Complete Guide On The Female Reproductive System
By Dr. Nikita Toshi +2 more

Get,

to manage your symptom
Get your,


4 Cr+ families
benefitted

OTP sent to 9988776655



You’ve successfully subscribed to receive
doctor-approved tips on
Whatsapp

Get ready to feel your best.

Hi There,
Download the PharmEasy App now!!


Register to Avail the Offer
Send OTPBy continuing, you agree with our Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions

Hi There,
Sign up on PharmEasy now!!
Trusted by 4 crore+ families

OTP sent to 9988776655



You have unlocked 25% off on medicines




Code: NU25
By Dr. Nikita Toshi +2 more
Table of Contents
Several organs and hormones constitute the complete female reproductive system. The functions include the production of egg cells required for reproduction, transporting the eggs to the site of their fertilisation and implanting a fertilised egg into the uterus walls (commencement of pregnancy). When fertilisation has not happened or the fertilised egg has not got implanted onto the wall of the uterus, the female reproductive system ejects the lining of the uterus (menstruation). The production of female sex hormones that maintain the reproductive cycle is also a function of the female reproductive system. Therefore, the system is an amalgamation of many organs, each with its specific role.
The female reproductive system has parts inside and outside the female body. These broadly are:-
There are two primary roles of the external female genitals. The first one is to permit the male sperms to enter the female body. The other is to protect the internal portions of the genitals from organisms that carry infections. There are four major parts to the external female genitalia. These are:
Female reproductive system is a complex organisation with interlinking of various hormones such as Thyroid, oestrogen, progesterone, Luteal hormone, Follicle stimulating hormone. These hormones are secreted by brain, thyroid gland and ovaries.
Dr. M.G. Kartheeka, MBBS, MD(Pediatrics)
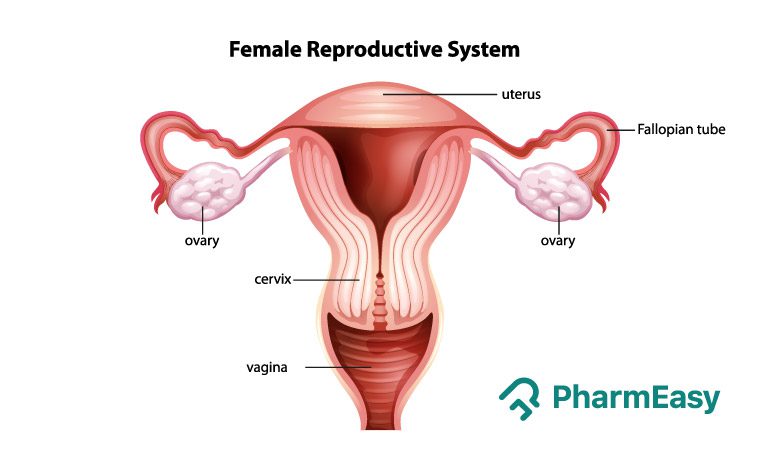
The vagina, the fallopian tubes and the uterus comprise the genital tract of the female reproductive system.
The ovaries are the primary reproductive organs or gonads. These two almond-shaped organs, one on each side of the uterus, are located in the walls of the pelvic cavity. The eggs and the female reproductive hormones are produced in the ovaries.
Female sexual dysfunction, fibroids, Polycystic ovarian disease and gynecologic cancers are common health conditions associated with the female reproductive system. Consultation with a gynaecologist is very important if you encounter any changes in your menstrual cycle or if you see any health-related changes in your body.
Dr. Ashish Bajaj, M.B.B.S., M.D. in Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology
Mammary glands are located in the breast. Though they are present both in males and females, their functionality is in females. Each breast has a nipple and the nipple is surrounded by the areola, which is a circular, pigmented area. An adult female breast contains lobes of glandular tissue. During puberty, the oestrogen hormone stimulates the growth of these glandular tissues. Progesterone causes the development of the duct system. Each lobe has lobules and a lactiferous duct transports milk collected from the lobules to the nipple.
During pregnancy, these two hormones further develop the mammary glands (breasts). Milk production in the glandular tissue is stimulated by prolactin, while oxytocin causes the milk to be ejected from the glands.
The menstrual cycle involves several different glands and their hormones in a complex process. Throughout the process, each gland and structure is influenced by the others involved in the process. The cycle is triggered by a structure in the brain known as the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus stimulates its neighbour, the pituitary gland, to produce sex hormones oestrogen and progesterone. With every menstrual cycle, a woman’s body prepares itself for a potential pregnancy. This biological cycle is independent of the wishes of the individual female.
A female must consult a doctor in case of any problems related to menstruation, pregnancy or sexual health without hesitation.
Starting off with about 1 to 2 million eggs at birth, a woman is likely to be left with about 300000 when she attains puberty. Of these, she will ovulate about 500 of these during her reproductive phase of life. The remainder will gradually die out through menopause.
Conceiving is all about timing. In a 28-day cycle, ovulation occurs on the 14th day. The best days of conception are three days before and after your ovulation. You will, however, be required to keep track of your periods over a few cycles to determine your ovulation dates.
You will need to keep track of your periods over time. The 5th to 9th day and 18th day after your last period started would signify the so-called safe days for intercourse. This can go wrong in case your ovulation is not regular. Additionally, the use of condoms can provide added protection not only from conceiving but also from sexually transmitted infections. Talk to your doctor about other methods of contraception that may suit you- IUD, contraceptive pills etc.
Every organ and hormone of the reproductive system is important. Considering childbirth, the uterus or the womb may be considered an extremely important part of the female reproductive system. That being stated, every part of the reproductive system needs to fulfil its role in a healthy state for the system to function for reproduction.
The life of male sperm inside a woman’s body is generally five days. Therefore, intercourse up to 5 days prior to ovulation may lead to conception and pregnancy.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any change

Leave your comment...
Comments