कोलेस्ट्रॉल टेस्ट एक खून परीक्षण है जो आपके शरीर में कोलेस्ट्रॉल की मात्रा को मापता है। यह परीक्षण आपकी धमनियों (arteries) में फैटी डिपॉजिट का बिल्ड-अप करने के जोखिम को निर्धारित करने में मदद कर सकता है।
कोलेस्ट्रॉल परीक्षण आपके खून कोलेस्ट्रॉल के स्तर को मापता है। यह आपके हृदय स्वास्थ्य का मूल्यांकन करने में मदद करता है और स्ट्रोक, हृदय रोग जैसी हृदय संबंधी बीमारियों के जोखिम कारकों का मूल्यांकन करता है।
हृदय जोखिम मूल्यांकन परीक्षणों के हिस्से के रूप में एक कोलेस्ट्रॉल परीक्षण निर्धारित किया जाता है। आपके खून में अत्यधिक कोलेस्ट्रॉल आपकी धमनियों (arteries) और खून वाहिकाओं को नुकसान पहुंचा सकता है। इससे आपको स्ट्रोक, हार्ट अटैक और दिल की अन्य बीमारियां होने का खतरा बढ़ जाता है।
यदि आपके पास निम्नलिखित में से एक या अधिक जोखिम कारक हैं – तो आपको कोलेस्ट्रॉल परीक्षण की आवश्यकता हो सकती है :
अध्ययनों में बताया गया है कि भारत में 25-30% शहरी आबादी और 15-20% ग्रामीण आबादी में उच्च कोलेस्ट्रॉल का स्तर है।
कोलेस्ट्रॉल परीक्षण के लिए आपको अपने खून का नमूना परीक्षण के लिए देना आवश्यक है। आप इस परीक्षण के साथ अकेले टोटल कोलेस्ट्रॉल के लिए परीक्षण कर सकते हैं या लिपिड प्रोफाइल परीक्षण के साथ अपने लिपिड स्तर की एक विस्तृत तस्वीर प्राप्त कर सकते हैं।
आपका डॉक्टर आपको निम्नलिखित कारकों के आधार पर कोलेस्ट्रॉल परीक्षण दोहराने के लिए कह सकता है :
लक्षणों के प्रकट होने से पहले संभावित स्वास्थ्य बीमारियों के निदान में एक कोलेस्ट्रॉल परीक्षण का उपयोग किया जाता है। कोलेस्ट्रॉल परीक्षण के परिणामों की मदद से, आप हृदय रोगों के विकास के लिए अपने जोखिम का निर्धारण कर सकते हैं।
दिल की समस्याओं के लिए अपने जोखिम कारकों के आधार पर, आपको स्क्रीनिंग के लिए कोलेस्ट्रॉल परीक्षण को दोहराना पड़ सकता है।
कोलेस्ट्रॉल परीक्षण रिपोर्ट आपके खून में टोटल कोलेस्ट्रॉल के स्तर को मापती है। यदि आप सभी प्रकार के कोलेस्ट्रॉल के स्तर का पूरा परिणाम चाहते हैं, तो आपको लिपिड प्रोफाइल टेस्ट का विकल्प चुनने की आवश्यकता हो सकती है।
कोलेस्ट्रॉल परीक्षण आपके शरीर में टोटल खून कोलेस्ट्रॉल के स्तर को मापता है। आपके खून में अलग-अलग तरह के कोलेस्ट्रॉल पाए जाते हैं। ये उच्च घनत्व (density) वाले लिपोप्रोटीन, कम घनत्व वाले लिपोप्रोटीन और बहुत कम घनत्व वाले लिपोप्रोटीन होते हैं। यह परीक्षण इन सभी कोलेस्ट्रॉल अणुओं के संयुक्त योग को मापता है। यदि आप कम घनत्व वाले लिपोप्रोटीन (एलडीएल) कोलेस्ट्रॉल, उच्च घनत्व वाले लिपोप्रोटीन (एचडीएल) कोलेस्ट्रॉल और ट्राइग्लिसराइड्स के व्यक्तिगत उपायों के लिए परीक्षण करना चाहते हैं, तो आपको लिपिड प्रोफाइल परीक्षण प्राप्त करने की आवश्यकता होगी।
यह भी पढ़ें: कैल्शियम टेस्ट (Calcium Test): क्या है, खर्च, नॉर्मल रेंज, कैसे होता है, क्यों और कब करना चाहिए?
35 साल से अधिक उम्र के दोनों लिंगों के लिए कोलेस्ट्रॉल टेस्ट निर्धारित है। निम्नलिखित मानदंडों वाले लोगों को अपने कोलेस्ट्रॉल खून परीक्षण को पूरा करने की आवश्यकता है :
यह भी पढ़ें: फेरिटिन टेस्ट (Ferritin Test): क्या है, खर्च, नॉर्मल रेंज, कैसे होता है, क्यों और कब करना चाहिए
एक साधारण खून परीक्षण आपको आसानी से अपने कोलेस्ट्रॉल के स्तर की जांच करने में मदद करेगा।
घर पर अपने कोलेस्ट्रॉल की जांच करने के लिए, आप एक पैथोलॉजी लैब से कोलेस्ट्रॉल जांच बुक कर सकते हैं। आपका सैंपल घर से ही कलेक्ट कर लिया जाएगा अगर लाभ होम कलेक्शन की सुविधा देती हो तो।
आपको अपने कोलेस्ट्रॉल परीक्षण से पहले 10-12 घंटे उपवास करने की आवश्यकता है। कोलेस्ट्रॉल टेस्ट से पहले 12 घंटे तक कुछ भी ना खाये या पीये।
कोलेस्ट्रॉल को कम करने का सबसे अच्छा तरीका स्वस्थ, पोषक तत्व-घन खाद्य पदार्थ जैसे फल, सब्जियां, साबुत अनाज और दुबला प्रोटीन खाना है। रोजाना 30-45 मिनट व्यायाम करें और ट्रांस फैट्स, सैचुरेटेड फैट्स, शुगर और प्रोसेस्ड फूड्स से बचें।अगर कोलेस्ट्रॉल लेवल ज्यादा है तो डॉक्टर की सलाह से उचित दवाइयां भी ले लेनी चाहिए।
यदि आप टेस्ट के पहले उपवास नहीं करते हैं तो आपके कोलेस्ट्रॉल का स्तर सटीक नहीं हो सकता है। 12 घंटे के लिए उपवास सबसे सटीक परिणाम देता है क्योंकि एलडीएल कोलेस्ट्रॉल का स्तर आपके खाने से प्रभावित होता है।
जीवनशैली की कुछ आदतों में सुधार के बाद समय के साथ कोलेस्ट्रॉल का स्तर गिर जाता है। यदि आप दवाओं पर हैं, तो आप 6-8 सप्ताह के भीतर अपने कोलेस्ट्रॉल के स्तर में परिवर्तन देख सकते हैं।
अध्ययनों से पता चला है कि कॉफी बाइल एसिड्स और न्यूट्रल स्टेरोल्स के स्तर को कम करती है। इसके कारण कोलेस्ट्रॉल का स्तर बढ़ जाता है।
नहीं, पानी पीने से कोलेस्ट्रॉल टेस्ट पर असर नहीं पड़ता है।
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any change
The trend of using simple, homemade drinks to stay healthy is on the rise. Natural drinks made from fruits and vegetables are becoming popular because they are easy to prepare using everyday ingredients. People who want to follow a healthy lifestyle often prefer such drinks as part of their daily routine1,2.
Okra, also known as lady’s finger or bhindi, is a commonly used green vegetable in many Indian dishes. It belongs to a plant family called Malvaceae and is rich in fibre and important nutrients. Usually, okra is eaten as a vegetable, added to soups, or cooked with other foods. In recent times, soaking okra in water to make okra water has become popular as a homemade wellness drink. Although okra water is not a medicine, some people include it in their daily routine to support general health3,4. In this blog, we will understand how okra water is made and its nutritional value, possible benefits, and side effects.
Okra water is a simple drink made by soaking okra pods in water overnight. Almost every part of the okra plant is useful, including its leaves, flowers, stem, seeds, and pods. The green pods are the young fruits of the plant and are usually eaten as vegetables. They can be boiled, fried, dried, or added to soups and stews. When boiled or soaked in water, they release a natural, sticky substance called mucilage. This substance gives okra water a slightly thick texture. Making okra water is easy. Fresh pods are cut into pieces and soaked in water overnight. The water absorbs some of the stickiness and flavour from the pods. This simple drink allows you to use okra without fully cooking it5,6.
Okra water has good nutritional value as okra pods are contain nutrients like protein, vitamins, minerals, and fibre. Drinking this is an easy way to get okra water benefits without cooking it. The green pods and their seeds are especially rich in protein and important amino acids that the body needs for growth and strength.
Key Nutrients in Okra (per 100 g pods)
| Nutrient | Amount |
| Energy | 33 calories |
| Carbohydrates | 7 g |
| Protein | 2 g |
| Dietary fibre | 3.2 g |
| Starch | 0.3 g |
| Natural sugars | 1.2 g |
| Total fat | 0.1 g |
| Saturated fat | 0 g |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg |
| Omega-3 fats | 0.001 g |
| Omega-6 fats | 0.026 g |
| Plant sterols | 0.024 g |
Minerals in Okra (per 100 g raw pods)
| Mineral | Amount |
| Potassium | 303 mg |
| Calcium | 81 mg |
| Phosphorus | 63 mg |
| Magnesium | 57 mg |
| Copper | 0.1 mg |
| Selenium | 0.7 µg |
| Manganese | 1.0 mg |
| Zinc | 0.6 mg |
| Sodium | 8 mg |
| Iron | 0.8 mg |
Okra pods contain 11 essential amino acids, including aspartic acid. These help the body grow, build muscles, and stay healthy. Although okra has fewer essential amino acids than soybeans, it is still a good source of plant protein3.
Okra is rich in vitamins A and C, which support vision, immunity, and overall health. The minerals in okra, like calcium, iron, magnesium, and zinc, strengthen bones, blood, and the immune system. The fibre in okra swells when soaked in water, forming a gel-like texture. This slows digestion, keeps you full for a longer duration, and helps manage portion sizes.
Okra seeds contain healthy fats called unsaturated fatty acids, such as linoleic acid, vitamin E, and 16-17% of protein.
Overall, okra water is a simple and nutritious way to get protein, vitamins, minerals, fibre, and healthy fats. Let us understand what does okra water do for our body7,8.
Okra water contains fibre, vitamins, and minerals and may provide several health benefits when it is a part of a healthy diet. Here are some okra water benefits:
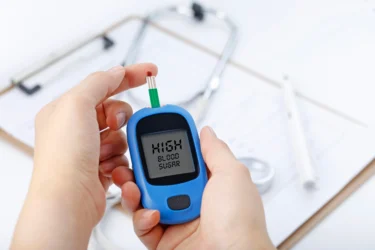
Okra contains a high amount of fibre, especially in its peel and seeds. This fibre may slow down how quickly sugar enters the blood from the intestines. Some natural substances in okra may work like insulin, helping support balanced blood sugar levels. For this reason, okra is often considered a diabetes-friendly food.

Okra contains a type of fibre called pectin. This fibre may help reduce the amount of bad cholesterol absorbed by the body and help remove extra cholesterol through waste. This may support heart health and reduce fat buildup.
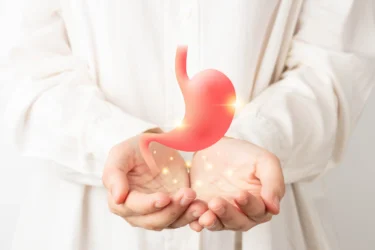
Okra supports good gut bacteria, which help keep the digestive system healthy. These bacteria also help produce certain B vitamins. Okra works like yoghurt by supporting a healthy balance of gut bacteria.
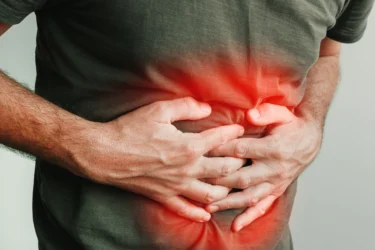
The fibre and natural slimy texture of okra help soften stools and make bowel movements easier. This supports smooth digestion and may help prevent constipation.
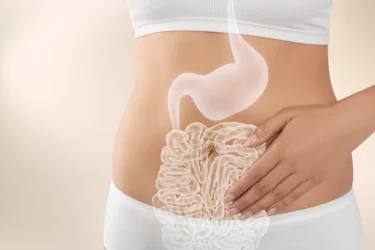
Okra contains insoluble fibre that helps clean the digestive tract by moving waste out of the body faster. This may lower the risk of colon-related problems.

Okra contains vitamin C and antioxidants that help the body fight harmful substances called free radicals. Minerals like calcium, iron, magnesium, and manganese also support immune health.

Okra provides vitamins such as vitamin A, B vitamins, and vitamin C; folic acid; calcium; zinc; and fibre. These nutrients support healthy baby growth and may help reduce constipation during pregnancy.

Okra has low calorie content and high fibre content. Fibre helps you feel full for longer, thus reducing overeating.
The sticky substance in okra may help bind cholesterol and waste products, supporting natural liver cleansing. Okra also contains antioxidants like glutathione.

Vitamin C helps repair skin tissues and may help reduce acne and pigmentation. Okra is also used as a natural hair conditioner that keeps hair soft and shiny.

The vitamin K in okra supports strong bones and blood clotting. Iron and folate in it help form healthy red blood cells.

Okra contains antioxidants like lutein and beta-carotene that support eye health. The flavonoids in it may help support memory, learning, and healthy blood vessels5,7.
Although okra water has many nutrients and possible benefits, you need to follow a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle along with it. Okra water should not be treated as a cure for any disease. Next, let us see how to make okra water.
Okra water can be easily prepared at home by soaking fresh okra pods in water so that some of their natural fibre mixes with the water. Follow this step-by-step procedure to make Okra water:
The best time to drink okra water may be early in the morning on an empty stomach. Okra water prepared by soaking sliced okra pods overnight may help digestion, act as a mild laxative, and support overall health. This practice has been followed for generations as a natural and simple health habit. It is believed to help in managing blood sugar levels and blood pressure because of its natural fibre content however, scientific evidence is limited. Therefore, okra water should be considered a supportive lifestyle practice and not a replacement for medical treatment6,9.
Okra water is mostly safe for regular use, but it may sometimes cause mild side effects. Drinking too much may lead to bloating, gas, or stomach discomfort as the fibre in it is difficult to digest. Rarely, some people may have allergic reactions, such as itchy skin, eye irritation, throat discomfort, or swelling. However, these reactions are extremely uncommon and usually occur in people who handle okra at work, like farmers or packers, rather than from drinking okra water. Children or people with severe pollen or food allergies may be more sensitive. If any unusual symptoms occur after drinking okra water, it is best to stop using it and talk to a doctor10,11.
Although okra water may offer many health benefits, it should be consumed with caution if:
Always drink enough water with it, as its fibre content may lead to constipation or dehydration10,12.
Okra water is a simple, natural drink made from fresh okra pods soaked in water. While okra water is not a medicine, it can be a helpful and nutritious addition to your daily routine. Benefits of drinking okra water include helping digestion, helping manage blood sugar, and providing vitamins and minerals. Since it is easy to make at home, you can include it as part of your healthy diet. For best results, drink it regularly but in moderation.
Also Read: Magnesium Rich Foods: Your Ultimate Guide to Essential Nutrition
You may drink okra water every day, as studies indicate daily use may be able to help regulate blood sugar. Some studies also suggest it may help avoid kidney disease. However, you should always check with your dietitian or doctor before consuming it9,12.
Yes, okra water can be beneficial during pregnancy when taken in moderation. It contains folic acid, vitamins, minerals, and fibre that may support healthy foetal development and may help ease common pregnancy issues like constipation.
Yes, okra water benefits may also extend to individuals with diabetes as the fibre in okra water slows sugar absorption, which supports blood sugar control. It may also help protect the kidneys from damage caused by diabetes. However, always check with your doctor before drinking it daily7.
There is no clear evidence that drinking okra water at night helps. Drinking it on an empty stomach in the morning may give better health benefits6.
Okra water can taste slimy or strong. You can make it more palatable by adding lime juice, spices, and a little salt13.
Okra water may be applied on the face. Animal studies have shown that it may have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant effects and may help in skin regeneration14.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
All of us need some morning fuel to start our day, don’t we? For some, it is tea and for others, it is coffee. But do you know that coffee is more than just a morning beverage? Particularly the black coffee? Black coffee has recently gained popularity among individuals trying to manage weight as it may have weight-management benefits1.
Black coffee may have several benefits that can support your weight management journey; however, it is essential to understand its effects and potential drawbacks. In this article, we will discuss aspects like black coffee benefits for weight loss, how to make it, and its side effects to help you make the right decisions.
Black coffee may be able to help with weight management, especially when combined with a healthy lifestyle. It contains bioactive compounds such as caffeine and trigonelline, which may improve body composition and metabolism in individuals who are overweight2. Some studies indicate that unsweetened caffeinated or decaffeinated coffee is linked to less weight gain over time1. Hence, the weight management effect of coffee is more prominent when it is plain and unsweetened.
In short, black coffee for weight loss may support weight management when paired with appropriate lifestyle and diet strategies and is best planned by a nutritionist to achieve good results.
Black coffee might help you support weight management through several mechanisms. Here are a few of them:

Caffeine, which is one of the main components in coffee, helps stimulate the central nervous system and improve metabolic efficiency. This may help the body burn more energy even when you are at rest3. A study published by The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition suggests that coffee/caffeine increases the calorie and fat burn in both obese and lean people4. This is because caffeine helps the body produce more heat and release stored fat, which can be used by the body for energy. This might be helpful for people who are trying to reduce or manage body fat3. However, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional before increasing your caffeine intake.

Coffee might help reduce hunger by influencing the body’s hunger and fullness signals. It can reduce the hormones that make you hungry and enhance the signals to make you feel full, especially after a meal. It also slows down the release of sugar into the blood. Overall, although coffee might help reduce your appetite, its effects vary from person to person3.

Black coffee, when consumed without sugar, cream or milk, has very few calories5. This makes it an good replacement for high-calorie beverages like sweetened coffee, soft drinks, or packaged juice. Choosing coffee over such beverages helps with reducing unnecessary calorie intake.

Studies indicate that consuming a caffeinated drink, such as black coffee, before exercise might help you burn more fat during workouts. Along with increased fat utilisation, caffeine also improves oxygen use during moderate-intensity workouts, whether you have eaten or not. Additionally, it can also improve alertness and energy, which might help you move more or exercise longer with better focus1.
Note: Drinking coffee may cause stomach discomfort in some individuals5. Therefore, avoid drinking coffee on an empty stomach or take it with a small snack, such as biscuits or nuts, to avoid acid reflux.

Some short-term studies suggest that caffeinated coffee might help the body process blood sugar. In a small study involving obese men with higher fasting blood sugar levels, men who consumed caffeinated coffee showed better glucose control after meals compared to those who consumed decaffeinated coffee or no coffee at all. The study also showed a reduction in waist size in the caffeinated group, showing that coffee may help support metabolic health1. Hence, coffee might help control blood sugar level, which in turn might help support fat metabolism and manage weight over time.
Now that you know the black coffee benefits for weight loss, it is also important to know how to make it to get the best out of it. Here is how to make black coffee for weight loss at home.
Enjoy your coffee once it is fully ready. Note that coffee alone cannot contribute to weight loss; you will need to combine it with proper exercise, diet, and lifestyle for the best results.
Although black coffee has many potential benefits, its excess consumption might cause several side effects. Following are some common side effects of black coffee:

The caffeine in coffee stimulates the central nervous system, which in turn triggers the release of adrenaline (a hormone). This might make you feel anxious or increase the risk of anxiety if consumed in excess. Studies indicate that this is more likely to happen when caffeine intake is more than 400mg1,6.

Although moderate coffee consumption is beneficial for the heart, its brewing method is very important. Boiled or unfiltered coffee might have excess diterpenes, which can increase blood cholesterol levels and that, in turn, can increase the risk of heart disease7. In addition, excess caffeine might also cause heart palpitations (a sensation of increased heart rate)5.

Since coffee is acidic in nature, excess coffee consumption might increase stomach acid production, causing gastric issues like acid reflux and peptic ulcers. This might lead to discomfort and long-term digestive issues3.

According to some studies, coffee might significantly interfere with sleep, reducing it by approximately 30-45 minutes1. It might also cause insomnia-related symptoms like trouble falling asleep, frequent awakenings during the night, and feeling sleepy during the daytime8.

The excess consumption of coffee might cause dehydration as it has a diuretic effect. This means it can increase urine output, thus leading to fluid loss3.

Although black coffee may offer some benefits for weight management, it is surrounded by many myths and misconceptions. Here are a few common ones, along with the facts.
1. Myth: Coffee alone is enough for weight loss.
Fact: No, coffee alone cannot significantly reduce weight. It might help increase metabolism and suppress appetite3, but effective weight management needs a balanced diet with calorie control and regular physical activity.
2. Myth: Consuming more coffee means more weight loss.
Fact: This is not true. A moderate amount of coffee consumption might help you in managing weight, while excess coffee consumption is associated with several health issues like anxiety, gastric troubles, and sleep issues3.
3. Myth: Black coffee or caffeine works the same for everyone.
Fact: This is false. Everybody processes caffeine differently; a moderate dose for one might be a high dose for someone else. Factors such as metabolism, body weight, and the use of several medicines might influence how caffeine affects an individual9.
4. Myth: Black coffee is effective at any time of the day.
Fact: No, this is not true. Consuming coffee in the morning may be more beneficial because it won’t disrupt the sleep pattern and may help reduce inflammation that occurs earlier in the morning10. Consuming coffee late at night might interfere with your sleeping patterns; therefore, studies recommend drinking coffee at least 8 hours before you sleep1.
5. Myth: Decaffeinated coffee does not play any role in weight management.
Fact: This is not true. Decaffeinated coffee, like caffeinated coffee, is linked with less weight gain, suggesting that it might help with weight management1.
6. Myth: Black coffee can suppress appetite for a long time.
Fact: No, black coffee might suppress your appetite only temporarily. This is because the caffeine in the coffee stimulates the hypothalamus, a part of the brain that regulates hunger, making you feel fuller for a short period3.
Black coffee might help you in your weight management journey by playing a role in improving functions like metabolism and appetite control. However, you can get better benefits from it when you combine it with a healthy lifestyle, regular exercise, and a proper diet. Do not forget that moderate intake of coffee is crucial, as excessive consumption may lead to serious side effects. It is best to consult a healthcare professional for personalised advice.
Drinking 1-3 cups of black coffee between morning and early afternoon is suggested to help boost metabolism and suppress appetite.
While research on caffeine’s effect on men and women has mixed opinions, it boosts exercise performance in everybody. Simply thinking that you have had caffeine might improve your performance, while some studies show men might benefit a bit more11.
Consuming coffee every day may be linked to a lower risk of health issues like diabetes, stroke, breathing issues, memory decline, and some types of cancer like liver and uterine cancer1.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Have you ever felt out of breath just walking up a hill or climbing the stairs? Or maybe you’re trying really hard to lose weight and wish you could see results more quickly? If so, you’re just like many others!
When people want to get fit and lose weight, one kind of exercise always comes up is Cardio, this just means any activity that gets your heart pumping, like walking fast, jogging, cycling, or dancing. Cardio is popular because it’s a fantastic way to make your body work harder, which burns off calories and helps you shed pounds. It’s the go-to exercise to help you not only reach your weight loss goals but also feel more energetic every day!
Let us explore the benefits of cardio for weight loss and overall health and see the different types of cardio exercises you can do to find the perfect fit for your routine!
Cardio exercise, also known as cardiovascular or aerobic exercise, is any physical activity that significantly increases and sustains your heart rate, prompting your heart to pump faster and harder to deliver the extra oxygen required by your working muscles1. Cardio exercise makes your heart and lungs work harder, which strengthens your lung health and improves blood flow throughout your body2.
If you are wondering ‘Is Cardio good for weight loss’, then the answer is, yes! Cardio exercise works by accelerating calorie expenditure and enhancing metabolic efficiency to help to lose weight. It:
While cardio can accelerate fat loss, it is not necessary to do it in excess. Prioritizing nutrition remains a critical factor for achieving your fat loss goals.
Cardiovascular exercise is typically categorized by the intensity level maintained during the workout. This helps determine how hard your heart and lungs are working.

This refers to any activity maintained for 30 minutes or more at a low pace, where the goal is to keep the heart rate controlled and steady throughout the duration.
This intensity level signifies working at a pace that causes harder breathing, an elevated heart rate, and a noticeable sweat. You know you have hit moderate intensity when you can talk freely but find it too difficult to sing your favourite tune.

This technique involves rapidly switching between short intervals of maximum intensity exercise and quick, controlled breaks for rest or light activity.
While HIIT quickly maximizes calorie burn, LISS is better suited for prolonged periods of fat burning4.
Regular cardio training offers a profound array of health benefits. Here is list of the health benefits of cardio exercises:

Regular cardio is a powerful workout for your heart and lungs, significantly strengthening them to boost cardiorespiratory endurance (the ability of your body to efficiently supply oxygen to muscles and utilize it for physical activities). They help improve blood circulation and regulate blood pressure, thereby avoiding the risk of hypertension. Moreover, regular cardio helps balance cholesterol levels, raising beneficial HDL (high density lipoprotein) and lowering harmful LDL (low density lipoprotein), keeping arteries clear and reducing the overall risk of heart disease and stroke3.

Cardio is essential for weight control because it actively burns calories during exercise3. Beyond immediate fat loss, this increased metabolic activity, when combined with a calorie-deficit diet, helps prevent weight regain and is crucial for maintaining a healthy body composition over time7.
As mentioned, cardio exercises help improve cardiopulmonary endurance and strengthen your heart and lungs. During exercise, your lung activity increases to meet the body’s demand for energy and the need to remove waste. When you do regular exercise, your lung capacity increases overtime to meet this demand8.

Regular activity releases mood elevating hormones like endorphins, serotonin, dopamine, and oxytocin, while simultaneously reducing the stress hormone cortisol. This powerful combination lessens anxiety and depression, enhances cognitive functions (memory and focus), and helps reset the circadian rhythm for deeper, more restorative sleep3.

When you exercise, your heart and lungs become more efficient, which means you won’t get tired as easily and will feel more awake. Stick to a daily cardio routine to boost your staying power. You may notice yourself getting fitter and faster every single day9.

Exercise is a powerful tool for dealing with certain chronic conditions. It reduces pain for people with arthritis (joint inflammation) and helps those with disabilities stay strong enough to handle daily life on their own9.
Thus, regular cardio exercise is a powerful step to your long-term physical and mental health, offering benefits that span from a stronger heart to improved mood and sleep.
Cardiovascular exercise is crucial for creating a calorie deficit, which is essential for losing weight. The American Heart Association recommends doing 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week, which would be approximately 30 min a day for 5 days5. Following are some best cardio exercises for weight loss:

Walking is an accessible and highly beneficial form of physical activity that is suitable for individuals across all fitness levels, if you have a treadmill this can be done at home itself.

High-intensity exercises, such as running, are excellent for burning your calories, which aids in weight management when combined with healthy eating.

Cycling (or bike riding) is an excellent, environmentally friendly activity that benefits your mental and physical health at the same time allows you to enjoy the outdoors and travel efficiently.

Swimming is a versatile, low impact sport suitable for all ages and fitness levels. By increasing your speed, swimming can become a high-intensity activity that significantly contributes to your fitness.

This fitness option is inexpensive, compact, and portable, making it an excellent tool for getting into shape quickly.
Dancing is a fun and social work out that strengthens your heart, bones, and muscles at the same time improves your balance. It is such an enjoyable way to stay active that you might not even realise you are exercising.

Hiking is a long, walk in nature, usually on trails or through mountainous terrain, done for exercise and enjoyment.
To avoid boredom and keep your routine engaging, plan to incorporate a variety of different exercises daily.
Note: Always consult your doctor before starting any new exercise plan, especially if you have an existing health condition.
Cardiovascular exercise, or cardio, should not be viewed as a burden or a chore; rather, it ought to be an activity that you find sustainable and genuinely enjoyable over long term. For this, you can make use of the following tips:
Always prioritize your safety and be mindful of your physical limits. If you experience any pain or tightness in your chest, sudden shortness of breath, or dizziness, you must immediately stop exercising and rest. Do not hesitate to seek medical help if your symptoms persist or worsen.
It’s time to debunk the persistent myths surrounding cardio exercise and weight loss, some common myths are as follows:
1. Myth: To achieve results, you must dedicate hours of cardio exercise daily.
Fact: Shorter bursts of exercise are also beneficial; the recommended amount is 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week. You can break this up. Multiple 10 or 15-minute sessions throughout the day can be just as effective as one long session. Incorporate movement into your daily life by taking short activity breaks like stair climbing, 10-minute walks, or spontaneous dancing on your favourite music etc.
2. Myth: Cardio is the Only Exercise You Need for Weight Loss.
Fact: While cardio is useful for calorie burn, sustainable weight loss requires the triple combination of cardio, strength training, and a nutritional yet low calorie diet18.
3. Myth: Cardiovascular exercise grants you complete dietary flexibility.
Fact: While physical activity is essential, it must be paired with mindful eating, as fitness and nutrition both together can give a better result.
Cardio exercise is a fundamental pillar for weight loss. It efficiently burns calories and boosts your metabolism, offering flexibility through intensity options ranging from the sustained pace of LISS to the rapid calorie-burning bursts of HIIT. Beyond slimming down, consistent cardio profoundly benefits your health by strengthening your heart and improving your overall mood. However, to unlock the most effective and sustainable weight loss results, combining your chosen, consistent cardio routine (aiming for about 150 minutes weekly) with dedicated strength training to maintain muscle mass, and a proper nutritional support is important. Finally choose an activity you enjoy to ensure long-term consistency.
Also Read: Best Aerobic Exercise for Weight Loss
HIIT exercise like running and jogging are some best way to burn fat, you can plan and add on some strengthening exercise along with a healthy diet plan for a better result. If you are a beginner, start with mild exercise steps and gradually progress, rather than immediately attempting high-intensity interval training4.
It is challenging but achievable to burn 500 calories in one hour. Focus on HIIT exercise like jumping rope, running, swimming etc. But listen to your body, don’t push through sharp pain; taking occasional rest is crucial for preventing injury and allowing muscles to recover and grow stronger19.
Yes, 30 minutes of cardio exercise can burn fat and calories, focus on moderate-to-high-intensity cardio exercise for better outcomes5.
There are certain exercises that can be done at home like jumping rope, burpees, running in place, climbing stairs, dancing and even some household work like mopping or vacuuming. If you have a treadmill at home, you can use it for walking, running, and jogging20,21.
Yes, cardio exercise can lower blood pressure by improving the health of blood vessels, specifically by reducing vascular stiffness and enhancing endothelial function. There are lot of studies that says cardio exercise can help lower blood pressure22.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Weight loss is a goal for many in the modern world; it is not only for a better appearance but also for improved health quality and self-confidence. Physical activity plays a role, but dietary control has to be prioritized for individuals looking forward to managing their weight. One such effective and healthy approach is the calorie deficit diet.
Calories are necessary for health and provide the body with essential energy but consuming too much of calorie leads to weight gain. Did you know? If you could cut down on at least 500 calories per day, you could lose up to 454 grams per week, which means nearly 2 kg in a month1. Isn’t it wonderful!
And this is why, despite a variety of specific eating plans like low-carb or keto diets, majority of people adopt a low-calorie diet plan. Studies also confirm that reducing daily calorie intake is the most crucial factor for weight loss and the calorie deficit diet does the same2. Let’s discuss in detail about this diet.
A calorie deficit diet is a diet pattern where you consume fewer calories than your body’s requirement, which results in a shortfall of energy forcing your body to use stored fat for energy, which further leads to weight loss3. There are different terms for this diet pattern for e.g. calorie restricted diet, energy deficit diet, low calorie diet, very low calorie diet etc. While calorie reduction is the goal, an effective way is to ensure your diet is rich in fibre, as fibre-rich foods make you feel full for longer4.
The food we eat gets converted into energy or calories. Our body utilises these calories for normal functions like regulating body temperature, pumping of heart, breathing and also for physical activity. When the calories consumed are in excess to those used, they are stored in the body as fat, which leads to weight gain. With a calorie deficit diet, the intake of calories is lesser than the body’s requirement. Burning more calories than intake creates a negative energy balance, which causes the body to start utilising the stored fat as source of energy, thereby resulting in weight loss3. However, it is important to note that factors like age, sex, body composition and metabolism play an important role in how well calories get utilized by our body and hence they may have an impact on how well these diet’s work.
So basically, despite the confounding factors, to lose weight, the body needs to burn more calories than it consumes. And this can be achieved either by increasing the levels of physical activity (regular exercise) or following a calorie deficit diet or best, a combination of both3.
The most widely accepted healthy weight loss strategy involves maintaining a consistent daily calorie deficit of 500 to 750 calories2. This level of deficit typically leads to a healthy weight loss rate of about 2 kg per month, which is considered safe for most people1. However, this also depends upon personal needs, your metabolism and physical activity levels. As per calorie deficit diets, the daily caloric allowance ranges from about 1200 to 1500 calories for women and 1500 to 1800 calories for men for healthy weight loss5.
High calorie deficit such as more than 800 calories is usually not recommended for long-term as it can result in adverse health effects, including low energy, fatigue, decreased bone density, and nutrient deficiencies6,7.
Note: Before beginning any new diet, you should always consult your healthcare provider or a dietitian to understand the right calorie deficit requirement for you.
Following a calorie deficit diet is the basic step to lose weight. Along with weight loss this diet may offer some other benefits too such as:
A healthy eating pattern should focus on replacing high calorie foods with choices that are lower in calories and fat, but high in fibre and water to keep you full4.

First calculate how much your daily calorie intake should be with this diet. You can calculate this by using an online calculator and get to know the daily caloric requirement for your body to maintain your weight. From this value, you can deduct about 500 calories to achieve a calorie deficit level.
Design a diet plan that is rich in both essential nutrients and fibre. Prioritizing foods that are nutrient dense and high in fibre will help you feel full for longer without adding excess calories. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fat-free or low-fat milk products and lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, eggs, and nuts. Modify recipes to reduce fat and calories. Choose grilled, broiled, or poached chicken or fish instead of fried4.

Include a combination of proteins, good fats and complex carbs in all your meals. Balance your diet by prioritizing nutrient rich foods and minimizing sources of unhealthy fats and sugars. For e.g. Use non-fat milk instead of whole milk, use plain low-fat yogurt or Greek yogurt instead of sour cream in recipes, replace butter with soft margarine that has no trans-fat. Review food content labels or using online resources to check the caloric value of everything you eat1,4.

Portion control means being more conscious on the amount of food you consume. For that skip seconds, that is, fill your plate at once and keep extras in the kitchen. If you still feel hungry, take a second helping of vegetables, fruit, or salad.
Serve one part of anything that you are going to eat in a bowl or a plate to avoid overeating directly from a bag or box1.
Note: This may vary based on individual’s metabolism and specific health conditions. It is always better to consult a nutritionist before starting a diet plan.
An individual on low-calorie diet can consume approximately 1000-1800 kcal per day2,5. The following sample plans can be a good start if you are looking to try out the calorie deficit diet9,10.
| Meal | Menu | Calorie |
| Breakfast | 0.5 cup (45g) cereals + 1 cup low fat milk or 175g yoghurt. | 275 kcal approximately |
| Lunch | 120g legumes + 1 cup rice (100g) + 1 cup mix vegetables, salad (cucumber, radish) | 520 kcal approximately |
| Snacks | 1 cup fruit salad (watermelon, papaya), 150g Greek Yoghurt or 20g roasted almonds/peanuts, 1 cup low sugar tea/coffee (can be divided and taken as morning and evening snacks) | 240 kcal approximately |
| Dinner | Vegetable soup with legumes (beans or peas)/cottage cheese OR vegetables 1 cup (broccoli or spinach) with a slice of wholegrain toast. | 220 kcal approximately |
| Total Calories | 1255 |
| Meal | Menu | Calorie |
| Breakfast | Omelette made of 2 egg whites and vegetables of choice, 50g diced ham + 1 slice toast. | 180 kcal approximately |
| Lunch | 120g lean meat/legumes + 1 cup rice + mixed vegetables bowl | 600 kcal approximately |
| Snacks | 20g snack bag of Popcorn or foxnuts, boiled egg, 1 cup low fat milk/tea/coffee (can be divided and taken as morning and evening snacks) | 210 kcal approximately |
| Dinner | 100g Fish (tuna or salmon) with 1 roti and salad (cucumber, tomato) or on a toast. | 300 kcal approximately |
| Total Calories | 1290 |
| Meal | Menu | Calorie |
| Breakfast | 100g baked beans, 1 slice wholegrain toast | 210 kcal approximately |
| Lunch | 0.5 cup cooked rice or pasta, 100g beans/chickpeas, Garden salad | 500 kcal approximately |
| Snacks | 50g nuts, 1 cup fruit salad, 2 wholegrain snack cracker, 1 cup herbal tea (can be divided and taken as morning and evening snacks) | 300 kcal approximately |
| Dinner | 1 small wholegrain roll, Tofu 80g, 1 cup steamed vegetable (carrot beans) | 220 kcal approximately |
| Total Calories | 1230 |
Please Note: Total calorie values may differ based on cooking methods and recipes.
Make up your mind on what all needs to be followed when you are starting with calorie deficit diet
Eat slowing and chew each bite properly so your brain gets signals of satiety and avoid overeating.
A calorie deficit diet is considered safe, provided it is followed properly and these common mistakes are avoided.
Tracking your weight loss journey will give you motivation to do a little better each day. There are different ways to track your weight loss:
Tracking can help you to evaluate on your progress, where you can see what is working well and which area needs to be a corrected.
Also Read: Thinking About the Pegan Diet? Here’s What You Should Know
The calorie deficit diet is a mostly supported and highly effective method for losing weight. By consistently consuming fewer calories than your body burns and by maintaining a safe deficit of about 500 calories daily, you can promote healthy fat loss, improve metabolic health, and establish better long-term eating habits. You can see a positive result if your diet is balanced, by focusing on nutrient dense foods, practicing strict portion control, staying hydrated, and avoiding common pitfalls like skipping protein or cutting calories too drastically. Combining dietary discipline with light physical activity and consistent tracking ensures both safe and sustainable results. Always consult a healthcare professional or dietitian before starting to ensure the plan is structured to your individual health needs.
Prioritize nutrient-dense foods to maintain a balanced intake of all essential nutrients, even on diet. Make sure to have enough fibre because fibre can make you feel full. You can have fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meat, egg etc. Adopt some fat-free or low-fat cooking techniques like steaming veggies instead of stir fry, all these changes will help you to maintain a healthy calorie deficit diet4,19.
Once you have established your target calorie deficit (typically 500 -750 calories), the next step is to create a detailed daily meal plan encompassing breakfast, lunch, snacks, and dinner. You must consistently track your daily calorie intake to ensure you stay within your established limits. Throughout the day, remember to practice portion control and mindful eating to support your deficit goal1.
To determine your appropriate daily calorie intake, you must first figure out how many calories you need to maintain your current weight. For that multiply your current weight (in pounds) by 15 (this roughly translates to the number of calories per pound of body mass) e.g. your weight is 155 pounds, 155 multiply by 15 is 2325, this should be you daily calorie intake to maintain your current weight. To achieve the safe weight loss rate of 1 to 2 pounds per week, you should consume at least 500 calories fewer than your total weight maintenance calories daily. For instance, if you require 2,325 calories to maintain your weight, your new daily calorie target should be between 1,325 and 1,825. Online calculators are also available for this calculation20.
Yes, you can continue with light workout along with your diet. For best results with your calorie deficit diet, incorporating mild exercise, such as a brisk walk for 30 to 40 minutes, is highly beneficial1.
Yes, calorie deficit diet is considered to be safe if properly managed, specifically by prioritizing nutrient-rich foods to meet your body’s nutritional needs. Avoid the temptation to cut too many calories too quickly in an effort to lose weight rapidly. If you have any underlying health issues, make sure to consult your doctor before starting your diet plan1,4.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Central obesity or belly fat, is the excess fat stored around your belly or abdomen. According to a meta-analysis of over 280 population-based studies worldwide, about 41.5% of people aged 15 years and older have central obesity1. The main reasons for this are changes in lifestyle such as a high calorie diet and reduced physical activity. Visceral fat, which is a type of belly fat, is more harmful as it is responsible for causing several diseases like diabetes and heart disease3. Due to the associated health risks and impact on appearance and confidence, belly fat has become a major concern for many individuals2.
A lot of people want to know how to lose belly fat. Here is the good news! In this article, we will discuss in detail about belly fat, its types and causes, exercises to lose belly fat, some tips for healthy weight loss and common mistakes you should avoid while trying to reduce your fat. So, let’s get started.
Belly fat has adipose tissue, which is basically fat cells. They store energy, cushion the body, and help regulate temperature. Based on the location, belly fats can be classified into two as, visceral belly fat and sub-cutaneous belly fat. These fats differ in structure, developmental patterns, and function4.
There are many factors which contribute to belly fat, which ultimately leads to obesity. Let us discuss them in detail.
Changes in the standard of living and globalisation contribute to unhealthy lifestyle that can lead to weight gain. Now-a-days people have longer siting hours, be it for work (in front of computers) or for recreation (like watching TV, playing video games). This combined with a lack of physical exercise increases the risk of developing belly fat. Regular exercise is important for reducing belly fat, especially the visceral fat which has a greater chance of causing serious diseases5.
Poor dietary habits are an important risk factor for belly fat gain. Eating more calories than required by the body causes excess calories to be stored as fat, leading to obesity6. Belly fat can increase due to the consumption of energy-dense, processed foods1. Greater consumption of foods that have saturated fat is another cause of belly fat. Limiting the consumption of food with added sugar is also important5.
Studies show a link between poor quality of sleep and an increase in body weight. Sleeping for less than 7 hours a night regularly might affect the hormones which control hunger5. This can make you overeat because your body does not recognise that you are full. This ultimately leads to belly fat gain.
Stress, whether long-term or short-term can influence your brain and trigger hormones like cortisol. These are the hormones that regulate energy and appetite5. Changes in these hormones can make you eat more, which can lead to weight gain5.
Genetics is also a cause of belly fat in many. Researchers have found about fifteen genes which can cause obesity7. People with certain genes are more likely to regain belly fat after weight loss, while the genes linked to overall body weight do not predict weight regain8. This says that genetics affects belly fat more than overall obesity8. Hence, in people with a history of belly fat, maintaining a healthy lifestyle might lower the risk of belly fat regain.
Some medicines can cause belly fat by affecting the signals which control your hunger. These include medicines like antidepressants, birth control pills, medicines used for autoimmune diseases, insulin etc5
Some health issues like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), Cushing’s syndrome, hypothyroidism, depression etc can cause weight gain or belly fat gain6. Eating-disorders like binge-eating and bulimia are the other causes wherein people consume a large amount of food and lose their control. Treatments are necessary for all these conditions6.
While it is difficult to reduce fat from a particular region of the body and most exercises focus on overall weight reduction, some cardio, high intensity and core strength exercises as well as certain yoga asanas can help tone the abdominal muscles. It’s ideal to do a combination of these for best results. Following are some great exercises you can do:





When exercising, ensure to start with warming up and end with cooling down and always listen to your body, don’t overdo. Remember, proper technique is very important while doing any form of exercise not just to get the ideal results but to prevent oneself from injury or muscle strain. If you are beginner, it is best to practise these under a trained profession for proper guidance.
Achieving healthy weight loss requires a combination of lifestyle changes. Here are some simple tips that you can follow to manage your belly fat.





Even small mistakes can slow down your progress. Below are some common errors to avoid when trying to lose fat.
Also Read: Walking Backwards: Benefits, Precautions & How to Do It
There are many factors influencing belly fat such as genetics, lifestyle, medical issues, environmental factors like stress etc, however, opting for the right approach can help manage this. Choosing balanced nutrition, staying active, sleeping well, and avoiding common mistakes are the basic things that you have to follow for a healthier body and mind. Although it is difficult to lose fat from a particular body part, combining cardio with HIIT and strength-building exercises focussing on the core can help with overall weight loss and toning of the abdominal muscles. Remember, consistency, patience, and sustainable habits are the key to long-term success when it comes to fat loss.
Also Read: How To Lose Face Fat At Home Naturally
Measure your waist to check your visceral fat. Your waist circumference (perimeter) tells how much fat surrounds your organs. For females, it is 80 cm and for males, it is 95 cm. A waist measure greater than these are clear sign of health issues3.
A 5-minute warm-up is essential before you start your cardio workout. This will prepare you heart muscles to gently into exercise and will reduce injuries9.
Taking enough calories for your workouts, proper fluid intake, cutting your workouts if you feel stressed, resting at least 6 hours before workouts are some methods to prevent your body from getting over strained25.
Dancing not only helps with weight management but also improves heart and lung functions. It can boost your mental health, self-confidence, self-esteem, and social skills. Anybody of any age can enjoy dance as a sport or hobby. Plus, there are several options you can choose from such as Zumba, Ballet, Hip-hop etc. Here are some tips you should follow if you practise dancing:
Drink enough water before you start.
Take proper rest between dance sessions.
Do warm-up before you start dancing.
Cool down your body with stretches after dancing29.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Did you know your body needs protein to build tissues and make hormones, enzymes, and haemoglobin? Proteins are the major structural components of tissues, including muscles, in our body1. Proteins are made of amino acids. Human body needs twenty amino acids for its growth and metabolism. Out of these, twelve are nonessential, that is, the body can synthesize them1. The remaining amino acids which cannot be synthesized by the body are essential amino acids, and these should be received from our diet1.
Not only non-vegetarian foods but vegetarian sources also play a significant role in meeting protein requirements2. Plant-based foods hold all the essential amino acids which are necessary for human body. If chosen smartly, they can satisfy the nutritional needs of an individual2.
In this article, we will discuss why proteins are important, some high protein vegan foods and their benefits, how to include them in your diet and if their excess could cause any harm. So, let’s get started!
Proteins are the main building blocks of muscles and other body tissues. They are also used to produce enzymes, hormones, and hemoglobin1. They may also be used as a source of energy (but not primary source). Missing any of the essential amino acids might affect tissue growth, repair, and maintenance1.
Proteins play a crucial role in tissue repair. Tissues lost during injury or illness are replaced by proteins, by supporting the growth of new tissues for wound healing. Body starts using proteins for energy after an injury3.
Enzymes are proteins, which are involved in almost all of the chemical reactions happening inside the cells, such as metabolism. Certain hormones like growth hormones, insulin etc are also proteins, which carry signals to help different cells, tissues, and organs to work together4.
Proteins are the major structural components of muscles. Muscle mass is essential, especially for athletes who do intense workouts. High protein intake promotes muscle protein synthesis and increase in muscle mass, thereby strengthening the muscles1.
Proteins bind to atoms and molecules and transport them within the cells or throughout the body4. They help transport nutrients, ions, and metabolites into and out of cells to support normal body functions. Some transport proteins are also involved in metabolism5.
Antibodies are special protein which recognise different foreign particles such as viruses and bacteria. They protect the body by killing these organisms and prevent future infections. Antibodies are a major component of our immune system4.
Daily protein intake is essential to meet different bodily functions. The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for an individual differs based on sex, age, and health.
Dietary requirement of protein differs from infants to adults based on their age. Here are the protein requirements for each age category according to WHO6.
Note: For healthy individuals’ consumption of 2 g / kg BW /day is considered safe.
The RDA for pregnant and lactating women differ from non-pregnant women. The need of protein is higher during this period.
Although getting too much protein from diet is usually rare, even a very high protein vegan diet consumed over long periods of time might affect your body and cause some health issues like:
There are wide variety of vegan protein sources which are beneficial for humans. Here’s a high protein vegan food list that can help you meet your daily requirements.

Lentils come under legume family, which are rich in protein, essential amino acids, and fibres. These are beneficial because they provide high quality plant protein with low cost. The protein content in raw lentils is about 25gm and cooked ranges between 9.0–17.8gm per 100gm. Lentils are also rich in folate, polyphenols and other bioactive compounds with antioxidant properties. They can help raise blood iron levels, lower sugar levels, manage weight, and support gut health8. Lentils are a common ingredient found in Indian kitchens, usually consumed cooked as curries or even boiled as salads.

Almonds are nuts which are high in proteins. The protein content in almonds ranges between 16.8–25.4gm. Apart from protein, they have vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals, that show anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. They are also rich in fibre. Due to their rich nutrient profile, regular consumption may help lower the risks associated with heart disease, diabetes, obesity, etc9. Almonds are a great snacking option that help curb hunger while meeting your nutrient requirements.

Chickpeas are good source of protein, which belong to legumes. Cooked chickpeas hold a protein of 8.86gm per 100gm. Besides, they are also rich in vitamins, folate, dietary fibre, and several minerals. They are especially helpful in reducing bad cholesterol (LDL), which is beneficial for heart health and also healthy for the gut10. Chickpeas can be included in your diet in several ways such as boiled chickpea salad, chickpea curries or ground chickpea (hummus).

Soya or soybeans, which belongs to legumes, are considered as high source of protein, approximately 40% protein. They are rich in isoflavones, phytosterols, other antioxidants and good fats that help balance blood lipid and sugar levels and keep the heart healthy. Soyabean may also have cancer-protective action, help lower the risk of osteoporosis (bone loss), and aid in managing menopause symptoms11. Soybean can be consumed cooked with veggies or rice, as tofu or tempeh in salads or curries or as soy milk in smoothies, desserts or with cereals.

Peanuts are a great source of proteins along with fibres, vitamins, and minerals. They have highest protein levels compared to any other legumes. 100gm of peanuts have about 25.8gm of protein. They are also rich in phenolic acids, flavonoids, and phytosterols and may help manage cholesterol levels. The resveratrol found in peanuts is an antioxidant which reduces the risks of cancer, heart disease, nerve diseases, tumours, and inflammation12. Roasted peanuts (when consumed in moderation) are thus a healthy snacking option. However, some individuals might experience the acidity issues with peanuts. Removing the peanut eye might reduce its intensity. Roasting the peanuts is also helpful.
Note: Those who have peanut allergy should avoid consuming it.

Quinoa, which is considered as a whole grain, is a very protein rich seed. It has all the essential amino acids needed for a human body. 100gm of quinoa contains 14.1gm of protein. Plus, it’s gluten-free and rich in vitamins, minerals, and folic acid. It has bioactive compounds which help prevent diseases such as heart diseases, diabetes, cancer, and obesity13. Quinoa can be substituted for rice or other grains, consumed with veggies, as khichdi, in salads or as a breakfast cereal.

Seeds such as chia seeds and pumpkin seeds have high amounts of proteins and omega-3 fatty acids. There are about 24.2 gm of protein in 100 gm of Chia seeds, and 9.75 g of protein in 32.25 g of pumpkin seeds. Seeds have bioactive compounds which have a beneficial effect on metabolic health, help improve blood sugar and lipid levels, and may also help boost immunity13,14. They can be added to desserts or trail mix for a healthy flavourful treat.

Leafy vegetables like amaranths, spinach, moringa etc are good sources of protein. These have a protein range of 9.31 g to 15.38 g per 100 g dry weight. They are also high in fibre and minerals like sodium, potassium, magnesium, and iron15. Other protein-rich vegetables include broccoli (4 g of protein per 148 g), asparagus (2 g per 93 g), sweet corn kernels (4 g per 90 g), and mushrooms (3 g per 84 g)16.

Oats are rich in protein and starch, and other nutrients like vitamin E, folate, and many minerals. They also contain dietary fibre, and phytochemicals17. They help in reducing cholesterol and have antioxidant properties. One cup of oats has about 4.75 g of protein18. Oats can be enjoyed with milk as breakfast cereals or with veggies as a replacement of high carb meals.

Beans are legumes rich in protein. They also contain other important micronutrients like magnesium, potassium, iron etc. They are beneficial in reducing the risk associated with heart disease, and diabetes. There are several types of beans. Black beans (86 g) contain 7.6 g of protein, Kidney beans (88.5 g) contain 7.7 g protein, Lima beans (94 g) contain 7.3 g protein, Navy beans (91 g) contain 7.5 g protein and Pinto beans (85 g) contain 7.7 g protein19. They can be consumed boiled as salads or cooked to make delicious curries.

Here are some easy-to-follow tips to include high-protein vegan foods in your routine diet and boost your protein intake:
The number of essential amino acids in different foods is different. Since all the essential amino acids are not found in all vegan sources, combining your high protein vegan foods is important25. Let’s see some examples:
Thus, consuming a diet which contains cereals, legumes, soy and nuts, will give all the essential amino acids required by the body25.
Myth: Vegan diets cannot supply enough proteins.
Fact: Vegans consume protein comparable to their requirement, and sometimes even more than the recommended value2. Average protein intake in vegans generally exceeds 0.8gm. Protein intakes of approximately 0.9–1.0 g/kg body weight was seen in several studies in vegans. A combined diet with plant-based sources like legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains provides all essential amnio acids, which is sufficient to meet the protein requirements for most adults.
Myth: Plant proteins lack essential amino acids, careful combination of vegan sources at each meal is essential.
Fact: Taking different protein rich vegan foods throughout the day is enough to meet the nutritional requirement (of all amino acids), and it is not necessary to combine them in every meal2.
Myth: Plant protein cannot keep muscle health, as they are of low quality.
Fact: Even though isolated plant proteins build muscle strength less efficiently than animal protein, with proper planning and sufficient intake, vegan diet will still provide enough protein for good long-term muscle health2,26.
Myth: There are not enough plant-based protein sources.
Fact: Vegans have several options like legumes, nuts, seeds, soy, vegetables, and whole grains, which will supply all essential amino acids when eaten in combination, to meet their protein need25.
Myth: Vegan protein is tasteless.
Fact: The taste of plant-based proteins can be improved through careful selection of ingredients and flavourings. Proper combinations of these can make vegan protein meals flavourful and enjoyable, like animal-based protein dishes27.
Also Read: Super Healthy Gluten Free Foods and Its Health Benefits
Proteins, which are essential for overall health, are made of essential and non-essential amino acids. The essential amino acids which should be supplied through food are abundantly found in a high protein vegan diet including legumes, nuts, cereals etc. These support muscle strength, immunity, and metabolic functions. There are several vegan options available, such soya, legumes, nuts, seeds, and protein-rich grains and vegetables, which can provide adequate protein and essential amino acids. Proper diet planning and intake can provide the daily RDA of protein from vegan sources, just as from animal sources, to meet an individual’s requirements.
Also Read: Calorie Deficit Diet: What Is It, How to Follow, Strategies and More!
There is no difference in the requirement of protein based on the type of source we consume. Protein requirements are regardless of any sources, provided the plant-protein diet includes a mix of sources2.
Human studies show that plant and animal proteins are almost equally digestible in humans, with only a tiny difference2.
High protein vegan diet rich in zinc such as chickpeas, nuts, lentils, and whole grains are best for immune system, as this mineral is essential for the development and proper functioning of immune cells28.
High protein vegan foods such as soy products (tofu and tempeh), legumes (beans and chickpeas) and wholegrains (quinoa) can be used as an alternative to meat or dairy sources for vegan athletes23.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Sattu is a roasted flour which is widely consumed across eastern India. It is traditionally valued for its nutrition, versatility, and long shelf life and is typically prepared by roasting and grinding cereals or legumes, most commonly Bengal gram (black chickpea)1.
India is the global leader in chickpea production, contributing nearly half of the nation’s total pulse output, with an estimated 13.75 million tonnes harvested in 2021 to 222. This strong production base supports the widespread use of chickpea-based Sattu as a staple functional food across the country.
In this article, we will explore the nutritional profile of Sattu, its preparation methods, health benefits, and its growing relevance as an affordable, functional food.
Sattu represents a traditional form of ready-to-eat flour that combines convenience, cultural relevance, and functional nutrition. It is an affordable and readily available food option. This makes it a common energy dense food for various strata of life.
Although various grains are used, Bengal gram (black chickpea) is the most common and preferred ingredient because of its high protein content and robust flavour1. The roasting process not only enhances taste but also improves shelf life, decreases moisture content, and increases digestibility3.
Sattu is often referred to as a “poor man’s protein” due to its affordability and dense nutritional profile. In many parts of eastern India, particularly Bihar and Uttar Pradesh, it serves as a staple food ingredient used in beverages and stuffed preparations4,5.
Note: Sattu composition may vary, with some versions including added spices, salt, or grains like barley or wheat1.
Sattu is a highly nutritious food that offers a balanced mix of carbohydrates, protein, fibre, and healthy fats, making it an excellent food option for daily consumption. The table below represents Sattu’s nutritional values6:
| Nutrient | Amount (per 100 g) |
| Energy | 413 kcal |
| Carbohydrates | 64 g |
| Sugar | 20 g |
| Protein | 25 g |
| Fiber | 18 g |
| Total Fat | 5.50 g |
| Sodium | 0.27 g |
| Cholesterol | 0 g |
Note: The nutritional profile given above represents average values; however, these may vary slightly depending on the raw material quality, processing method, and the manufacturer.
Sattu offers a wide range of health benefits due to its rich nutrient profile. Common Sattu benefits include:

Sattu is naturally rich in insoluble fibre. This may add bulk to the stool and stimulate intestinal motility. In addition to this, its very low sodium content helps avoid bloating and gastric discomfort that could promote smoother digestion6. Thus, regular intake may support individuals with constipation and improve overall gut function.

Sattu may help improve metabolism because of its high protein and low sodium composition6. Protein is known to increase satiety (feeling of fullness), which in turn reduces excess calorie intake throughout the day7. Thus, Sattu may indirectly contribute to weight reduction efforts.
Sattu has 0 g cholesterol per 100 g6. It is seen that a low-cholesterol diet has the potential to support cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of lipid-linked disorders8. This makes it suitable for individuals with high cholesterol or hypertension6.

Sattu has an extremely low glycaemic index, meaning it releases glucose slowly into the bloodstream6. This may help avoid sudden spikes in blood sugar9. This property makes Sattu a safe and beneficial food option for individuals with diabetes.

Sattu helps maintain body fluid balance and has a natural cooling effect (especially when consumed with water). During the summer months, it could also help avoid dehydration and protect from heat stress and sunstroke6.

The presence of minerals like potassium and magnesium may help stimulate appetite when Sattu is consumed on an empty stomach. Further, its balanced nutrient profile also provides sustained energy. This makes it suitable for people recovering from a loss of appetite6.

Sattu may contain natural cleansing compounds that help flush out toxins from the body6. Regular consumption may also support metabolic detoxification and contribute to better immunity6,10.

Sattu is high in iron6. This supports red blood cell formation and may help avoid fatigue and anaemia6,11. Adequate iron intake is also linked to reduced hair fall and improved overall health12.

Sattu gives around 25 g of protein per 100 g. This could make it a highly efficient plant-based protein supplement6. Protein also supports muscle repair and improves metabolic rate13. This makes Sattu a suitable option for vegetarians needing high-quality protein.
Note: While initial studies have revealed the health benefits of Sattu, further large-scale human trials are needed to confirm these. Therefore, although Sattu consumption can be beneficial for health, it should not replace professional dietary advice, medical consultation, or individualised nutrition plans.
Sattu is a versatile ingredient widely incorporated into traditional dishes across different parts of eastern India. Its roasted flavour, high nutrient density, and ease of use make it suitable for beverages, snacks, and stuffed preparations. The following are some of the most popular culinary applications of Sattu6:

This is a culinary identity of Bihar that is also a long-lasting snack suitable for train journeys, evening snacks, or as a morning energy food.
How to prepare

This is a festive preparation made using Sattu as stuffing.
How to prepare

A popular summer drink made with water, commonly sold in Bihar and Uttar Pradesh.
How to prepare

Sattu is also used to prepare several traditional sweets and snacks, including6:
While black chickpeas (kala chana) offer many health benefits, potential side effects may arise (generally from overconsumption). Although rare, Sattu side effects may include:
Like with any natural product, if you consider including Sattu in your routine diet, the following should be kept in mind:
Traditional Ayurvedic practices suggest that Sattu should be taken by mixing it with ghee and sugar. It should be avoided in the night, immediately after meals and in very large quantities. It is also suggested to not chew Sattu with teeth or consume it along with water19, although scientific evidence is limited in this regard.
While clinically significant drug interactions are not well-documented in humans, research indicates that certain bioactive compounds in chickpeas may theoretically interact with some medications:
Also Read: Raw Banana: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects and More!
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans (DGA) recommend consuming 1.5 to 2.5 cups per week of cooked mature beans, peas, and lentils (including chickpeas). This intake may be used as a practical daily guideline for chickpea-based foods such as Sattu22.
Note: Since Sattu is high in fibre, it is best taken in moderation and (if needed) divided across the day. For personalised guidance on the appropriate amount, consult a doctor or dietitian.
Also Read: Brown Sugar: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects & More
Sattu is a versatile functional food with high protein, fibre, and minerals that make it valuable for both rural and urban diets. Its affordability, long shelf life, and use in dishes like litti chokha, sattu paratha, and cooling summer drinks further highlight its cultural and culinary significance.
While the benefits of eating Sattu (such as improved digestion and sustained energy) are well recognised, Ayurvedic texts recommend moderating intake and following proper consumption practices. Lastly, although no major drug interactions are documented, individuals with specific health concerns should consume it mindfully.
Also Read: Cherries: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects and More!
Sattu is generally safe, but consuming it in excess may cause bloating, gas, or constipation due to its high fibre content14,15. So, people with sensitive digestion or those not used to high-fibre foods may experience discomfort if they consume Sattu in excess.
Sattu may be taken daily in moderate amounts, especially as part of a balanced diet. While regular consumption supports digestion, hydration, and energy, it is best to avoid overconsumption due to its fibre load6.
Sattu has a low glycaemic index (GI). This means that it releases glucose slowly into the bloodstream and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels6. This property makes it a suitable dietary option for people with diabetes when consumed in moderation and without added sugar.
Sattu is traditionally considered a cooling food in Ayurveda. It is commonly consumed in summer with water to offer protection from dehydration and heat stress6.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Medohar Guggulu, a classic ayurvedic formulation, is based on the traditional use of guggul (an oleogum resin) that is obtained from the Commiphora mukul tree1,2.
Medohara in Sanskrit means ‘fat-eliminating’ and in Ayurveda, Medohar Guggulu has been used to manage a wide range of metabolic and inflammatory conditions1,3. Modern research identifies guggulsterone as one of the major bioactive constituents of guggul, which supports the growing relevance of guggul-based formulations in contemporary health care2.
And with increasing interest in plant-based and mechanism-driven therapies, Medohar Guggulu remains a well-known classical formulation that continues to be explored for its potential benefits, active constituents, and mechanisms of action. Therefore, through this article, we aim to explore scientifically backed evidence for Medohar Guggulu uses, benefits, side effects, and more.
Medohar Guggulu is a traditional Ayurvedic formulation that contains Shuddha Guggulu (purified Guggulu) as its base, which is combined with other synergistic herbs. These may include
1. Sunthi (dry ginger)
2. Pippali (long pepper)
3. Marich (black pepper)
4. Chitraka (leadwort)
5. Haritaki (chebulic myrobalan)
6. Vibhitaki (beleric myrobalan)
7. Amalaki (Indian gooseberry)
8. Musta (nutgrass)
9. Vaividanga (embelia).
This herbal blend containing guggul is traditionally crafted to support balanced metabolism and healthy fat processing in the body4.
According to Ayurveda principles, descriptions and traditional beliefs, Medohara Guggulu acts through several mechanisms4:
Through these combined traditional actions, Medohara Guggulu is used in Ayurveda to support metabolic balance and healthy processing of lipids. However, clinical evidence confirming these effects and benefits is still limited.
Although Medohara Guggulu is primarily valued for its metabolic and lipid-modulating actions, an understanding of the nutritional and techno-functional properties of its key constituent, which is guggul (Commiphora mukul gum), will help provide insight into its broader relevance as a functional ingredient.
A recent analytical study investigating the nutritional profile of C. mukul gum powder reported the following5:
| Parameter | Value |
| Moisture | 2.07% |
| Fat | 17.43% |
| Protein | 9.77% |
| Ash (mineral content) | 6.73% |
According to this study, the gum exhibits a bulk density of 0.63 g/cm³, which indicates good compressibility and ease of incorporation into various formulations. It also possesses notable phytochemical richness, containing 6.91 mg GAE/g of total phenolics and 1.68 mg QE/g of total flavonoids, both contributing to its antioxidant potential.
Together, these characteristics position C. mukul gum as a nutritionally valuable and bioactive component, reinforcing Medohara Guggulu’s uses in obesity and metabolic disorders.
Medohar Guggul demonstrates several key advantages for metabolic and systemic well-being by combining traditional Ayurvedic principles with modern biochemical insights. Common Medohar Guggulu benefits include:

Medohar Guggulu helps improve digestion, boost metabolism, break down fat, and improve insulin function4,6. In a study on 58 obese adults, those taking Medohar Guggul with diet and exercise lost more weight than those on lifestyle changes alone, especially people weighing over 90 kg7. This suggests it may enhance weight reduction efforts in heavier individuals.

Medohar Guggulu shows anti-inflammatory properties which may help ease joint discomfort in osteoarthritis patients. A study showed that guggul extract may facilitate improvement in osteoarthritis of the knee by reducing knee pain, stiffness and enhancing mobility8.

Guggulsterone, the active compound in guggul, may help lower cholesterol. It does so by improving how the liver removes cholesterol and by reducing inflammation1. This supports healthier lipid levels and overall cardiovascular wellness.
Guggulipid has shown benefits in reducing nerve-related pain in animal studies by easing burning sensations and sensitivity9. These effects may be due to guggulipid’s action on nerve inflammation. This suggests it could help support the management of neuropathic pain.
Guggul (guggulsterone) may help support diabetes management. It helps to reduce high blood glucose levels by improving glucose tolerance and supporting better insulin function, suggesting it’s potential as adjunct in diabetes management10.

Due to the presence of bioactive compounds like phenolics and flavonoids, Guggul may help regulate inflammatory mediators and support immune health. This helps to balance the body’s immune response11.

Guggulsterone may help support healthy thyroid function. It can increase thyroid hormone activity and boost metabolic processes (as seen in animal models)12. This points towards its potential support to manage hypothyroid symptoms

Lab studies indicate that guggulsterone may slow the growth of cancer cells and help harmful cells self-destruct13. While more human research is needed, early evidence suggests guggulsterone may have protective, anti-tumour benefits.
While initial studies have shown positive results, more high-quality human research is needed to confirm the above-mentioned Medohar Guggulu benefits.
Note: Medohar Guggulu is an Ayurvedic formulation that may offer supportive health benefits, but it should never replace modern medical treatment for conditions like cancer, nerve disorders, diabetes, or heart disease.
Medohar Guggulu is traditionally taken in tablet or powder (churna) form, usually under the guidance of an Ayurvedic physician. The general approach focuses on supporting digestion, fat metabolism, and overall balance of Kapha and Vata.
Below mentioned are typical usage guidelines (general Ayurvedic practice):
As per Ayurvedic practice, certain foods and habits are said to support Medohar Guggulu’s benefits. These include4:
While Medohar Guggulu is generally well-tolerated when taken in recommended doses, modern clinical and toxicological studies show that some individuals may experience mild to moderate side effects. Possible Medohar Guggulu side effects include:

The most common side effects reported include stomach upset, loose stools, belching, and hiccups. These were noted in human studies of guggul resin and extracts and not directly with Medohar Guggulu14.

Higher doses may occasionally cause skin reactions such as redness or itching in some individuals14,15.

Hepatotoxicity has been documented in case reports following use of concentrated guggul extracts14,16. While uncommon, liver-related adverse events have been described and should prompt immediate medical review.

Animal studies show that guggul might stimulate thyroid hormone activity11,14. This may cause adverse symptoms in sensitive individuals.
Like with any natural product, if you consider including Medohar Guggulu in your routine diet, the following should be kept in mind:
Also Read: Tejpatta (Bay Leaf): Benefits, Side Effects, Nutritional Value & More
Guggul and its active compound, guggulsterone, influence liver enzymes, cholesterol pathways, and hormone receptors. And because of this, Medohar Guggulu may interact with some modern medicines. Possible drug interactions include:
Always consult a qualified doctor before starting Medohar Guggulu, especially if you have any medical conditions or are on medication.
Usually, 1-2 tablets per day after meals, often used for 6 to 12 weeks may be suggested, but the recommendation varies depending on the individual’s condition and the doctor’s advice4,7.
Also note that commercially available Medohar Guggulu tablets differ significantly in potency due to varying formulation, purification methods, and resin content. So, Medohar Guggulu dosage can vary depending on your needs and also the brand used.
Important: Since Medohar Guggul has metabolic and digestive effects, dosage should be personalised. Always consult a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner to know the right dosage based on your overall health and needs.
Also Read: Guggul: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects and More!
Medohar Guggulu is an Ayurvedic formulation enriched with the therapeutic benefits of guggul and other metabolism-supporting herbs. Both classical Ayurvedic texts and modern scientific research highlight its helpful role in supporting healthy weight management, improving metabolism, regulating lipids, promoting joint comfort, and enhancing overall systemic wellness. Research on guggulsterone (the active compound in Commiphora mukul) further reinforces its pharmacological value due to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cholesterol-balancing properties.
However, its effectiveness and safety depend greatly on product quality and correct dosing. More well-designed, long-term clinical studies are needed, and Medohar Guggulu should be used only as a supportive measure and not as a substitute for modern medical treatment.
When taken responsibly, along with a balanced lifestyle, a wholesome diet, and proper medical guidance, Medohar Guggulu has the potential to provide meaningful support for metabolic health and overall well-being.
Also Read: Kanchanar Guggulu: Benefits, Side Effects, Precautions & More!
Weight reduction varies from person to person. In a small clinical trial, people who used Medohar Guggulu along with diet and walking showed slightly more weight reduction, especially those above 90 kg, who were all able to reduce some weight6. However, Medohar Guggulu cannot cause major weight loss on its own; it works best as a supportive aid when combined with a healthy diet and regular exercise.
Medohar Guggulu is generally taken after meals with warm water, as this helps digestion and enhances its metabolic effect4. However, dosing may vary by brand and practitioner, so it is best to follow your doctor’s/manufacturer’s instructions.
To use Medohar Guggulu effectively, it should be combined with a balanced lifestyle. Most brands recommend taking 1 to 2 tablets, once or twice daily after meals, depending on the tablet strength and guggulsterone content. For best results, you may pair it with a light diet, regular physical activity, warm water intake, and controlled meal timings4. The formulation works by improving digestion, boosting metabolism, and helping the body burn excess fat more efficiently, but it is not a standalone weight-loss treatment. Always consult an Ayurvedic doctor (especially if you have existing medical conditions or take other medications) to determine the correct dose and suitability for your body type.
Yes, it is generally safe for prolonged use if consumed as and when recommended by a certified ayurvedic practitioner. Although, it’s ideal to consult the specialist at regular interval in between to monitor progress.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Gond Katira (scientifically known as gum tragacanth) is a natural gum derived from plants that is valued for its unique cooling properties. Such gums form as pathological exudates (secretions) produced by plants in response to injury or stressful environmental conditions (like drought) through a process known as gummosis1.
Gond Katira is primarily sourced from Central Asia and Eastern regions, with Iran being the world’s largest producer and exporter. It exports approximately 300 to 500 metric tons annually to major markets in Europe, North America, and Asia. Although India is not a major producer, small-scale cultivation in the northwestern parts of the country contributes approximately 50 to 100 metric tons annually to the domestic market2.
Gond Katira continues to gain prominence in both traditional and modern applications because of its emulsifying, stabilising, and cooling properties. So, through this article, we aim to help you understand the potential Gond Katira uses, its composition, benefits, and any possible side effects.
As mentioned earlier, Gond Katira is the hardened exudate obtained from certain shrubs. These shrubs belong to the genus Astragalus (family Fabaceae), which typically grows in arid and semi-arid mountainous regions. The major species commercially used to produce Gond Katira include Astragalus gummifer, Astragalus microcephalus, and others adapted to harsh climates in Western Asia1.
Gond Katira is produced when the plant is injured or under environmental stress. When this happens, the sap of the plant comes out from the stems or branches. This sap eventually dries and forms flakes or ribbon-like structures1,3.
Gond Katira has two main fractions1:
Commercially available gum is found in ribbon or flake form, with ribbons generally considered of higher quality due to their uniformity and purity1.
Note: The physical grade depends on species, collection and drying method, which in turn affect purity and the swelling capacity of Gond Katira.
Gond Katira is used mainly as a gum/thickener (food additive) rather than a food commodity, so the nutritional profile of Gond Katira varies across commercial sources4.
Below are some commonly reported values for Gond Katira nutrition1:
| Item | Moisture | Carbohydrate | Protein | Bassorin fraction | Tragacanthin fraction |
| Gond Katira (per 100 g) | 8.79 to 12.94 g | 83.81 to 86.52 g | 1.65 to 2.59 g | Around 60 to 70% | Around 30 to 40% |
Gond Katira has been traditionally used in Ayurveda and is known for its health-supportive and promising functional properties. Common Gond Katira benefits include:

Gond Katira is traditionally valued for its cooling effect in hot weather, where it is consumed to moderate body heat and support hydration. Its ability to swell and form a gel-like mucilage helps retain water, potentially supporting fluid balance and providing a soothing effect during heat stress5.

Gond Katira may aid bowel movement regulation and help relieve mild constipation. The mucilaginous nature may coat the gastrointestinal lining gently, which could reduce irritation and support smoother passage of stool5.

Gond Katira has been promoted as a natural skin-supportive agent. The gel-matrix that forms when it absorbs water may help maintain skin hydration from within. It may also help with skin problems such as dryness, minor burns, rashes, and prickly heat when applied externally5.
The anti-inflammatory potential of Gond Katira suggests that it may help to support muscular or joint discomfort5. While not a substitute for medical therapy, it may possibly serve as a supportive adjunct.

Gond Katira’s mucilaginous fibres increase satiety5. This may help in reducing overeating and unnecessary snacking, making it a supportive natural ingredient for individuals aiming to manage weight.

The oligosaccharides in Gond Katira may help protect the liver by reducing damage, lowering oxidative stress, and improving blood sugar levels6. This suggests they may support liver health and help manage fatty liver conditions.

Gond Katira has immunomodulatory properties that may help support the body’s natural defence processes. In Ayurveda, it is traditionally believed to boost immune function, though more human research is needed to confirm these effects3.

Gond Katira has the ability to form gel. This along with its mild antimicrobial/antioxidant properties can make it useful in biomedical materials (such as hydrogels) for wound dressings and tissue scaffolds7.
Note: While several Gond Katira benefits are rooted in traditional Ayurvedic and Unani practices, only some are supported by emerging scientific evidence. Further large-scale human trials are needed to corroborate the traditional uses. Therefore, it should not be considered a substitute for medical advice. Moreover, individual responses may vary based on grade, species, quality, preparation, and dosage of Gond Katira.
Gond Katira is a highly adaptable natural ingredient and can swell into a soft and jelly-like consistency when soaked. This makes it ideal for preparing refreshing summer foods and drinks. Let us see how to prepare Gond Katira with a step-by-step preparation guide5:
Once soaked and prepared following the above guide, Gond Katira can be incorporated into a wide range of foods, beverages, and functional preparations. The following are some practical and enjoyable ways to include Gond Katira in the diet5:

Its jelly-like texture enhances taste while helping the body retain moisture. This makes these Gond Katira drinks a refreshing option in summer.
To prepare: Take the soaked Gond Katira and mix it into rose sherbet, lemon coolers, or sweetened herbal drinks.

Gond Katira adds a soft, slippery texture that complements other cooling ingredients, making falooda a refreshing drink.
To prepare: After soaking, layer the swollen Gond Katira with falooda sev, soaked basil seeds, chilled milk, and rose syrup.

Gond Katira’s mucilaginous fibre can give creaminess and enhance hydration. It may also support digestive comfort when added to blended beverages.
To prepare: Blend the soaked gel of Gond Katira with yoghurt or milk along with fruits like mango, banana, or berries.

Gond Katira adds a refreshing element to chilled fruit salads. This may help enhance its cooling effect during hot weather.
To prepare: Mix the soaked Gond Katira gel gently with cut fruits such as watermelon, muskmelon, citrus, or pomegranate.

Gond Katira’s natural gelling property creates light as well as hydrating desserts with a smooth and soft consistency.
To prepare: Combine the swollen gel of Gond Katira with milk or plant-based bases and flavour it with rose, cardamom, saffron, or vanilla.

Gond Katira enhances the smoothness of frozen desserts by improving texture and possibly reducing ice-crystal formation. This offers a naturally creamy finish without synthetic stabilisers.
To prepare: Blend the soaked Gond Katira into kulfi mixes or ice cream bases before freezing them.
And not just in your meals, Gond Katira may also be used in experimental skincare formulations as topical gels and natural cosmetic bases. It’s moisture-retention and soothing properties make it it suitable as a hydrating base in skincare formulations. You can prepare a smooth gel with the soaked Gond Katira and incorporate it into topical formulations (like after-sun gels, cooling masks, and lightweight lotions) to enhance hydration.
Gond Katira is usually well tolerated, and no major adverse effects are reported. Even long-term toxicity assessments have found no carcinogenic, genotoxic, or systemic toxic effects at tested doses in animals3,8.
However, Gond Katira is a viscous soluble fibre, and such fibres may increase the viscosity of intestinal contents, which can slow down the movement of food in the gut9. This may slightly delay digestion and reduce the speed at which certain nutrients are absorbed. In addition, as with any natural product, there may be a possibility of allergic reactions. Thus, Gond Katira should always be consumed in moderation.
Note: Gond Katira should never be consumed in its dry form, as it rapidly swells and may pose a choking risk.
As already discussed, Gond Katira is generally safe and beneficial, but certain precautions, such as the following, must be followed to ensure proper and safe use.
Important: Gond Katira should be sourced from reputable suppliers, free from contaminants, adulterants, or preservatives. Remember to prefer organic or pharmaceutical-grade material for both dietary and topical use.
Gond Katira may influence the effect of certain medications in the body:
Due to its mild cooling and potential blood-pressure-lowering effects, Gond Katira may enhance the action of antihypertensive medications. This may increase the risk of dizziness or hypotension5. Thus, people taking these medications should consult a doctor before using Gond Katira.
If you have any medical conditions or are taking any medication, it’s ideal to consult your doctor before incorporating any natural remedy in your routine diet including Gond Katira.
Also Read: Malkangani: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects & More!
A traditional and commonly recommended amount of Gond Katira ranges from 5 to 10 grams per day, depending on individual needs and digestive comfort5.
This quantity is typically enough to provide cooling, hydrating, and mild digestive benefits. Yet, it’s best to consult a registered ayurvedic practitioner to know the right dose for you depending upon your needs.
Also Read: Radish (Mooli): Uses, Benefits, Side Effects and More!
Gond Katira is a multifunctional natural gum valued for its cooling, hydrating, and digestive-supportive qualities. This makes it beneficial during hot climates and for overall wellness. Its unique ability to swell into a soothing gel allows it to be used in a wide variety of traditional and modern preparations that range from refreshing beverages and desserts to cosmetic formulations. While generally safe when properly soaked and consumed in moderation, mindful use is essential, particularly for individuals with specific health conditions or those taking medications.
As scientific interest grows, Gond Katira holds promising potential for future applications in natural health products, skincare, and functional foods.
Also Read: Sattu: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects & More
Gond Katira can generally be consumed daily in small amounts (around 5 to 10 g soaked) as traditionally practised. It is safe for most people, but overuse may cause bloating due to its high mucilage content5. However, individual tolerance may vary, so it is advisable to discuss regular use with a doctor, especially if you have medical conditions, take medications, or are pregnant or breastfeeding.
For both males and females, Gond Katira can be used for cooling, hydration, and digestive comfort, especially in hot weather. To use Gond Katira, it should be soaked beforehand for 6 to 8 hours. It can then be added to sherbets, milk drinks, smoothies, yoghurt, or lassi. It is important to keep in mind that pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult a doctor first due to limited safety data5.
Yes, Gond Katira mixes well with both hot and cold milk once soaked. It is often used in falooda, thandai, flavoured milk, kulfi mixes, and smoothies. Remember, to always use the soaked gel, never the dry crystals5.
Traditional practices (Ayurveda/Unani) have used Gond Katira as a natural cooling and strengthening agent, but there is no strong scientific evidence proving direct benefits for sperm count or motility5. It may support overall hydration and gut health, but it should not be considered a fertility treatment.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Next Page »