulating for quite some time, and it is time to bring the truth to light:
After debunking these myths, let’s look at how brown and white eggs stack up nutritionally.
It is important to note that brown and white eggs have about the same nutritional value5. The only difference lies in the eggshell colour, which is determined by the chicken breed and genes.
Both brown and white eggs are rich in high-quality protein and healthy fats and have trace amounts of carbs with no significant differences in macronutrient profiles6. Regardless of the egg size, grade, and colour, they will provide all the vital nutrients your body needs.
Eggs, both brown and white, are loaded with essential vitamins and minerals, such as vitamins D, B12, A, and E, as well as iron, calcium, and phosphorus6. These nutrients support various functions like boosting immunity, improving brain function, and strengthening the bones6.
Cholesterol is crucial for our cells and helps provide vital hormones. Studies have shown that dietary cholesterol doesn’t affect blood cholesterol levels for most people6. Since both brown and white eggs have similar cholesterol levels7, whether you eat brown eggs or white, the chances of them hurting your heart’s health are low.
As seen earlier, there is no major nutritional difference between brown and white eggs. But does the colour of the eggshell matter when it comes to taste and cooking?
Whether an egg is tasty or not is not determined by its outer shell. It depends on factors like the hen’s diet, the environment it was raised in, and how fresh the egg is4. Therefore, brown, and white eggs do not have any inherent taste differences.
You can use white or brown eggs interchangeably in almost all recipes without noticing any changes in flavour, texture, or appearance. Please note that minor differences may be noticed during cooking based on egg freshness and size.
Baking with brown or white eggs gives the same results. Just make sure to use eggs of the same size as mentioned in the recipe, regardless of shell colour, and you should be fine.
Whether your eggs are scrambled, fried, or hard-boiled, you will not taste or feel any difference based on egg colour. You can switch between brown and white eggs when making these dishes without altering the final outcome.
From my observations, it appears that both white and brown eggs, regardless of their shell colour, may offer a consistent nutritional profile. Each egg, whether white or brown, may offer a substantial 6 grams of protein while containing only around 70 calories!
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Studies suggest that chicken breeds, eggshell pigments, and a chicken’s living conditions and diet determine the egg colour. Let us see how these factors affect egg colour.
Different chicken breeds lay different coloured eggs. For instance, White Leghorn chickens lay white-shelled eggs, while chickens like Plymouth Rocks and Rhode Island Reds lay brown-shelled eggs8.
The chicken produces pigments that colour the eggshell. For instance, brown eggshells get their colour from protoporphyrin IX, while blue eggshells owe their colour to biliverdin2. Both pigments come from compounds known as porphyrins that form when heme (found in red blood cells) breaks down9.
The chicken’s diet, environment, and stress level can slightly alter the eggshell colour1. However, these factors cannot fundamentally change the colour of the eggshell.
Eggshells can have various other colours, like blue, green, and even pink2,5! Different chicken breeds, e.g., Araucana, Lushi, and Dongxiang, produce these uniquely coloured eggs2. The porphyrins, the same compounds that give colour to brown and blue eggshells, are responsible for these colour variations.
Based on my years of experience, I’ve come to believe that when it comes to nutritional value, both brown and white eggs might offer similar benefits. Notably, both types of eggs contain a significant amount of choline per 100g, potentially surpassing many other common food options. So, including brown or white eggs in your diet might be a simple and effective way to enhance your choline intake11.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Have you ever noticed that brown eggs are usually more expensive than white eggs at the grocery store? Let us dissect the reasons behind this price difference.
As we mentioned earlier, brown eggs usually cost more because the hens that lay them eat more because of their larger size. This increased cost of feed gets passed onto consumers through higher prices for brown eggs.
Additionally, consumer perception influences pricing. As brown eggs gain popularity, producers may raise their prices, taking advantage of the common belief that brown eggs are healthier or tastier than white ones, even though no scientific evidence supports these ideas. Even customers are ready to pay premium prices for brown-coloured eggs10.
Brown egg–laying hens might have slightly higher breeding, rearing, and feeding costs because of their larger size. Even so, these costs are not dramatically different and probably do not entirely explain the price disparity we see in supermarkets.
Brown eggs have become more popular recently; therefore, the demand for brown eggs has shot up, leading to potential price adjustments by producers. Increased consumer preference for brown eggs affects their pricing, despite no clear-cut differences in taste or nutritional value between white and brown eggs.
I may emphasize that if you have any heart-related condition or high cholesterol levels, it is important to be cautious about consuming brown or white eggs. In such cases, it may be advisable to limit your intake to three to four whole brown or white eggs per week. This precautionary approach might help manage the potential risk of adverse effects on your cardiovascular health12.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
So, how do we decide which eggs to buy since brown and white eggs are equally nutritious and differ only in appearance?
When shopping for eggs, it is best to look beyond the colour. Think about other factors that truly affect the taste and nutritional value of the eggs, which include:
These factors can have a significant effect on the quality and taste of the eggs you eat. They are more relevant to your health than the colour of the eggshell.
Based on the multifactorial comparison between brown and white eggs, there is no significant difference between the two in nutrition, taste, or even cooking. The main thing that sets them apart is eggshell colour, determined by the breed and genetic makeup of the laying hen. Factors like the hen’s diet and living conditions play a much bigger role in the egg’s nutrition profile and taste.
To make the best choice when buying eggs, focus on aspects that really influence egg quality and taste, such as organic farming techniques, whether the hens are cage-free or free-range, and if the eggs are omega-3-enriched. This approach will ensure that you not only consider the eggshell colour but also the aspects that really matter.
There may be minor shell thickness variation within the same breed due to factors like chicken genes or age. However, the colour of the eggshell doesn’t determine shell thickness.
Usually, chickens with white earlobes lay white eggs, and those with red earlobes lay brown eggs. However, there are exceptions, and earlobe colour isn’t a foolproof way to predict what colour eggs a chicken will lay.
Brown and white eggs have similar environmental footprints. The production method (organic, cage-free, free-range, etc.), rather than the colour, influences the environmental impact of eggs.
A single chicken can’t lay both brown and white eggs. But, you can have a mixed flock of chickens that lays both brown and white eggs. The chicken breed and genetics determine the colour of the eggs they lay.
No, the colour of the eggshell doesn’t influence the yolk colour. The chicken’s diet plays a major role in determining the yolk colour. For instance, a diet loaded with carotenoids (found in leafy greens and some yellow and orange fruits and vegetables) can make the yolk deep orange.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability, or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation of the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Choosing the healthiest cooking oil can be challenging, especially when deciding between avocado oil and olive oil. Understanding their nutritional profiles, potential health benefits, and cooking uses can help you make a more informed choice. This blog will give you a scientific breakdown of these two favoured cooking oils, their extraction steps, nutritional details, and health benefits.
Avocado oil is becoming popular as a healthy and tasty cooking oil. It is derived from the fruit of the avocado tree (Persea Americana), which is native to Central America1.
There are two main ways of extracting avocado oil:
Avocado oil holds many helpful compounds like:
Avocado oil, full of flavour and flexibility, has many uses in the kitchen and cosmetic products. Its mild, butter-like flavour enhances a lot of dishes1. Also, its softening nature makes it a great add-in for skin and hair care items.
From what I have seen, avocado oil might be highly placed for its numerous potential benefits, particularly in the realm of skincare. One notable advantage of avocado oil might be its rapid absorption rate when applied to the skin. This characteristic may allow for quick absorption, delivering its nourishing qualities effectively18.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
A staple in the Mediterranean diet, olive oil is made by pressing olives. There are various kinds of olive oil, each with its unique traits and nutritional properties.
Olive oil is available in different forms, depending on how it is processed3:
Like avocado oil, olive oil is made by either cold-pressing or heat and chemical processing methods4.
Olive oil is made up of a number of good compounds, including:
Olive oil is often used for cooking, dipping, drizzling, and finishing dishes, showing its cooking versatility. Add to this, its moisturising and emollient properties, which make it a go-to ingredient in beauty products. They also form the base of many traditional medicine remedies6.
Based on my observations, I may say that olive oil might serve as a considerably healthier alternative to dietary fats, particularly those derived from animals. When it comes to cooking, olive oil may provide a nutritious substitute for butter, margarine, and various other types of fat. Moreover, a study conducted in this regard demonstrated a remarkable correlation: replacing unhealthy fats with olive oil might be linked to a reduced risk of mortality19.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
To make a smart choice between avocado oil and olive oil, it’s vital to understand their nutritional differences.
Although avocado oil and olive oil are mainly made of monounsaturated fats, their fatty acid profiles differ slightly:
Although both oils have important vitamins and minerals, the quantities can vary.
Calories per tablespoon (15 mL) are similar for both avocado and olive oil. Each provides around 120 calories.
I may attest to the benefits of avocado oil in skincare products. When incorporated into soaps, it might noticeably improve lathering, creating a luxurious and abundant foam. Additionally, when used in creams, it may impart a smoother texture, resulting in a delightful and velvety application18.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
Avocado oil and olive oil provide loads of health benefits, but they differ slightly in the benefits they offer.

The high content of monounsaturated fats and oleic acid in both oils improves cholesterol levels. It also helps regulate blood pressure.

Adding either oil to your diet could help with managing your weight. The unsaturated fats in both oils can curb hunger/help with appetite control. This prevents eating too much and helps with managing meal sizes10.
Oleic acid, polyphenols, carotenoids, and tocopherols add up to the anti-inflammatory properties of avocado oil and olive oil. These compounds work well together to lower inflammation in the body1.
Adding avocado oil or olive oil to your diet could boost digestive health. The monounsaturated fats in these oils reduce inflammation in the gut1. Also, the flavonoids in olive oil are known to have antibacterial effects11. They could protect against harmful gut bugs.
Menopausal women may often face challenges due to hormonal changes, such as emotional fluctuations, hot flashes, depression, anxiety, and vaginal dryness. During these times, I think that olive oil might be a helpful solution. It possesses antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that may help ease symptoms and help cope with menopause20.
Dr. Anuja Bodhare, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)

Antioxidants are needed to fight oxidative stress and they protect body cells.

Avocado oil and olive oil provide soothing and nourishing effects due to their natural ingredients. Therefore, they are popular picks for skin care.
Knowing the value of smoke point in cooking oils is key to retaining their nutritional value. It also keeps the overall quality of the dishes you’re preparing.
The smoke point is the temperature at which an oil starts to break down and release harmful free radicals. Cooking oils at or below their smoke point will maintain both their flavour and their health perks.
Avocado oil’s smoke point is higher than that of olive oil, which means it’s less likely to degrade during high-temperature cooking methods. Avocado oil’s unrefined smoke point is about 480℉ (250℃), while extra virgin olive oil’s smoke point is between 350℉ – 410℉14,15.
Avocado oil is fitting for high-heat cooking techniques, like sautéing, grilling, searing, and baking. This is due to its higher smoke point. On the other hand, olive oil fits best for lower heat methods, like simmering, stewing, and medium-heat sautés.
Both avocado oil and olive oil play a key role in nutrient absorption, especially when consumed with beneficial nutrients in other foods.
Fats, like those found in avocado oil and olive oil, aid in absorbing fat-soluble nutrients, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K. Consuming high-fat foods along with these nutrients improves their availability and uptake by the body.
Both oils help absorb nutrients due to their content of monounsaturated fats. A study found that dressing a salad with avocado oil greatly boosted the absorption of carotenoids from the veggies16. Likewise, adding olive oil to tomato juice was seen to boost the absorption of the carotenoid lycopene17.
Although both avocado oil and olive oil offer countless health benefits like heart health, weight management, anti-inflammatory properties, and skin care, there might be times where one is more beneficial. For example, olive oil might be better for people who put a premium on its higher polyphenol content. Meanwhile, avocado oil might be a better fit for high-heat cooking due to its higher smoke point.
In general, both avocado oil and olive oil add health benefits to your diet. However, do think about personal tastes and specific health needs before buying the oil. This will guide you in choosing the right oil for how you live or as per your lifestyle.
Summing it up, avocado oil and olive oil provide a lot of health benefits, flexibility in cooking, and taste. Knowing their nutritional differences and proper uses, you can make an educated choice on the best oil for your diet.
Ultimately, personal taste and individual needs will play a big part in deciding the best oil for you. Grab the chance to test and try out each oil. Then, find your own balance. Logic and some new insights can help you make an educated choice on the best cooking oil.
In many cases, yes. However, remember that their taste profiles and smoke points differ. For high-heat cooking methods, avocado oil might be a better fit. At the same time, olive oil is more suitable for lower-heat applications or as a finishing oil.
Extra virgin olive oil and cold-pressed avocado oil often rank higher in terms of quality and nutritional worth. Yes, they’re pricier. But if your main goal is getting the max health benefits, paying more might be worth it.
Keep both oils in a cool, dark place. Keep them away from heat and direct sunlight. This will extend their shelf life and keep their flavour and nutrients. Also, always seal the container tightly after each use.
As long as they’re part of a balanced diet, there are little risks with avocado oil or olive oil. But it’s important to pick quality products. Also, pay attention to the oils’ smoke points while cooking to avoid harmful free radicals.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Most of the time, we don’t feel our heartbeat. And this is because, when our heart’s rhythm is normal, we usually don’t notice it. But, when it changes, we start to feel it. This is known as heart palpitation. It could be your heart beating too slow or too fast or even feeling like it stopped. Heart palpitations often feel like a fluttering, rapid, or irregular heartbeat. Individuals may feel that their heart is pounding, racing, or experiencing a skipped beat. Palpitations usually aren’t harmful, but they can be uncomfortable causing worry. Sometimes, they may be associated with underlying medical conditions.
Palpitations can arise for many reasons. These might be stress, heavy doses of caffeine or nicotine, excessive alcohol, hormones changing in women, certain medications or anaemia. Other heart palpitations reasons can be hyperactive thyroid, low potassium, or hypoglycaemia, irregular heartbeat or serious heart disease. In rare cases, a heart attack might also cause them1.
Did you know?
To effectively manage heart palpitations, you first need to diagnose the underlying cause. You must know when to get help and understand what your doctor may suggest.
If heart palpitations come with chest pain, shortness of breath, intense dizziness or a feeling of doom, it needs immediate medical attention. These heart palpitations symptoms could mean severe issues like arrhythmias or heart disease1.
Your healthcare provider will give you a physical check-up, listen to your heartbeats and look at your medical history. They may suggest some additional tests1.
The following cardiovascular assessments may be advised:
Dealing with heart palpitations requires multiple simultaneous approaches. Medical procedures, home remedies, and changes in diet can all come into play.
If heart palpitations are arising due a heart condition, medical procedure or medicine use may not be needed. In case of other underlying causes too such as hormonal issues or anaemia, medical management may be necessary. Your doctor can advise you best based on your condition1.
At home, you can also take some steps for managing heart palpitations. Avoiding things that spike palpitations can help. Controlling stress is also important. Yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can assist in this. Be sure not to use drugs like cocaine as they can cause palpitations too1.
Vagal maneuvers can slow your heart rate by stimulating the vagus nerve. This can involve putting cold water on your face, trying to gag, or dunking your face in cold water. But before trying these steps, consult your healthcare provider5.
Changing your diet can help avoid foods causing palpitations and increase those calming them.
Caffeine might potentially exacerbate heart palpitations in susceptible individuals. Therefore, if you experience heart palpitations, I strongly advise avoiding drinks or foods that contain caffeine, such as cola12.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Did you ever think about how much our diet influences heart palpitations? Some foods can lead to palpitations, while others can lessen them.
If you’re wondering what foods to avoid if you have heart palpitations, these are some of the foods that can actually set off or intensify palpitations in people prone to them.

Caffeine and energy drinks can stimulate the nervous system causing heart palpitations. Even though occasional use is safe, too much caffeine can cause palpitations6,7.

Excessive alcohol use can also cause heart palpitations. Cutting down or avoiding alcohol can help manage them1,6.

Red meat, high in saturated fats, can raise cholesterol and trigger palpitations. Swapping red meat for plant-based protein can aid in reducing this risk8.

Highly processed foods such as canned soups or packaged meals often contain too much salt and preservatives. These could disturb the heart rhythm causing palpitations. Opting for fresh foods instead of processed ones is a more heart-healthy option6.

Excessive sugar intake can contribute to heart palpitations, as it may lead to sudden spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. Limiting high-sugar foods can help manage blood sugar and lowers risk of heart diseases, thereby reduce the likelihood of associated palpitations6.

More salt means increased risk of high blood pressure thus more chance of palpitations. So, cut down on salt and keep palpitations in check6.
It’s ideal to avoid or consume the above-mentioned food items in limited quantity if you suffer from palpitations. However, for a more personalized plan, it’s best to discuss with a certified nutritionist.
But it’s not all doom and gloom. Some foods could help reduce frequent heart palpitations and support overall heart health.

Fresh fruits are heart-healthy. They contain essential vitamins and potent antioxidants. Their soluble fibre can also lower bad cholesterol levels decreasing palpitations9.

Whole grains support heart health through ample fibre content. This removes harmful cholesterol types, thus reducing the chance of heart disease and palpitations9.

Soy foods are rich plant-based proteins. They offer various heart benefits like reducing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, helping in reducing palpitations10.

Magnesium is a mineral that helps proper functioning of heart. Magnesium administration has been shown to be beneficial in certain heart rhythm disoorders7. Thus, consuming foods rich in magnesium such as dark chocolate, avocado and nuts can help lower palpitations6.
Although further research is needed, some studies have found the benefits of a plant-based diet to help support normal heart rhythm7. It’s a good idea to follow a balanced diet and include the above-mentioned foods in your diet if you suffer from palpitations. But discuss with your doctor before including anything new in your routine diet if you suffer from underlying medical conditions.
Based on my understanding gained over the years, it is worth noting that certain foods, such as salami, and aged cheeses might potentially contribute to heart palpitations. These foods may contain a compound called tyramine, which has been associated with increased blood pressure13.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Lifestyle changes can have a big role in managing heart palpitations and keeping your heart healthy. Let’s see on how to do that.
I may suggest to stay away from consuming spicy foods, particularly when it comes to conditions such as heart palpitations. In my experience, I have observed that spicy foods might potentially trigger heart palpitations in certain individuals14.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
Knowing more about heart palpitations, triggers, and effective management helps you lead a healthier life. Keeping active, having a balanced diet, getting enough rest and reducing stress can manage palpitations. Avoid food items like caffeinated drinks, excessive alcohol, red meat, processed or sugary foods and too much salt. But don’t forget that medical issues can also cause palpitations. So, always stay alert and seek medical help when needed.
Also Read: Food Items To Include In Your Diet If You Have Varicose Veins
A diet containing less known cardiac irritants and good amount of exercise, sleep and stress management can care for your heart.
If changing diet doesn’t ease heart palpitations, reach out to your healthcare provider. The palpitations might point to a hidden health issue needing medical attention.
While most palpitations are harmless, they can be discomforting. If they come with chest pain, loss of consciousness, uncommon sweating, dizziness or light-headedness, it’s serious. Seek medical help right away in such cases.
While occasional heart palpitations while sleeping can be normal, persistent or disruptive cases may indicate an underlying issue and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional for a comprehensive assessment.
In some cases, excessive gas and bloating may lead to increased pressure on the heart, causing palpitations. If symptoms persist or worsen, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
To alleviate heart palpitations, try practicing deep breathing exercises, staying hydrated, and avoiding stimulants like caffeine. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical advice for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Yes, dehydration can contribute to heart palpitations by reducing blood volume and affecting electrolyte balance. Maintaining adequate hydration is important for cardiovascular health and may help prevent palpitations.
Vaping may contribute to heart palpitations, as certain substances in e-cigarettes can impact cardiovascular function. The long-term health effects of vaping, including its impact on heart health, are still being studied. Consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended for individuals experiencing palpitations related to vaping.
Yes, hormonal changes during menopause, particularly the decrease in oestrogen levels, can lead to heart palpitations in some women. While usually temporary, persistent or severe symptoms should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Yes, gastro oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) can be associated with heart palpitations. The irritation of the oesophagus due to reflux may stimulate the vagus nerve, impacting heart rhythm. Consultation with a healthcare professional is advised for a proper evaluation.
The duration of heart palpitations varies, and they may last for a few seconds to several minutes. If palpitations persist or are accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
Heart palpitations after eating can be triggered by various factors, such as the release of digestive hormones, increased blood flow to the digestive system, and consumption of stimulants like caffeine or high-sugar foods. Additionally, overeating or underlying medical conditions may contribute to this phenomenon.
Certain vitamins like magnesium and potassium play a role in maintaining heart rhythm, and deficiencies may contribute to palpitations. Ensuring a balanced diet with adequate levels of these vitamins can help support heart health and reduce the occurrence of palpitations.
For minimizing heart palpitations during sleep, lying on your left side is often recommended. This position can help reduce pressure on the heart and promote better blood flow, potentially decreasing the likelihood of palpitations.
Factors like anxiety, hormonal fluctuations, or sleep apnoea can contribute to heart palpitations at night; managing stress, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, and addressing underlying health issues may help alleviate nighttime palpitations.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Beautiful yellow sunflower fields are a delight. It is from such blossoms’ seeds from where sunflower oil is derived. This bright-hued oil is a regular feature in supermarkets. But what goes into making it? Is it truly a health must-have? Or should we worry about its usage?
To answer these questions, let’s dive into an exploration of sunflower oil. We’ll look at its origin, nutritional makeup, pros and cons, and how it fares against other oils.
Did you know ?
Sunflower oils are extracted from the seeds of the Sunflower plant which is scientifically know as Helianthus annuus1. This oil is considered the second most widely oil in healthy diets due to its high nutritional contents2. It contains vitamins, minerals, proteins, flavonoids, amino acids, antioxidants, unsaturated fatty acids and fibers, which contributes to its various health benefits1. This is the only oil which has 46% of oil and 16% proteins, which makes it to rule both the market which has sell oil and proteins separately3.
Originating from North America, sunflowers were used by Indigenous people for thousands of years. Widespread usage of sunflower oil started in the 18th Century, after reaching Russia. They made use of sunflower seeds for food, ornaments, and medicinal purposes4.
To extract sunflower oil from sunflower seeds, it should undergo either cold-press method or refined method.
Did you know sunflower oil comes in different types? Let’s look at those.
Each type of sunflower oil offers unique benefits. High-oleic oil survives high heat, while high-linoleic oil doesn’t do well when heated. Mid-oleic oil offers a bit of both: stability under heat and a good mix of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats9.
Here’s a quick comparison of their key traits9:
Let’s delve into what makes sunflower oil a nutrient-dense option10.
From what I’ve seen, I have observed that incorporating sunflower oil into your diet might have positive effects on your lipid profile, specifically by reducing plasma triacylglycerol levels19.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, BAMS, MD (Ayu.)
Sunflower oil, boasting key nutrients, offers quite a few health benefits.

High-oleic sunflower oil, rich in monounsaturated fats, is linked with heart health. Some studies credit these fats with normalizing cholesterol, blood sugar, and blood pressure, hence lowering the risk of heart disease11. Although further studies are needed to confirm this benefit.

Sunflower oil also helps skin care. It’s rich in vitamins, proteins and fatty acids10. Hence it can act as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, that may help protect the skin barrier, reduce inflammation, promote wound healing, provide hydration and soften the skin12.

Sunflower oil is rich in Vitamin E, which aids the body’s defense system. It beefs up immunity and may help protect against infections, yet more research should be done13.
Based on my experience, I have seen that including sunflower oil in your diet may help protect your stomach from the side effects of certain medications. This is likely because sunflower oil can enhance your body’s natural anti-inflammatory response, which can reduce inflammation in the stomach19.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
But beware, sunflower oil also has potential pitfalls. Specifically, the high-linoleic variant carries some risks.
Also Read: Sunflower Oil: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects By Dr. Rajeev Singh
Sunflower oil has several rivals on supermarket shelves. How does it compare?
Olive oil tops the health chart among cooking oils. Compared to sunflower oil, it stands up better to heating. It also boasts heart-health by lowering the bad cholesterol and increasing the good cholesterol16.
Canola is also considered as a healthy oil but it has a chemical substance called hexane which is added while extracting the oil, which affects the oil’s stability by removing omega 3 and producing the trans-fat. Even this oil cannot withstand over heating like sunflower oil. But in the market cold-pressed oil or virgin canola oil are available, which are very expensive17. Hence both the oils have same effects only and we need to know how to use them to gain better health benefits.
Coconut oil, despite its saturated fat content, doesn’t harm your heart if eaten sparingly and as part of a varied diet. However, there are few studies showing that it causes harm to heart health17.
Also Read: Olive Oil: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects and More!
American Heart Associates recommends following cooking oils to be included in diet for better heart health18:
However, there are a few measures that need to be taken while consuming them18.
Also Read: Health Benefits of Coconut Oil for Skin and Hair
Sunflower oil is a mixed bag. On one hand, it’s rich in nutrients and good fats. On the other hand, certain types (like the high-linoleic version) have potential downsides. The secret lies in knowing which type of sunflower oil you’re dealing with. High-oleic sunflower oil is a healthier choice, offering heart-helping monounsaturated fats. But traditional high-linoleic sunflower oil, rich in omega-6 fats and with less heat stability, isn’t its equal. So, choose wisely! Remember, mixing oils in your kitchen can diversify your diet’s nutrition and health benefit profile.
Also Read: 7 Amazing Health Benefits Of Brown Rice
It depends on the sunflower oil type. High-oleic sunflower oil, rich in monounsaturated fats and stable under heat, is a healthier pick. But traditional high-linoleic sunflower oil, though filled with essential fats, is not as heat-resistant.
When compared to high-oleic sunflower oil, olive oil provides similar heart-healthy monounsaturated fats. But, olive oil, especially the extra-virgin kind, also offers a wide range of beneficial plant compounds and nutrients. This makes it an overall healthier choice.
High-linoleic sunflower oil is high in omega-6 fats. Too much of these can trigger inflammation, which can be a springboard for many health problems. Therefore, it is always recommended to consume in moderation.
Sunflower oil can be a healthy choice when used in moderation. It’s rich in unsaturated fats, particularly omega-6 fatty acids, which can benefit heart health when consumed as part of a balanced diet. However, it’s important to choose high-quality, cold-pressed oils and avoid excessive consumption due to their high-calorie content.
Sunflower oil can help improve cholesterol levels by increasing HDL (good) cholesterol and reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol when used as part of a balanced diet. Moderation and choosing healthier cooking methods, like baking or sautéing, are key to maximizing its benefits.
Sunflower oil is beneficial for hair health due to its high content of vitamin E, essential fatty acids, and antioxidants. It helps nourish the scalp, strengthen hair strands, and protect against damage from environmental stressors. Applying sunflower oil to hair and scalp regularly can promote shine and overall hair health. Although more research is needed to prove this benefit.
Sunflower oil is not directly related to weight loss but when used in moderation as part of a balanced diet, it can support weight loss due to its healthy fat content. Moreover, adopting a healthy lifestyle such as avoiding processed food high in calories can help maintain or reduce the weight.
Sunflower oil is primarily composed of unsaturated fats, with very low levels of saturated fat. It is considered a healthier cooking oil option due to its high content of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which can help lower cholesterol levels when used in place of saturated fats.
Sunflower oil provides essential fatty acids, such as omega-6 and omega-9, which support cell structure and overall body function. It can help maintain healthy cholesterol levels, promote heart health, and contribute to skin and hair health when used in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Are you aware of the buzz about oat milk and almond milk? These plant-based milk options have become very popular recently, especially for those who want to avoid dairy. This blog discusses in detail about these newer milk options. We’ll explore their nutritional facts, weigh their good and bad sides, evaluate their green credentials and safety concerns.

Oat milk is a non-dairy option made by blending soaked oats with water and filtering out the pulp. The result is a delicious, creamy drink that’s taken the plant milk world by storm.
Making oat milk is simple. You start by grinding whole oats, stirring them into water, and heating the mix. This process splits the oat starches. The liquid is separated from the oat mush and filtered. The end result is a thick creamy milk packed with fibres, especially beta-glucans.
Unlike some plant milks, oat milk boasts a smooth, buttery texture. It’s almost as rich as full-fat dairy milk. As for taste, oat milk is naturally sweet with a subtle oaty aftertaste. That’s why it is so popular in creamy dishes.

Now let’s check out almond milk. This non-dairy favourite has origins dating back to medieval times. It’s made mostly from almonds and water. Its mild texture and slightly nutty flavour have earned it many fans.
How do we make almond milk? First, we soak almonds in water overnight. Next, we drain the almonds and blend them with more water. Finally, we strain the mixture to remove the solids. What remains is a silky, pale milky-white liquid.
Almond milk has a light, thin consistency with a hint of nuttiness. Unsweetened versions are less calorie-dense. That’s why it’s popular among diet watchers and health buffs.
Though oat milk and almond milk are top-notch non-dairy options, their nutritional profiles can be quite different. These differences matter when picking one over the other.
Based on what I have observed, almond and oat milk are popular choices for non-dairy alternatives in India. These plant-based milk alternatives are often chosen by individuals who are lactose intolerant, have dairy allergies, or follow a vegan diet. The consumption of almond milk in India was found to be about 54% as compared to oat milk, which was about 29%9.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Apart from being lactose-free and vegan, oat milk and almond milk offer unique health perks tied to their ingredients. However, there are some drawbacks of both.

Oat milk is tasty and packed with nutrients, making it a great non-dairy milk stand-in, especially for individuals allergic to tree nuts.
From what I have observed, a 240ml serving of oat milk contains approximately 130 calories, 24g of carbohydrates, 4g of proteins, and 2.5g of fats. Oat milk can be a suitable option for those looking for a plant-based alternative to dairy milk, providing essential nutrients in a convenient form9.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS

Almond milk is favourable because of its lesser carbohydrate content. This makes it a good choice for those on a low-carb diet. But if you are allergic to nuts, it’s a no-go.
Almond and oat milk offer different levels of nutrient richness. Almond milk has fewer calories, but it also provides less protein, carbs, and fibre. On the other hand, oat milk has more calories, but it also provides more of these vital nutrients.
Oat milk generally contains more added B vitamins than almond milk, and almond milk contains more vitamin E.7 However, both fortified almond and oat milks have the necessary vitamins and minerals like vitamin D and calcium. But remember, not all fortified brands are equal. Some may include thickening agents, artificial flavours, and excessive salt. So beware when you buy.
Oat milk has about 120 calories per cup, which is almost three times the calories in almond milk. Almond milk has just 37 calories per cup. For those counting calories, almond milk might be a better option1,2.
Oat milk has higher protein that is about 3 grams per cup. Almond milk trails with 1.5 grams per cup1,2. But cow’s milk has much higher protein that both, that is about 8 grams of protein per cup.8 In terms of carbs, oat milk is the clear winner with 16 grams per cup. Almond milk has just one gram per cup. As for fat, almond milk has more than oat milk1,2.
Based on what I have read, a 240ml serving of almond milk typically contains around 59 calories, 6g of carbohydrates, 1g of protein, and 4g of fats. These nutritional values make almond milk a viable option for individuals who are lactose intolerant or follow a plant-based diet9.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
Both oat milk and almond milk leave a mark on the environment. Here we’ll explore water use, carbon emissions, and energy use in making these milks.
Think about allergies, additives, and sugar when thinking about safety.
Some people are allergic to almonds, so there’s a risk with almond milk. Oat milk could indirectly trigger allergies. This happens through possible gluten contamination. Those allergic to gluten need to be careful here and opt for gluten-free options.
Many varieties of oats and almond milk use things like gums to tweak their consistency and shelf life. Usually, these are safe. However, studies suggest that eating too much might mess up your digestion. Some almond milk brands use carrageenan, which has links to digestive troubles and gut inflammation.
Sugar content in these milks can vary a lot across brands. Unflavoured, unsweetened types have very little sugar, but flavoured types can be high in sugar. Always read the nutrition label to avoid extra added sugars.
Also Read: Soy Milk: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects By Dr. Rajeev Singh
Choosing between oat milk and almond milk rests mainly on personal taste, dietary needs, and green concerns.
If you’re trying to lose weight or if you’re diabetic, almond milk might be a good choice due to its low calorie and carb content. But if you’re looking to manage cholesterol or want a filling drink, oat milk wins due to its high fibre content.
Whether you prefer the creaminess of oat milk or the nuttier taste of almond milk guides your everyday choice.
If you’re looking for an eco-friendly option, oat milk wins hands down. It uses less water, land, and emits less CO2 during production.
Also Read: Goat Milk: Benefits, Uses, Side Effects & More!
In this blog post, we’ve dug deep into oat milk and almond milk. Both have a rightful place in the dairy-free movement. Both have their strengths. Almond milk wins with fewer calories, oat milk scores with higher fibre. One thing to note is that neither oat milk nor almond milk reach the protein content of cow’s milk. But you can get calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin B12 from fortified oat and almond milk versions.We didn’t intend to pit one milk against the other. Rather, we’ve tried to give you a clear picture of the pros and cons of each. Remember, the ultimate goal isn’t to find the ‘best’ milk, but to find the milk that’s ‘best for you’.
Also Read: Almond Milk: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects by Dr. Rajeev Singh
It depends. If you’re aiming to lose weight or are diabetic, almond milk with its lower sugar and calorie content might be right for you. On the other hand , oat milk is high in fibre and nutrients, which boosts heart health and immunity, and helps muscle grow. Consult a health professional for tailored advice.
Different types of milk suit different people. Each has its unique set of nutrients and caters to different diet needs or restrictions. Oat milk is as creamy as cow’s milk, but it provides less protein and more sugar. Cow’s milk offers protein and calcium but might trigger allergies. The ‘healthiest’ milk is the one that matches your particular health goals.
Both are suitable. Both oat milk and almond milk do not contain lactose. So, both are safe for individuals who are lactose intolerant or choose to avoid dairy.
Oat milk and almond milk both have low calorie options, but almond milk generally has fewer calories, making it a better choice for weight loss. However, the best option depends on individual nutritional needs and preferences.
Almond milk is better for managing cholesterol as it contains no cholesterol and is low in saturated fat. Oat milk, while slightly higher in calories, also helps lower cholesterol due to its beta-glucan fibre content.
Almond milk is generally better for diabetics because it has a lower carbohydrate content and glycaemic index compared to oat milk. However, unsweetened varieties of both can be suitable depending on individual dietary needs.
Almond milk tends to blend well with coffee without overpowering its flavour, while oat milk offers a creamier texture and natural sweetness that some prefer. The best choice depends on personal taste preferences and desired coffee experience.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Next Page »« Previous Page