Many people are on the hunt for the ideal diet that fits their body, goals, and likes when striving for a healthier way of life. The Pegan diet is a fresh and unique eating approach that seeks to offer the best bits of two popular diets: Paleo and vegan. Does this one-of-a-kind blend actually bring noteworthy health gains? We’ll find out in this article!
Through this detailed blog, we’ll delve into the concept and key principles of the Pegan diet. Also, we will cover the foods to munch and ditch, the potential pros and cons, a sample Pegan meal plan, and finally, answer some common questions about the diet. Come and join us to figure out if the Pegan diet is right for you!
Did you know?
Dr. Mark Hyman crafted the Pegan diet as a mix of the Paleo and vegan diets1.”Peganism” aims to find a middle ground between these two dietary approaches. About 66% of the Pegan diet is plant-based foods, and the rest 33% is top-notch animal proteins1.
The Pegan diet tries to provide a perfect combo of Paleo and vegan diets by majorly focusing on nutrient-rich whole foods1. It stays away from highly processed foods, refined carbs, bad fats, additives, and toxins. It also cuts out most grains, beans, and dairy. As Pegan eat some animal proteins, you can think of the diet as a plant-focused twist of Paleo or an altered version of the vegan eating plan1.
The Pegan diet, rooted in both Paleo and vegan diet rules, has its own guidelines designed for long-term use. It centres on whole foods, especially vegetables (mostly those with low starch or ranking low on the glycemic index, such as broccoli, carrots, peas, and tomatoes ), fruits, nuts (e.g., almonds, pistachios, and walnuts), seeds (e.g., chia, flax, and pumpkin), healthy fats, grass-fed meats (e.g., beef, chicken, and pork), fish high in fats and low in mercury (e.g., salmon, herring, and cod), eggs, and occasionally, gluten-free grains (e.g., quinoa, brown rice, oats, and amaranth). It restricts or avoids certain food groups that may affect blood sugar levels, inflammation, and gut health1. You can have sugar when on the Pegan diet, but only as an occasional treat.
A Pegan diet puts a variety of nutrient-packed whole foods on your plate. These can help boost your overall health1. Let us take a good look at the main food groups and choices under this eating plan:





An additional benefit of Pegan diet is that it excludes processed foods and sweets. These foods typically don’t have much nutrient value. Furthermore, eating sugary foods might increase your appetite, which may result in overeating and unintended weight gain2.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
The Pegan diet suggests not eating certain food groups and processed items. Here’s what needs to be cut down or avoided while following this eating plan:

Since the Pegan diet gets a lot from Paleo diet rules, it usually suggests cutting out grains with gluten, like wheat, barley, and rye2. These grains could cause tummy issues and inflammation in some people, mainly those with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease9.

The Pegan diet suggests avoiding high-sugar fruits such as bananas, pineapples, and watermelon, and going for low-sugar fruits1,2 like berries, will keep your blood sugar level normal, especially for those who need to keep their blood sugar in control.

Dairy is not allowed in the Pegan diet due to possible inflammatory, allergenic, and hormonal impacts. This includes milk, cheese, and yogurt made from cow’s milk2. Organic sheep or goat dairy products can be allowed at times as a treat.

Fish with lots of mercury, like tuna, swordfish, and king mackerel, should be avoided to minimise exposure to toxic substances. Instead, choose low-mercury options like salmon, trout, sardines, and herring2.

The Pegan diet stresses fresh, unprocessed foods. That means processed and packaged items, artificial ingredients, and other chemical additives need to be off your shopping list2.

To help control blood sugar and reduce inflammation, added sugars such as white sugar 1,2, corn syrup, and even natural sweeteners like honey or maple syrup should be used seldom and in small quantities.

Bad processed vegetable oils like soybean, canola, corn, and sunflower oils are not advised on the Pegan diet. Instead, choose healthier fats found in olive oil, avocado oil, nuts, and seeds1,2.

Artificial colourings, flavourings, preservatives, and other additives are avoided10.
Due to their perceived impact on blood sugar and/or inflammation in your body, most of these foods are not allowed.
Several foods and food groups are limited or avoided in the Pegan diet. However, it is somewhat flexible. Limited amounts of banned foods may be allowed occasionally.
The Pegan diet, focusing strongly on nutrient-rich whole foods, might offer several health benefits:
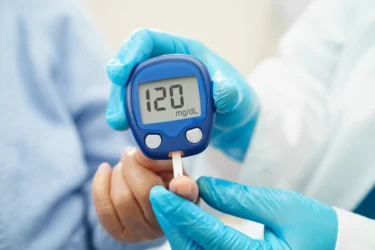
The Pegan diet can help back a healthy eating pattern packed with nutrients by focusing on a wide mix of fruits, veggies, lean proteins, and healthy fats1. This may help in keeping away and help manage long-term health problems such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain kinds of cancer1,2.
In my experience, the Pegan diet may lower inflammation and blood sugar levels in the body, which may lower your chance of developing some chronic illnesses like heart disease and type 2 diabetes2.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.

Eating fibre-rich fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds provides prebiotic fibre to back a healthy gut ecosystem1. A balanced and diverse gut microbiota is linked to various good health results, such as better immune function, improved mental health, and controlled weight11.
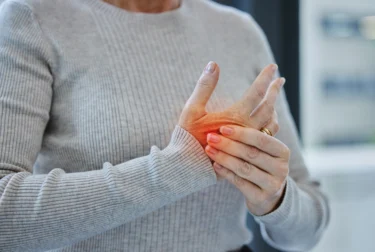
With its focus on anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3-rich fish, as well as cutting out potential triggers of inflammation like gluten and dairy, the Pegan diet might help to bring down long-term inflammation in the body. This is a key element in the build-up of many long-term health issues1.

The Pegan diet is naturally low in refined carbs and sugars, which can add to unwanted weight and unstable blood sugar levels1. By focusing on nutrient-rich whole foods, those who follow the diet may see that it supports healthy weight control and makes them feel fuller.
In my opinion, if you’re looking for a weight loss diet plan, you can consider a Pegan diet. You will consume an abundance of fruits and vegetables if you closely adhere to this diet. These foods are typically low in calories and high in fibre, vitamins, and minerals2.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Despite the possible benefits, a few worries regarding the Pegan diet should be noted, as follows:
Some of the rules set by the Pegan diet, mainly avoiding whole grains, beans, and dairy products, might not be needed for most people. Consuming them in moderation is recommended1. In fact, these food groups have well-recognized health benefits. Their full removal could lead to a lack of nutrients if we don’t swap them for something else1.
Following a Pegan diet as suggested, with a strong reliance on organic produce, grass-fed meats, and sustainably sourced seafood, could be quite costly and may not be doable for everyone2,10. Also, the ban on processed foods could make going out to eat and socializing tough, and cause confusion in the long run, regarding what to eat and what not to10.
Although the Pegan diet encourages choosing sustainably sourced animal products, it still promotes the eating of meat, but in moderate amounts. Critics argue that a more plant-centred approach, like a mostly vegetarian or vegan diet, would be eco-friendlier and more last longer.
To help you kick-start your Pegan diet, here is a sample meal plan for a week:
The Pegan diet is a cross between the Paleo and vegan diets. It offers a unique eating plan that puts the focus on whole foods, fresh fruits and vegetables, nuts, seeds, and mindfully sourced proteins. Its possible benefits include keeping long-term health problems away, backing gut health, lowering inflammation, and managing weight. However, the Pegan diet also comes with potential worries, including seemingly needless restrictions, possible nutrient deficiencies, and worries about ease of access and sustainability.
Ultimately, choosing to follow the Pegan diet depends on personal likes and life conditions, along with a thoughtful look at the pros and cons. It’s important to talk with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian before making big changes to your eating habits.
The Pegan diet may not be fit for everyone due to changing individual nutritional needs, likes, and budget constraints. Before starting any new diet, chat with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to see if it matches you.
Move to the Pegan diet slowly by gradually eating plant-based foods, healthy fats, and lean proteins while reducing the intake of grains, dairy, and beans. This lets your body adapt to the new eating pattern and helps you figure out how these changes affect your overall well-being.
Some people with certain health issues, such as diabetes or celiac disease, may find the Pegan diet useful as it stresses on low-sugar fruits and cuts out gluten. However, always chat with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian before making major changes to your diet, especially when handling a health issue.
To ensure you get all the needed nutrients while following the Pegan diet, aim to eat a range of nutrient-dense whole foods, plan your meals well, and watch your serving sizes. If you’re worried about certain nutrient deficiencies, chat with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to discuss if adding certain supplements might be good.
Eating out while following the Pegan diet could be hard but still doable with thoughtful planning and picking. Go for eateries that offer easy options and choose dishes that stick to the Pegan rules, such as plant-based salads with lean protein, grilled seafood or meat dishes filled with veggies, or simple stir-fries made with minimal oil and without processed elements.
No in-depth studies have looked at the health effects and possible benefits of the Pegan diet. Experts say more evidence is needed before they can determine its health value for you.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any change
Headaches are common during pregnancy. By knowing the types of headaches, their causes, the best ways to manage them, and when to ask for professional help, you can ensure your well-being and your baby’s health.
In this blog, we take a deep dive into the kinds of headaches that can happen during pregnancy. We will understand what causes these headaches and what triggers them. Also, we will learn about the most effective management options. We’ll also talk about the vital role played by your healthcare provider and how to reach out to them in need. So, let’s be prepared and make your pregnancy experience better.
Did you know?
Pregnant women may get headaches for many reasons. By understanding the cause of your headache, you can find a better way to deal with it. Some important causes of headaches are discussed below.
A change in hormone levels, during pregnancy, is a known cause of headaches1.
Changes in blood circulation due to the increased blood volume during pregnancy can also cause headaches1.
Dehydration is a common cause of headaches, not only during pregnancy but also in general. Be sure to drink lots of fluids to hydrate yourself well1,2. You should aim to drink at least 2 to 3 litres of water every day (modification based on the climate and your activity levels)3.
Bad sleep quality or sleeping on and off can lead to headaches. Make sure you have a set bedtime routine and get 7 to 9 hours of good sleep every night2.
Skipping meals or eating unhealthy food can result in low blood sugar. This low sugar level can cause headaches. Following a balanced diet plan and eating regular meals with healthy snacks in between may be helpful1,4.
Stress and anxiety can trigger headaches. Using relaxation methods like deep breathing, meditation, and prenatal yoga can help control stress levels during pregnancy2.
Cutting back on your caffeine intake because you are pregnant may lead to headaches due to withdrawal symptoms1. Less than 200 mg of caffeine (1-2 small cups) per day is usually considered safe but be sure to talk with your healthcare provider about having a safe level of caffeine during pregnancy1.
Pregnancy can worsen sinus congestion, which can further cause headaches. So, if you think your headaches are due to sinus issues, you should check with your healthcare provider to evaluate for sinus infection and prescribe suitable treatment options, e.g., nasal steroids like budesonide1,6.
The number and severity of headaches may change during different phases of pregnancy. Let’s see what commonly causes headaches during each trimester of pregnancy.
In the first trimester, your body goes through rapid changes. These changes make you more susceptible to headaches.
For some women, headaches may become rarer or less severe during the second and third trimesters. Despite this, certain factors may still lead to headaches during this period8,9.
It is important to consult with your healthcare provider before taking any medication or seeking medical help for headaches during pregnancy.
It helps to know what type of headache you have. This knowledge will guide you to find the right way to deal with it. Let’s discuss the three main types of headaches that can occur during pregnancy:

Tension headaches are quite common among expecting moms. They feel like dull, never-ending pain on your head or neck. It’s often like a tight band wrapped around your head1,10,19.

Compared to tension headaches, migraines are usually more severe and are often accompanied by additional symptoms. Individuals usually feel an intense throbbing pain on one side of their head12,13.

Cluster headaches are quite rare, particularly during pregnancy. The term “cluster” refers to them occurring in groups, or patterns. They are mainly marked by sharp, stabbing pain around the eye or one side of the head14.
It is recommended that you consult your healthcare provider if you are suffering from frequent headaches, particularly when you are pregnant. Your headache may also signal a more severe condition such as preeclampsia or high blood pressure, which can have severe consequences for both mother and the baby if not dealt with immediately.
Want to deal with frequent headaches during pregnancy? Well, there are a few things that might trigger the headache, such as chocolate, yoghurt, vintage cheese, peanuts, fresh yeast-baked bread, cured meats, and soured milk. By avoiding these typical triggers, one may also reduce the risk of getting a headache23.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
High blood pressure or hypertension can also show up during pregnancy and can be risky. If left unchecked, hypertension can cause serious problems15.
Your healthcare provider may suggest working with a diet expert to make a meal plan that is low in salt (sodium) and high in fib. Regular, moderate workout can also help lower your blood pressure.
In some cases, your healthcare provider may prescribe medication to control your blood pressure. Always check with your healthcare provider before starting any new medicines during pregnancy15.
Hypertensive headaches can indicate complications like preeclampsia (serious condition associated with high blood pressure) or eclampsia (seizures due to high blood pressure). If not managed properly, hypertension can cause serious problems such as stroke, low oxygen to the baby, preterm delivery, low birth weight or placental detachment. You must get swift medical care to avoid risks to lives of the mother and baby15.
If you’re pregnant, paracetamol is the first pain reliever you should choose for headaches. If you must take paracetamol during pregnancy, do it only when it is absolutely essential. Your chemist, midwife or general practitioner will give you guidance on the dosage and the time period of the medicine22.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
When having headaches during pregnancy, it’s key to find alternatives that are safe. These should also work well and not put the mother and her baby at risk15.
While it’s best to avoid medicines during pregnancy, acetaminophen (Tylenol) is usually thought to be least damaging for occasional use. Always talk with your healthcare provider before taking any medicine during pregnancy to make sure it is safe for you and your baby.
You can lessen the need for medicines during pregnancy by using home remedies to ease headache pain. Doing this may lower the risk of harming your unborn baby. Here are some helpful home remedies16,17,18:

Keep hydrated to prevent headaches caused by dehydration. Plan to drink at least 2-3 litres of water every day1,2,16.

A balanced diet gives all the vital nutrients to support your body and your baby’s growth. Don’t skip meals and stick to a regular eating routine. If certain foods trigger your headaches, don’t eat them during pregnancy17,19.

Massage your head, neck and shoulders to relieve muscle tension and ease headache pain. Deep breathing workouts, meditation and prenatal yoga can also help you manage stress and promote relaxation16,18.

Make sure you get enough sleep by inculcating good sleep habits and aiming for seven to nine hours of sleep each night. Take short naps during the day to ease headaches even more16,19.

Putting a cold or warm press on your head or neck may give relief from headache. You can try out both cold and warm presses and decide which one is better for you16.

Light workouts like walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga can relieve tension and lead to better circulation and level hormone amounts. Doing a workout on a regular basis also helps you keep a healthy weight during pregnancy18.
Every pregnant woman has a unique journey. If you are having a difficult pregnancy, it’s advisable that you consult your doctor before initiating any home remedy for your headaches as some of these may not be suitable for you based on your particular condition.
A majority of headaches during pregnancy are not serious. You may be able to manage them with the right home remedies and medicine when needed. However, there are exceptions:
If you have a severe headache that occurs along with blurry vision, swelling, pain in the belly, or quick weight gain, get in touch with your healthcare provider right away. These symptoms can indicate preeclampsia or another risky condition.
A sudden, severe headache, sometimes called a “thunderclap” headache, could mark a more serious health issue. For example, it could be a burst aneurysm or reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Get medical care right away if you have this type of headache20.
Vision changes mixed with a headache may be a sign of a migraine. Symptoms like blood pressure higher than 140/90, sudden oedema, epigastric pain, visual disturbances and reduced urine output can be a sign of a more serious condition like preeclampsia21. Call your healthcare provider if you have a headache along with blurred vision, seeing spots, or any other vision problems20.
If you have a headache that keeps going despite trying home remedies and taking the right medicine, reach out to your healthcare provider. Constant headaches may show an underlying issue. You may need more checks and the right treatment20.
You can lessen the chance of getting headaches during pregnancy by doing these things:
Develop a habit of doing regular workouts, eating balanced meals and hydrating yourself well. Set up a routine sleep time-table for enough rest. Manage stress by using relaxation techniques. These could include deep breathing, meditation, or prenatal yoga18,19.
Find and avoid specific foods, activities or situations that may bring on headaches during pregnancy. Keeping a record of your headaches to find likely triggers and patterns can help19.
Attend all prenatal visits regularly. Share all your worries with your healthcare provider, even about headaches. They can give you personalized tips depending on your situation and needs.
Also Read: Home Remedies For Vaginal Itching
Understanding the types of headaches caused during pregnancy and their potential triggers, measures to tackle them and the necessity of professional help is vital. With the correct precautions and by following your healthcare provider’s advice, you can lessen discomfort and make sure you are okay during pregnancy.
Remember, it matters to know the triggers, relievers and when to ask for help. Be upfront and be in control of your welfare and the well-being of your unborn child.
Also Read: Best Guide to Breast Pumping For New Mothers
If the headache is intense, sudden and severe, bundled with other symptoms, or continues without getting better despite home remedies, then you should get in touch with your healthcare provider right away.
To ease headache pain during pregnancy, you could use a cold or warm compress, light massage, relaxation methods, drink enough fluids, or have a regular sleep schedule. After talking with your healthcare provider, you may also take low doses of acetaminophen (Tylenol) for relief.
While headaches happen often during pregnancy, having them daily is not the norm. If you have headaches every day, get in touch with your healthcare provider to find the causes and for the right treatment plan.
Headaches can come up at any part of pregnancy. But, some women may have fewer or less serious headaches in their second trimester. This happens because the body gets used to certain hormonal changes by then.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Ever think about using light for healing? That’s what red light therapy does. It helps fix many health and beauty issues. Medical and beauty fields are taking notice of this new treatment. It helps with skin problems, heals wounds, eases physical pain, and more.
In this blog, we’ll look at what red light therapy is, its past, how it works, and what its main uses are.
Did you know?
Red light therapy started with a Hungarian doctor named Endre Mester back in the 1960s. He found that laser light helped the healing of wounds on rats and boosted their hair growth. After that, people started using light therapy more often2. Now, red light therapy devices are common in hospitals, doctor’s offices, and wellness centers.
You may ask, how can light heal? The answer lies in red light therapy’s power. It goes deep into the tissues. The cells inside absorb and use the light energy for healing.
Low-level red light touches the mitochondria in your cells. These mitochondria make a key molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). More ATP means more cell energy and better cell work plus revival. This improved action speeds up tissue repair and healing1.
Here’s a brief summary of how red light therapy works:
There are various types of red light used in therapy. The two main ones are visible red light and near-infrared light. The first has wavelengths between 620 and 750 nm. The second has longer wavelengths, between 750 and 1,200 nm. The type of light used depends on the depth of treatment required visible red light therapy is used for mild penetration and near-infrared light is used for deeper penetration3.
LED devices are often used to give red light therapy. They are safer than traditional lasers.
I strongly recommend that if you decide to buy a red light therapy device, be sure to cover your eyes, adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions, and take proper care of the equipment4.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
More people are getting interested in red light therapy. Researchers are studying its uses for many health and beauty issues. Let’s dig into these studies.

Red light therapy is getting noticed for its ability to improve skin health. Here’s what it can do:
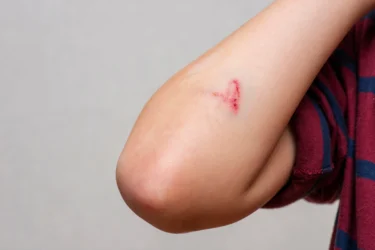
RLT can stimulate cell healing and revival, thus aiding in wound recovery. It does this by reducing inflammation, enhancing tissue regrowth and fostering new blood vessel formation5.

Another use of RLT is to help hair growth. Studies6 show that red light can touch hair follicles to address hair loss. It isn’t entirely clear how this happens yet. It might be about upping blood flow, collagen growth, or reducing inflammation.

Many people seek red light therapy for pain relief. RLT’s ability to stimulate cell repair and reduce inflammation may help eliminate discomfort from sports injuries, chronic diseases like arthritis and other long-term pain. Plus, RLT may be promising in helping bone recovery after injury7.

Bright light therapy has strong anti-inflammatory power. It could prove beneficial in managing inflammation and arthritis symptoms, such as pain, stiffness and swelling8.

Dental experts use red light therapy to relieve pain and inflammation from temporomandibular dysfunction, manage gum disease and to help tacklemouth sores9.

RLT could help address painful side effects from certain cancer cures. It can help with mouth or throat swelling and inflammation often seen in people receiving radiation for head and neck cancers.

Sun damage can hurt the skin’s looks and health. But RLT might be able to help. By speeding up skin repair and collagen production, RLT could be helpful in managing sun-damaged skin and lessen the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles10.
In my opinion, at least when used briefly and as instructed, the red light therapy (RLT) seems to be risk-free and has no known negative effects. In comparison to various topical skin healing, this therapy is less harsh, non-invasive, and harmful4.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Though generally safe and painless using RLT wrongly could have side effects. If you use it wrong or too much, you could potentially damage your skin or eyes, or cause lesions or burns.
For red light therapy at home, always follow the maker’s instructions. It’s even better if a healthcare provider can help. Also, remember that while RLT looks promising, more studies are needed to know it will always work and is safe long term.
Also Read: Squalane: What Is It, Uses, Benefits, Side Effects, & More
If red light therapy isn’t right for you, or you need more help, consider other methods. Acupuncture, anti-inflammatory diets, cognitive behavioral therapy, or other light therapies like blue light for acne could work under the consultation of a qualified healthcare professional11.
Ask your healthcare provider about the best mix of methods for your unique health needs.
Here’s an overview of potential alternatives:
You can get professional red light therapy in many places. Hospitals, doctor’s offices, wellness centers, spas and tanning salons often have it. Before you start RLT, talk to a doctor about treatment choices, how often to go, and expected benefits. They can show you the most reputable places for red light therapy.
Red light therapy is a remarkable and promising tool to help heal, lessen inflammation and help managemany beauty and health issues. While research continues to dig into its potential benefits and risks, it’s important to talk with a healthcare provider who knows about red light therapy. That way, you’ll use it safely and effectively.
Red light therapy isn’t a miracle cure, but with its many uses and little invasiveness, it’s a good choice for anyone looking for new treatments or adding to their current health routines.
How often you need red light therapy changes based on the issue being treated and how well you respond. Often, you should get treatments once a week for a month. After that, you might go for follow-ups based on what your healthcare provider advises.
Many doctors say red light therapy has potential benefits. Yet they want more research to know more about how it works and if it is safe for long term use. Your healthcare provider can best tell you if RLT is right for your special needs and guide you to trusted places for treatment.
You may lie in a full-body LED red light bed or pod or be treated by a professional with a device that’s outfitted with panels of red lights. During treatment, you will lie in the bed for a designated amount of time or a practitioner will “apply” the light device to a specific body part.
Yes, you can get FDA-cleared red light therapy devices for use at home. However, always ask your healthcare provider before starting any at-home RLT program to make sure you use it right and avoid potential risks.
Generally, red light therapy is safe for most. Yet, certain individuals like those with sensitive skin, diabetes, or who are pregnant, should talk to their healthcare provider before getting RLT. They can tell if the treatment is good for them.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Native to New Zealand, Manuka honey stands out for its multiple health benefits. It’s a natural remedy that works wonders for our health. From promoting oral and gut health to helping deal with coughs, stomach ulcers, and skin troubles, it can do all! Ready to uncover the facts about this honey? Let’s start!
We’re also going to guide you on how to pick top-notch Manuka honey, its proper dose, and any safety concerns that may arise. By the end of this blog, you’ll be fully equipped to decide if Manuka honey is just what your health routine needs.
Did you know?
Manuka honey beats regular honey in so many ways. Made by bees who feast on the Manuka bush found in New Zealand and Australia, Manuka honey has powerful health perks. These come straight from the unique traits of the Manuka bush only found in these regions1.
It has a stronger germ-fighting ability and a better nutritional balance as it contains some special compounds. For instance, regular honey gets its bacteria-fighting power from hydrogen peroxide. However, for Manuka honey, a compound called methylglyoxal (MGO), which is a stronger antimicrobial, does this work. Manuka honey also packs bioactive compounds like flavonoids and polyphenols. These commando compounds play a big role in its strong antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and germ-killing abilities2.
Plus, Manuka honey is rich in vitamins, minerals, and amino acids, far better than regular honey. More than that, it contains leptosperin. This compound, from the nectar of Manuka bushes, is a sure sign of pure Manuka honey2.
This is a grading system you should know about. Here, Manuka honey’s germ-killing strength is rated based on its MGO, DHA (a type of fatty acid) and Leptosperin levels. The higher the UMF, the stronger its bacteria-blasting power. That means you have top-quality Manuka honey in your hands2!

Manuka honey helps in managing wounds, cuts, burns, and even bed sores. It works by keeping the injured area moist and safe from germs. It can even take down tough ones that resist antibiotics, like MRSA. Clinical trials show that this honey, when used topically, may help wounds heal faster3. It may be helpful for the growth of new tissues, may lessen pain in burn patients and even may help fight diabetic ulcers.
I recently found an article that suggests that the antioxidant and antibacterial properties of manuka honey are important in the healing of wounds. It’s also important to note that manuka honey has a pH that is lower than other honey, which may aid in promoting the best possible wound healing13.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
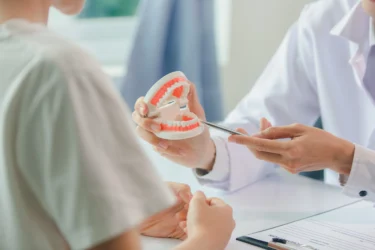
Manuka honey can keep your teeth and gums healthy. It can help avoid dental plaque formation by means of its anti-microbial action and can stop bad mouth bacteria in their tracks. Less plaque means fewer cavities and gum diseases.
According to one study, sucking on a chew of manuka honey might be more efficient at reducing plaque and gingival bleeding. I strongly recommend the consumption of manuka honey13.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS

Manuka honey can help you find relief from cough and sore throat due to an upper respiratory tract infection. Thanks to its soothing coat for the throat, Manuka honey can lessen the pain of a sore throat. Clinical studies suggest that honey, including Manuka kind, may be helpful to tone down cough symptoms even better than over-the-counter cough suppressants4.

Studies hint that Manuka honey may be helpful to shield against stomach ulcers by curbing inflammation and supporting healing in your stomach lining. Animal and lab studies validate that Manuka honey may be useful in managing stomach ulcers5. However, to seal the deal, more human studies are needed.

Manuka honey can boost gut health and ease digestive woes like belly pain and diarrhea. As a prebiotic, Manuka honey encourages the growth of helpful gut microbes such as bifido bacteria and lactobacilli. Lab studies show that it may hold some promise for people with bowel disease. They reveal that Manuka honey may be able to fight harmful gut bacteria causing severe diarrhea and bowel swelling, like Clostridioides difficile6.
Manuka honey might possibly be beneficial for cystic fibrosis patients. It helps deal with cystic fibrosis-related infections Studies show Manuka honey used with antibiotics can be helpful to manage infections resistant to standard treatments such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Mycobacterium abscessus, which are common in cystic fibrosis7,8.
If you’re looking to try out Manuka honey, you must pick a top-quality one for best health benefits. Moreover, proper storage and correct dosage are essential to reap all its perks. We’ve got some tips to share on this.
The usual serving of Manuka honey is 1-2 teaspoons (5-10 grams) per day. But always remember, while this honey offers health benefits, it is high in sugar. So, moderation is key!
Manuka honey is usually safe. But do check with your doctor if you have diabetes, honey or bee allergies, or any health concerns. If you’re a diabetic, allergic to honey or have developed allergies to honeybee stings in the past, or have infants under one year, Manuka honey may not be suitable for you. It could hike up your blood sugar levels or cause botulism trouble for babies11,12. Its high sugar content could also upset your gut. Also, pregnant and breastfeeding ladies must always consult their healthcare provider before using any natural remedy, including Manuka honey.
Also Read: 15 Amazing Benefits of Poppy Seeds (Khus Khus)
Manuka honey is a great natural remedy packed with a diverse range of health benefits. Its potent antibacterial qualities come in handy with its potential in the management of wounds. Not just that, it may offer relief in oral health troubles and some potential benefits in the relief of symptoms of upper respiratory infections as well. Besides that, it may be beneficial in bolstering gut health, it may be helpful in aiding tackling of gastric ulcers, and is a boon for people suffering from cystic fibrosis. But, when you’re buying Manuka honey, opt for a top-quality product with UMF rating. Take it in measured amounts and do check with your doctor about how to use it. Keeping these pointers in mind, you just might find that Manuka honey is a great addition to your health routine.
Set apart by its super antibacterial properties and rich nutrition, Manuka honey offers a host of health benefits. This makes it unlike your everyday honey.
Bees who feed on the Manuka bush produce this honey. Unlike regular honey, Manuka honey has an added compound called MGO. Due to this compound, it has a stronger antibacterial shield.
Yes, you can generally consume 1-2 teaspoons (5-10 grams) of Manuka honey daily. But remember, Manuka honey contains high sugar. So too much of it could spike your blood sugar levels or disturb your gut. It’s best to discuss with your healthcare provider about the right dosage based on your needs.
It’s because of its unique source and manufacturing in Australia and New Zealand. Its mighty antibacterial features and high nutrient worth also bump up its price. So, when you are buying Manuka honey, remember, you’re investing in a health-booster packed with numerous benefits.
Manuka honey isn’t a cure-all strategy, but it can be used alongside other kinds of conventional treatments, medical opinion might be needed for appropriate treatment as it is not a substitute for medical or surgical treatments.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Did you know that some foods can mess with your medicines? This can happen even with everyday foods like grapefruit or coffee. It is important to avoid such food-drug interactions to prevent any adverse events and maintain the effectiveness of the medicine1.
In this article, we’ll discuss about the food interactions which can occur with the drug, metformin. Metformin is a common medicine prescribed for the management of Type 2 Diabetes. We’ll talk about Metformin’s intricate relationship with foods, when to take it, and more2.
Did you know?
Metformin is a drug that helps bring down your blood sugar levels. It is mainly used to manage Type 2 diabetes3.
Metformin is available in different doses and forms. These include tablets, oral solutions, and even extended-release tablets. Your doctor will prescribe the right form and dosage based on your health condition and lifestyle.
Mostly, Metformin is stored at room temperature. It should be placed away from moisture or heat. Also, keep it out of reach of children.
Metformin mainly works by reducing glucose production by the liver. By doing so, it helps lower overall blood sugar levels. It also improves the body’s response to insulin and helps cells use insulin better, making it easier for them to take in glucose from the blood4,5. If you have type 2 diabetes, your healthcare provider may prescribe Metformin.
Certain food items and alcohol can affect Metformin’s effects6,7. We will discuss this in detail in the coming sections.
In my experience, I have observed that use of metformin might lead to vitamin B12 deficiency. It is important to be aware of the potential risk and consider regular monitoring of your vitamin B12 levels, as well as discussing the need for supplementation with your healthcare provider13.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, BAMS, MD (Ayu)
Food choices play a big role in managing type 2 diabetes. While they don’t directly counteract Metformin’s actions, overeating or bad food choices can increase its efforts to control blood sugar.

Certain foods can get in the way of Metformin. These are processed carbohydrates, saturated fats, trans fats, and too much sodium. While not opposing Metformin directly, they can spike up your glucose and insulin levels.
Detailed list of Foods to Avoid
Saturated fats can also make you more insulin resistant, which can make weight loss and blood sugar management more difficult. Fatty foods can delay gastric emptying and contribute to, prolonged postprandial hyperglycaemia (high blood sugar levels after food), which can be problematic over the long term. Sodium does not directly affect blood glucose or Metformin, but it increases cardiovascular risk and blood pressure, which are comorbid concerns in diabetes8. Also, some studies6 have found that a high-fat, high-calorie diet can slow the absorption of metformin.
So, although these foods don’t directly interfere with Metformin’s pharmacologic action, they can oppose its intended effect by raising blood glucose levels, adding to Metformin’s workload.

Some foods can make it hard for Metformin to work. Yet, some others support Metformin’s actions. These are complex carbohydrates, healthy fats, fibre, lean proteins, and select fruits and vegetables9.
Detailed List of Beneficial Foods
Consuming these foods along with Metformin can support your blood sugar balance. Plus, it can help keep your weight in check. But please note that not all fruits are low glycaemic. Portion control and glycaemic index should be considered especially if you are diabetic. Your doctor can guide you best on what type of foods you can eat based on your blood sugar control.
Based on my experience, I have found that metformin typically does not cause low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia) when taken alone. However, it is important to be cautious when combining metformin with other diabetes medications like insulin or gliclazide, as these combinations may increase the risk of hypoglycaemia13.
Dr Rajeev Singh,BAMS
Food choices matter a lot in diabetes, especially if they interact with drugs like Metformin. Here are some specific food items that can affect metformin.
Grapefruits are beneficial but found to interact with many drugs including Metformin. An old study on non-diabetic rats showed grapefruit juice might trigger a potentially fatal condition called lactic acidosis when mixed with Metformin10. Lactic acidosis is a rare but serious side effect of metformin, typically in patients with renal impairment or other risk factors.
Grapefruit inhibits CYP3A4 enzymes, affecting drugs metabolized by this pathway (e.g., statins, calcium channel blockers). However, Metformin is not significantly metabolised by CYP enzymes, including CYP3A4. So, this seems to be an overemphasised claim. Yet, we don’t have any human case studies indicating a similar reaction with Metformin and grapefruit so far. More research is needed here.
Alcohol consumption may also interact with Metformin’s action. Taking alcohol and Metformin together may cause lactic acidosis, a rare but serious condition7. Still, this could happen only if you drink alcohol heavily and regularly. It can also swing your blood glucose levels both ways – high (hyperglycaemia) and low (hypoglycaemia). Moderate drinking usually isn’t problematic unless you have kidney or liver issues. (Note that moderation as per guidelines is termed as no more than one drink per day, for women, and for men, a moderate amount is no more than two drinks per day.)
Drinking alcohol regularly can also exacerbate kidney and liver issues, so talk with your doctor if you suffer from non-alcoholic liver disease or kidney disease before consuming alcohol with Metformin.
Wondering how to take metformin the right way? Let’s see how and when to take Metformin for best results.
When taking Metformin, timing is important for minimizing side effects (like GI upset) and optimizing blood glucose control. Normally, immediate-release tabs are taken twice a day while extended-release tabs are taken once daily. Keeping to this schedule helps manage diabetes effectively.
Taking Metformin with meals can cut down its side effects like gas, bloating, nausea, and diarrhoea. Extended-release Metformin is usually taken with the evening meal to reduce gastrointestinal side effects and enhance overnight control.
Metformin, a widely prescribed medication for managing Type 2 diabetes, offers significant benefits, but users should be aware of potential side effects. Commonly reported metformin side effects include gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, diarrhoea, and abdominal discomfort, although these often subside with continued use.
Continued use often leads to a gradual diminishment of these symptoms.
Metformin Side Effects in Females:
Metformin Side Effects in Males:
If your health changes or you spot signs like muscle pain, feeling tired, abdominal complaints, uneven heartbeats, or problems in breathing, get immediate medical help. These could be early signs of lactic acidosis. It’s a serious but rare side effect of Metformin.
Also Read: Pantoprazole Foods to Avoid
When taking metformin for PCOS, it’s advisable to be mindful of certain foods. Limiting high-carbohydrate and sugary foods can enhance its effectiveness. Avoid excessive alcohol consumption and consider reducing intake of processed foods. Incorporating a balanced diet with whole grains, fruits, and vegetables is beneficial. Consulting with a healthcare professional for personalized dietary recommendations is essential for optimal PCOS management with metformin.
Another interesting aspect of Metformin is its effect on body weight. Over time, people using Metformin have reported a slight weight loss. But remember, this isn’t guaranteed for all users.
Researchers have noticed a link between Metformin and weight loss, which might be due to reduced hunger cues12. However, metformin’s weight loss effect is thought to be multifactorial, including improved insulin sensitivity, decreased hepatic glucose production, possible mild appetite suppression, and effects on gut hormones like GLP-1. But keep in mind, weight management isn’t only about medicine. It’s also about eating healthy and exercising regularly.
Also Read: Foods to Avoid While Taking Duloxetine
Long-term weight loss linked with Metformin varies from person to person and may not be as much as you’d want. An average drop of around six pounds after a year of treatment is seen. To kickstart and keep up the weight loss, diet tweaks and exercise are crucial elements as well.
Simply put, no. Metformin is specially made for patients with Type 2 diabetes. Though it has shown results in helping non-diabetic obese patients lose weight, this is an ‘off-label’ use and not approved by the FDA for non-diabetics. However, metformin is sometimes used off-label in PCOS and prediabetes with some evidence of benefit.
Also Read: What To Eat During Food Poisoning?
Dealing with food-drug interactions can be hard. However, understanding your body’s specific reactions can help keep good health and make your medication work best.
In short, matching wise food habits with Metformin can boost its effects in controlling Type 2 diabetes while making the wrong choices can increase its workload. Often, it’s about learning the potential interactions and making small food swaps in our daily meals. If you have diabetes, it’s best to discuss with your doctor and design the best diet plan that is suitable for your condition and does not impact your medications.
Moreover, simple things like watching your salt intake, staying hydrated, and exercising regularly can have a beneficial impact on your overall health. Remember, tiny tweaks in your diet and lifestyle can yield big health gains over time!
Also Read: 12 Foods That Are Necessary For A Healthy Liver!
As of now, there’s not enough proof to say coffee messes up Metformin. But remember, too much of caffeinated drinks might cause hydration issues. So, drink moderately.
Metformin may cause nausea, and if you also take insulin, Metformin can cause low blood sugar levels. This can be dangerous if you’re unable to keep liquids down, so call your doctor immediately if this is the case and you’re having trouble treating low blood sugars.
There are no adequate studies in women for determining infant risk when using this medication during breastfeeding. However, studies have shown that Metformin passes into breast milk in very low amounts but is generally considered compatible with breastfeeding. The American Academy of Paediatrics (AAP) and other authorities regard Metformin as usually safe during lactation. However, consult a doctor who will weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks before prescribing this medication while breastfeeding.
You may notice improvement in your blood glucose control in 1 to 2 weeks, but the full effect of blood glucose control may take up to 2 to 3 months. Ask your doctor if you have any questions about this.
Health pros suggest a low-carb, high-protein breakfast might work well with Metformin. Think eggs, lean meats, whole grains, and fresh fruits. It gives you main nutrients, lowers glycaemic spikes, and keeps you full till lunchtime.
Metformin-induced diarrhoea is thought to result from its impact on the gastrointestinal tract, causing increased fluid secretion and alterations in gut motility. Metformin increases intestinal glucose and bile acid concentrations, which can cause osmotic effects leading to increased fluid retention in the bowel. It may also alter gut microbiota and serotonin pathways affecting motility. Consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended for those experiencing persistent or severe diarrhoea while using metformin.
Metformin typically does not cause hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar) when used as a monotherapy. However, in combination with other diabetes medications that can lower blood sugar, there may be a higher risk of hypoglycaemia. It’s essential to follow healthcare provider guidance and monitor blood sugar levels regularly.
Metformin is occasionally prescribed during pregnancy for gestational diabetes but should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Individual health considerations and potential risks to the mother and foetus need to be carefully evaluated before making any decisions about medication during pregnancy.
While metformin is generally considered safe for the kidneys, there’s a rare risk of lactic acidosis, a serious condition. It’s crucial for individuals with kidney issues to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriateness of metformin and to monitor kidney function regularly.
Yes, metformin is known to reduce insulin resistance, a key factor in type 2 diabetes. It improves insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to better respond to insulin and promoting better regulation of blood sugar levels.
No, metformin is not habit-forming. It is an oral medication commonly prescribed to manage type 2 diabetes and does not possess addictive properties. Always follow your healthcare professional’s guidance on medication use.
Metformin for prediabetes can be effective in slowing or preventing the progression from prediabetes to diabetes. However, individual responses vary, and it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on its use and to incorporate lifestyle changes for comprehensive prediabetes management.
Stopping metformin suddenly can mess with your blood sugar. Always talk to your doctor before making any changes to your medication, so they can help you do it the right way.
Metformin is generally considered safe for the liver, but in rare cases, it may cause an increase in liver enzymes. Regular monitoring and consultation with a healthcare professional are recommended to ensure the medication’s safety and address any potential concerns.
Signs that metformin is working include stable blood sugar levels, better insulin sensitivity, and reduced symptoms related to the medical condition. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional help track and confirm its effectiveness for each individual.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Ever found yourself confused at the grocery store, not sure if you should go for brown or white eggs? No need to feel alone, most people are in the same boat. Some folks think that one kind of egg might be a better pick health-wise or flavour-wise over the other. This article aims to wipe away such confusion by breaking down the facts about brown and white eggs. We will delve into what affects the colour of an eggshell, compare the nutritional values of brown and white eggs, and talk about how they influence taste, cooking and cost. In the end, you will be able to make a wise choice when buying eggs and know what truly sets brown eggs apart from white ones.
Many people believe that the colour of an egg determines its health benefits or nutrients. But the colour of an egg, whether white, brown or even blue, is determined by the chicken breed and its genes. The primary pigment in brown eggshells is something called protoporphyrin IX, and blue eggshells get their colour primarily from the pigment biliverdin1,2. While factors like the chicken’s feed or environment might bring in shade variations, they don’t change the eggshell’s main colour.
Did you know?
Several myths about egg colour have been circulating for quite some time, and it is time to bring the truth to light:
After debunking these myths, let’s look at how brown and white eggs stack up nutritionally.
It is important to note that brown and white eggs have about the same nutritional value5. The only difference lies in the eggshell colour, which is determined by the chicken breed and genes.
Both brown and white eggs are rich in high-quality protein and healthy fats and have trace amounts of carbs with no significant differences in macronutrient profiles6. Regardless of the egg size, grade, and colour, they will provide all the vital nutrients your body needs.
Eggs, both brown and white, are loaded with essential vitamins and minerals, such as vitamins D, B12, A, and E, as well as iron, calcium, and phosphorus6. These nutrients support various functions like boosting immunity, improving brain function, and strengthening the bones6.
Cholesterol is crucial for our cells and helps provide vital hormones. Studies have shown that dietary cholesterol doesn’t affect blood cholesterol levels for most people6. Since both brown and white eggs have similar cholesterol levels7, whether you eat brown eggs or white, the chances of them hurting your heart’s health are low.
As seen earlier, there is no major nutritional difference between brown and white eggs. But does the colour of the eggshell matter when it comes to taste and cooking?
Whether an egg is tasty or not is not determined by its outer shell. It depends on factors like the hen’s diet, the environment it was raised in, and how fresh the egg is4. Therefore, brown, and white eggs do not have any inherent taste differences.
You can use white or brown eggs interchangeably in almost all recipes without noticing any changes in flavour, texture, or appearance. Please note that minor differences may be noticed during cooking based on egg freshness and size.
Baking with brown or white eggs gives the same results. Just make sure to use eggs of the same size as mentioned in the recipe, regardless of shell colour, and you should be fine.
Whether your eggs are scrambled, fried, or hard-boiled, you will not taste or feel any difference based on egg colour. You can switch between brown and white eggs when making these dishes without altering the final outcome.
From my observations, it appears that both white and brown eggs, regardless of their shell colour, may offer a consistent nutritional profile. Each egg, whether white or brown, may offer a substantial 6 grams of protein while containing only around 70 calories!
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Studies suggest that chicken breeds, eggshell pigments, and a chicken’s living conditions and diet determine the egg colour. Let us see how these factors affect egg colour.
Different chicken breeds lay different coloured eggs. For instance, White Leghorn chickens lay white-shelled eggs, while chickens like Plymouth Rocks and Rhode Island Reds lay brown-shelled eggs8.
The chicken produces pigments that colour the eggshell. For instance, brown eggshells get their colour from protoporphyrin IX, while blue eggshells owe their colour to biliverdin2. Both pigments come from compounds known as porphyrins that form when heme (found in red blood cells) breaks down9.
The chicken’s diet, environment, and stress level can slightly alter the eggshell colour1. However, these factors cannot fundamentally change the colour of the eggshell.
Eggshells can have various other colours, like blue, green, and even pink2,5! Different chicken breeds, e.g., Araucana, Lushi, and Dongxiang, produce these uniquely coloured eggs2. The porphyrins, the same compounds that give colour to brown and blue eggshells, are responsible for these colour variations.
Based on my years of experience, I’ve come to believe that when it comes to nutritional value, both brown and white eggs might offer similar benefits. Notably, both types of eggs contain a significant amount of choline per 100g, potentially surpassing many other common food options. So, including brown or white eggs in your diet might be a simple and effective way to enhance your choline intake11.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Have you ever noticed that brown eggs are usually more expensive than white eggs at the grocery store? Let us dissect the reasons behind this price difference.
As we mentioned earlier, brown eggs usually cost more because the hens that lay them eat more because of their larger size. This increased cost of feed gets passed onto consumers through higher prices for brown eggs.
Additionally, consumer perception influences pricing. As brown eggs gain popularity, producers may raise their prices, taking advantage of the common belief that brown eggs are healthier or tastier than white ones, even though no scientific evidence supports these ideas. Even customers are ready to pay premium prices for brown-coloured eggs10.
Brown egg–laying hens might have slightly higher breeding, rearing, and feeding costs because of their larger size. Even so, these costs are not dramatically different and probably do not entirely explain the price disparity we see in supermarkets.
Brown eggs have become more popular recently; therefore, the demand for brown eggs has shot up, leading to potential price adjustments by producers. Increased consumer preference for brown eggs affects their pricing, despite no clear-cut differences in taste or nutritional value between white and brown eggs.
I may emphasize that if you have any heart-related condition or high cholesterol levels, it is important to be cautious about consuming brown or white eggs. In such cases, it may be advisable to limit your intake to three to four whole brown or white eggs per week. This precautionary approach might help manage the potential risk of adverse effects on your cardiovascular health12.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
So, how do we decide which eggs to buy since brown and white eggs are equally nutritious and differ only in appearance?
When shopping for eggs, it is best to look beyond the colour. Think about other factors that truly affect the taste and nutritional value of the eggs, which include:
These factors can have a significant effect on the quality and taste of the eggs you eat. They are more relevant to your health than the colour of the eggshell.
Based on the multifactorial comparison between brown and white eggs, there is no significant difference between the two in nutrition, taste, or even cooking. The main thing that sets them apart is eggshell colour, determined by the breed and genetic makeup of the laying hen. Factors like the hen’s diet and living conditions play a much bigger role in the egg’s nutrition profile and taste.
To make the best choice when buying eggs, focus on aspects that really influence egg quality and taste, such as organic farming techniques, whether the hens are cage-free or free-range, and if the eggs are omega-3-enriched. This approach will ensure that you not only consider the eggshell colour but also the aspects that really matter.
There may be minor shell thickness variation within the same breed due to factors like chicken genes or age. However, the colour of the eggshell doesn’t determine shell thickness.
Usually, chickens with white earlobes lay white eggs, and those with red earlobes lay brown eggs. However, there are exceptions, and earlobe colour isn’t a foolproof way to predict what colour eggs a chicken will lay.
Brown and white eggs have similar environmental footprints. The production method (organic, cage-free, free-range, etc.), rather than the colour, influences the environmental impact of eggs.
A single chicken can’t lay both brown and white eggs. But, you can have a mixed flock of chickens that lays both brown and white eggs. The chicken breed and genetics determine the colour of the eggs they lay.
No, the colour of the eggshell doesn’t influence the yolk colour. The chicken’s diet plays a major role in determining the yolk colour. For instance, a diet loaded with carotenoids (found in leafy greens and some yellow and orange fruits and vegetables) can make the yolk deep orange.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability, or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation of the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Do you wonder what duloxetine is? Duloxetine belongs to the serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) class of drugs and is used in the management of mental health conditions like major depressive disorder (MDD) and generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) and other conditions like diabetic neuropathy1, fibromyalgia2, and chronic musculoskeletal pain. For individuals on duloxetine, it is vital to know about food and drug interactions of the medication and its side effects as these factors may influence the effectiveness of the medicine3.
Before exploring which foods and substances to avoid when on duloxetine, let’s first understand how the medicine works and its interactions with other drugs, supplements and herbal products along with other considerations. Each person responds differently to a medicine, so you should consult your doctor before making any major changes to your medicine.
Duloxetine works by increasing the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain. These are important chemicals that affect mood and pain sensations. Duloxetine does not let these chemicals be reabsorbed, allowing them to stay active in the spaces between nerve cells.
This action helps improve communication between nerve cells, influencing mood positively and reducing the perception of pain signals. Essentially, duloxetine’s role is to enhance the effects of serotonin and norepinephrine, making it effective in treating conditions like major depressive disorder, generalised anxiety disorder, and certain types of chronic pain. Individual responses to the drug may vary; therefore, it’s essential for individuals to consult their doctor for personalised information and guidance regarding duloxetine uses.
Did you know?
If you’re on duloxetine, some foods and drinks are best avoided. Here’s some foods you should watch out for.

It is safer to avoid alcohol if you are on duloxetine as the combination may increase some side effects of the drug and may lead to potentially harmful interactions. Both alcohol and duloxetine can cause CNS depression, potentially leading to excessive sedation. Alcohol may also interfere with duloxetine’s ability to improve mood, reducing its therapeutic benefit. Additionally, since both are metabolised in the liver, using them together increases the risk of liver toxicity4.
Taking alcohol with duloxetine could cause:
Both the manufacturer (FDA label) and doctors strongly recommend limiting or avoiding alcohol, particularly if you have a history of liver disease or depression. Always check with your doctor before consuming alcohol during duloxetine treatment4.
I want to emphasise that when prescribed to take duloxetine, it is important to especially avoid drinking alcohol as it may potentially increase the risk of liver damage. Prioritising your health and adhering to your doctor’s recommendations will ensure the safest and most beneficial use of this medication.

Keep an eye on your caffeine intake while taking duloxetine. Although caffeine doesn’t directly interfere with how the medicine works, it may worsen certain side effects, such as jitteriness, anxiety, or trouble sleeping, especially if you’re sensitive to stimulants. In some cases, too much caffeine may reduce duloxetine’s calming benefits by increasing restlessness or anxious feelings5.
To manage your caffeine intake:

Although duloxetine is not a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), some people worry about its interaction with high-tyramine foods. However, current research has not shown any significant risk, and duloxetine does not inhibit the MAO enzyme. That said, if you want to be cautious, it’s you may limit foods high in tyramine, such as:
If you are curious to know the drugs that may not work well with duloxetine, let’s find out. Always inform your doctor about all the medicines, supplements, or herbal products you currently take or are planning to take, to help avoid any possible interactions.
Taking duloxetine with other medicines for mental health issues may increase side effects or cause complications.
Some examples of such medicines include:
How to manage drug interactions?
Here are a few simple precautions to help manage drug interactions while on duloxetine:
NSAIDs could increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding when used with duloxetine, which could lead to:
How to manage this interaction?
Here are a few precautions to manage the interaction of NSAIDs with duloxetine:
Combining amphetamines with duloxetine may lead to side effects like:
How to manage this interaction?
These precautions may help you manage the interactions of amphetamines with duloxetine:
You need to know how supplements and herbs can interact with duloxetine. So, always discuss all supplement and herbal product use with your doctor7.
There are no specific reported interactions between duloxetine and most vitamins or minerals. However, it’s still important to inform your doctor about any supplements you take, as certain combinations may affect how well the medicine works.
Some herbal supplements may not be safe to take with duloxetine. For example, combining St. John’s Wort with duloxetine may increase the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially serious condition linked to excess serotonin in the body6. Kava, another herbal product, may increase the risk of liver damage when taken with duloxetine. While there is no strong evidence that these herbs reduce the effectiveness of duloxetine, they can increase its side effects or lead to harmful interactions.
Some tips on safe herbal usage:
If you feel nauseous or unwell while taking duloxetine, it is advisable to avoid heavy meals and spicy or greasy foods. Easily digestible foods can reduce stomach discomfort and make you feel more at ease. Always let your doctor know if your nausea persists or worsens.
Also Read: 13 Foods That Are Difficult To Digest!
Certain factors like an individual’s vaccination status, laboratory test requirements, and health history can influence the effect of duloxetine.
Based on available data, there are no known interactions between duloxetine and most vaccines. However, it is advisable to consult your doctor before taking a vaccine if you are on duloxetine.
Duloxetine is not known to interfere with common lab test results. However, if you have been scheduled for any tests, let your doctor know you are taking duloxetine for better interpretation of your test results.
Your past and present health conditions can influence the effect of duloxetine. It is advisable to share your full medical history with your doctor, especially if you are pregnant or plan to conceive or have or have had:
Also Read: 12 Foods That Are Necessary For A Healthy Liver!
Some duloxetine side effects may specifically affect women and may vary from person to person:
Duloxetine may lead to certain side effects that are more commonly seen in men:
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult your doctor and discuss your concerns openly.
Duloxetine may affect sexual health in both men and women. These effects can vary but may include:
Also Read: What To Eat During Food Poisoning?
Understanding how duloxetine may interact with certain foods, beverages, drugs and more supports better health and more effective use of the medication. It is important to consider your overall health and lifestyle when taking medication.
While on duloxetine, it is recommended you stay in touch with your doctor. Always share details of other medications and supplements you are taking with your doctor as they can influence your treatment. This allows your doctor to check for possible interactions, devise coping strategies, and adjust your treatment if needed.
Also Read: Pantoprazole Foods to Avoid
The onset of duloxetine’s therapeutic effects varies, but many individuals may start experiencing improvement in their symptoms within 1 to 4 weeks after initiating treatment. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalised guidance on the duration of duloxetine’s effectiveness.
Taking duloxetine during the third trimester of pregnancy may increase the risk of neonatal adaptation syndrome, which can cause symptoms such as tremors, irritability, feeding issues, and breathing problems in newborns9.
Speak to your doctor before using duloxetine during pregnancy to weigh the possible risks and benefits based on your health and your baby’s well-being.
Taking duloxetine at night is generally acceptable, but it’s advisable to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendation for the most effective and personalised dosing schedule. Always consult with your healthcare professional to ensure the dose timing aligns with your specific health needs.
Duloxetine and Wellbutrin should be used cautiously together because they affect different neurotransmitters in the brain. Taking them together may increase the risk of side effects or adverse reactions. Consulting a doctor may help manage potential drug interactions, ensuring a safer and more effective treatment plan10.
Taking duloxetine and gabapentin together requires caution because both medications can have central nervous system effects. The combination of these two medicines may increase the risk of side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, or difficulty concentrating. Consulting a doctor is crucial to assess individual factors, minimise risks, and ensure a safe treatment plan.
Yes, fatigue is a common side effect of duloxetine. If you experience excessive tiredness or drowsiness while taking the medication, you should inform your doctor and discuss potential adjustments in dosage or alternative treatment options.
Yes, constipation is a recognised side effect of duloxetine. If you encounter persistent constipation while using duloxetine, it is recommended to consult with your healthcare provider for potential management strategies or adjustments to your treatment.
Duloxetine may contribute to increased energy levels in some individuals as it affects neurotransmitters. However, individual responses vary, and if you experience concerns about energy levels or fatigue while taking duloxetine, consulting your doctor is advisable for personalised guidance.
Duloxetine may not be suitable for individuals with bipolar disorder, as it can potentially trigger manic or hypomanic episodes. It is essential to discuss any history of bipolar disorder with a doctor before starting duloxetine to ensure an appropriate treatment plan.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Grits have been enjoyed at the breakfast table for generations. But do you really know their health impact? This in-depth blog will take you on a journey through the world of grits. We’ll study their origin, types, and nutritional content.
In the coming sections, we’ll dig into the details of what grits are made from. We’ll look at what they provide nutritionally and how they may improve your health. We’ll also cover potential negatives and how to make them tasty.
What comes to mind when you think about a Southern U.S. breakfast? Grits, right? But are grits good for you? Ever wondered what are these creamy bits that have gained so much fame in recent times? Grits date back to Indigenous communities in North America and have been a key component in their diet for centuries.
Grits are made from corn, specifically a type called dent corn. To make grits, this corn is ground or crushed and then cooked until it turns into a creamy, soup-like dish1.
Different kinds of grits are available, such as white grits, yellow grits, hominy grits, and instant grits.
Regardless of your preferred type, making grits usually involves boiling ground corn in some form of liquid1. Once you end up with a creamy mix, you can add other ingredients to bring out different tastes.
Over the years, I have observed that for individuals with celiac disease, grits may be a favourable choice as they are made from gluten-free corn. This might also make grits a suitable and enjoyable option for those following a gluten-free diet11.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
What makes grits so fascinating is their unique nutritional content. Grits are nutrient-dense and contain many vitamins and minerals.
Here’s an overview of the key nutrients in 1 cup corn grits:
You’ll note that grits are packed with iron and B vitamins. However, the regular types of grits have fewer nutrients compared to those made from whole corn kernels. This is due to the varying production techniques that are involved.
In my opinion, grits are a nutrient-dense option, containing a variety of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Interestingly, these nutritional qualities may aid in reducing the risk of anaemia. So, individuals at risk of anaemia may consider incorporating grits into their diet.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
As grits are made from corn, they contain many of the nutrients found in corn and may offer several health benefits, such as:

Hominy grits, made via a process known as nixtamalization3, are high in key nutrients like calcium and iron4. Additionally, they serve as an excellent source of complex carbohydrates, providing sustained energy for daily activities. It’s a wholesome meal for many.

Grits are full of strong antioxidants that keep damaging free radicals away5. These antioxidants, such as vitamin E and selenium, play a crucial role in supporting the body’s immune system and overall well-being6.

Do you have gluten intolerance? Grits don’t contain gluten, making them useful in a gluten-free. Their gluten-free nature makes grits a versatile and inclusive option for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity7,8.

The antioxidants found in grits could help protect your eyes from various problems. Specifically, the presence of lutein and zeaxanthin in grits may contribute to maintaining eye health and help in reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration5,9.

Grits are high in iron and folate, both of which are useful for anemia4. These essential nutrients support the production of red blood cells and contribute to overall health10, helping to avoid and alleviate anaemia-related issues.
Based on what I have seen, the antioxidants lutein and zeaxanthin found in grits have demonstrated benefits for vision and eye health. They might also offer potential protection against age-related diseases.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
Although grits are high in nutrients and contain many beneficial properties, they may not be ideal for everyone’s dietary needs as they:
If you want to know how to make grits or are bored with the same grits recipe, here are some different ways grits can be made.
Grits are a versatile food option that are packed with iron, B vitamins, antioxidants, and several other nutrients. However, they may lose some nutrients during production and have a high carbohydrate content, so moderation in consuming them is important. Choosing healthier cooking methods can make grits a more balanced and interesting part of your diet.
Because grits have a high carb content, they can increase blood sugar levels. So, if you have diabetes, you need to eat them in moderation. You should also pair them with lean proteins and non-starchy veggies for a balanced meal.
Yes, they can be! However, it depends on how they are prepared. For a healthier grits recipe, cook them with water or low-fat milk, not full-fat milk or cream. Then include fresh fruits or veggies and lean proteins.
If losing weight is your goal, grits may not be the best food. They are high in carbs and are often served with high-calorie foods like cheese, butter, and milk. For weight loss, it may be better to turn to other whole grains or high-protein foods.
While both grits and oatmeal are nutritious, they have different strengths. Oatmeal has more fibre and protein, grits have more iron and B vitamins. However, oatmeal has a lower glycaemic index and could be a better option for blood sugar control. When made appropriately and accompanied by the right foods, both oatmeal and grits can fit into a healthy diet.
Grits themselves are not known to cause constipation. However, a diet lacking in fibre, which is important for regular bowel movements, might contribute to constipation. Incorporating a balanced mix of high-fibre foods alongside grits can help maintain digestive health.
Traditional grits are high in carbohydrates and not suitable for a keto diet. However, there are low-carb alternatives like cauliflower grits or almond flour-based versions that can be enjoyed in moderation while following a ketogenic eating plan.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Choosing the healthiest cooking oil can be challenging, especially when deciding between avocado oil and olive oil. Understanding their nutritional profiles, potential health benefits, and cooking uses can help you make a more informed choice. This blog will give you a scientific breakdown of these two favoured cooking oils, their extraction steps, nutritional details, and health benefits.
Avocado oil is becoming popular as a healthy and tasty cooking oil. It is derived from the fruit of the avocado tree (Persea Americana), which is native to Central America1.
There are two main ways of extracting avocado oil:
Avocado oil holds many helpful compounds like:
Avocado oil, full of flavour and flexibility, has many uses in the kitchen and cosmetic products. Its mild, butter-like flavour enhances a lot of dishes1. Also, its softening nature makes it a great add-in for skin and hair care items.
From what I have seen, avocado oil might be highly placed for its numerous potential benefits, particularly in the realm of skincare. One notable advantage of avocado oil might be its rapid absorption rate when applied to the skin. This characteristic may allow for quick absorption, delivering its nourishing qualities effectively18.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
A staple in the Mediterranean diet, olive oil is made by pressing olives. There are various kinds of olive oil, each with its unique traits and nutritional properties.
Olive oil is available in different forms, depending on how it is processed3:
Like avocado oil, olive oil is made by either cold-pressing or heat and chemical processing methods4.
Olive oil is made up of a number of good compounds, including:
Olive oil is often used for cooking, dipping, drizzling, and finishing dishes, showing its cooking versatility. Add to this, its moisturising and emollient properties, which make it a go-to ingredient in beauty products. They also form the base of many traditional medicine remedies6.
Based on my observations, I may say that olive oil might serve as a considerably healthier alternative to dietary fats, particularly those derived from animals. When it comes to cooking, olive oil may provide a nutritious substitute for butter, margarine, and various other types of fat. Moreover, a study conducted in this regard demonstrated a remarkable correlation: replacing unhealthy fats with olive oil might be linked to a reduced risk of mortality19.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
To make a smart choice between avocado oil and olive oil, it’s vital to understand their nutritional differences.
Although avocado oil and olive oil are mainly made of monounsaturated fats, their fatty acid profiles differ slightly:
Although both oils have important vitamins and minerals, the quantities can vary.
Calories per tablespoon (15 mL) are similar for both avocado and olive oil. Each provides around 120 calories.
I may attest to the benefits of avocado oil in skincare products. When incorporated into soaps, it might noticeably improve lathering, creating a luxurious and abundant foam. Additionally, when used in creams, it may impart a smoother texture, resulting in a delightful and velvety application18.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
Avocado oil and olive oil provide loads of health benefits, but they differ slightly in the benefits they offer.

The high content of monounsaturated fats and oleic acid in both oils improves cholesterol levels. It also helps regulate blood pressure.

Adding either oil to your diet could help with managing your weight. The unsaturated fats in both oils can curb hunger/help with appetite control. This prevents eating too much and helps with managing meal sizes10.

Oleic acid, polyphenols, carotenoids, and tocopherols add up to the anti-inflammatory properties of avocado oil and olive oil. These compounds work well together to lower inflammation in the body1.
Adding avocado oil or olive oil to your diet could boost digestive health. The monounsaturated fats in these oils reduce inflammation in the gut1. Also, the flavonoids in olive oil are known to have antibacterial effects11. They could protect against harmful gut bugs.
Menopausal women may often face challenges due to hormonal changes, such as emotional fluctuations, hot flashes, depression, anxiety, and vaginal dryness. During these times, I think that olive oil might be a helpful solution. It possesses antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that may help ease symptoms and help cope with menopause20.
Dr. Anuja Bodhare, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)

Antioxidants are needed to fight oxidative stress and they protect body cells.

Avocado oil and olive oil provide soothing and nourishing effects due to their natural ingredients. Therefore, they are popular picks for skin care.
Knowing the value of smoke point in cooking oils is key to retaining their nutritional value. It also keeps the overall quality of the dishes you’re preparing.
The smoke point is the temperature at which an oil starts to break down and release harmful free radicals. Cooking oils at or below their smoke point will maintain both their flavour and their health perks.
Avocado oil’s smoke point is higher than that of olive oil, which means it’s less likely to degrade during high-temperature cooking methods. Avocado oil’s unrefined smoke point is about 480℉ (250℃), while extra virgin olive oil’s smoke point is between 350℉ – 410℉14,15.
Avocado oil is fitting for high-heat cooking techniques, like sautéing, grilling, searing, and baking. This is due to its higher smoke point. On the other hand, olive oil fits best for lower heat methods, like simmering, stewing, and medium-heat sautés.
Both avocado oil and olive oil play a key role in nutrient absorption, especially when consumed with beneficial nutrients in other foods.
Fats, like those found in avocado oil and olive oil, aid in absorbing fat-soluble nutrients, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K. Consuming high-fat foods along with these nutrients improves their availability and uptake by the body.
Both oils help absorb nutrients due to their content of monounsaturated fats. A study found that dressing a salad with avocado oil greatly boosted the absorption of carotenoids from the veggies16. Likewise, adding olive oil to tomato juice was seen to boost the absorption of the carotenoid lycopene17.
Although both avocado oil and olive oil offer countless health benefits like heart health, weight management, anti-inflammatory properties, and skin care, there might be times where one is more beneficial. For example, olive oil might be better for people who put a premium on its higher polyphenol content. Meanwhile, avocado oil might be a better fit for high-heat cooking due to its higher smoke point.
In general, both avocado oil and olive oil add health benefits to your diet. However, do think about personal tastes and specific health needs before buying the oil. This will guide you in choosing the right oil for how you live or as per your lifestyle.
Summing it up, avocado oil and olive oil provide a lot of health benefits, flexibility in cooking, and taste. Knowing their nutritional differences and proper uses, you can make an educated choice on the best oil for your diet.
Ultimately, personal taste and individual needs will play a big part in deciding the best oil for you. Grab the chance to test and try out each oil. Then, find your own balance. Logic and some new insights can help you make an educated choice on the best cooking oil.
In many cases, yes. However, remember that their taste profiles and smoke points differ. For high-heat cooking methods, avocado oil might be a better fit. At the same time, olive oil is more suitable for lower-heat applications or as a finishing oil.
Extra virgin olive oil and cold-pressed avocado oil often rank higher in terms of quality and nutritional worth. Yes, they’re pricier. But if your main goal is getting the max health benefits, paying more might be worth it.
Keep both oils in a cool, dark place. Keep them away from heat and direct sunlight. This will extend their shelf life and keep their flavour and nutrients. Also, always seal the container tightly after each use.
As long as they’re part of a balanced diet, there are little risks with avocado oil or olive oil. But it’s important to pick quality products. Also, pay attention to the oils’ smoke points while cooking to avoid harmful free radicals.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Pantoprazole is a medication that belongs to the drug group ‘proton pump inhibitor (PPIs)’, which are often prescribed by doctors for stomach acid-related issues. These commonly include health conditions like peptic ulcer disease, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, NSAID-induced ulcer and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), among others1. But like any other medicine, there are some do’s and don’ts with pantoprazole as well. Understanding these are key to safe usage and optimal results.
So, in this guide, we’ll talk about pantoprazole. What is it? Why is it needed? Which foods and drinks should be avoided while on this medication? We’ll also discuss drug and nutrient reactions that might occur. Plus, useful tips on food choices will be shared, which can help improve your treatment results. Lastly, preventive steps and monitoring measures are discussed to make the treatment safer for you.
Drawing from my observations and experience, I strongly recommend avoiding food items that may exacerbate gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) when undergoing medication. So, it might be best to refrain from consuming spearmint and peppermint while taking medications like pantoprazole.
Let’s begin the discussion with an overview of pantoprazole. We’ll discuss what it is, why it’s used and how it works. Then, delve into what food and drinks to avoid while taking this medication.
It’s a type of PPI (proton pump inhibitor) which doctors prescribe for some gastric health problems. These helps manage issues wherein too much acid is produced in the stomach, leading to certain health conditions such as-
Pantoprazole should ideally be taken 30–60 minutes before a meal, usually in the morning, for optimal proton pump inhibition. Pantoprazole can have adverse effects, including , headache, and upper respiratory tract infection. Thus, pantoprazole should only be taken with a doctor’s prescription.
Now, let’s talk about its uses1.
Pantoprazole inhibits proton pumps in stomach wall lining cells, known as parietal cells. They make and release hydrochloric acid into the stomach. Pantoprazole irreversibly inhibits the H⁺/K⁺ ATPase enzyme in the apical membrane of parietal cells, leading to suppression of acid secretion. So, it helps manage symptoms related to acid reflux, hyperacidity, or mucosal damage due to excess acid1.
As someone who has made observations and collected experience in this matter, I would suggest avoiding the consumption of orange juice while taking medications for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), such as pantoprazole. Orange juice, due to its high acidic nature, may have the potential to exacerbate GERD symptoms. Thus, opting for alternative beverages with lower acidity might be a more suitable choice when taking GERD medications and minimise discomfort.
Certain food and drinks may worsen GERD symptoms even while consuming pantoprazole. To get the best out of your medication, avoid the following items:

Acidic foods can worsen GERD. They stimulate your stomach to produce even more acid. Plus, they can irritate the lining of your oesophagus or reduce lower oesophageal sphincter (LES) tone, worsening reflux2. It’s a common myth that they cause more acid to be produced. Examples of acidic foods are:

Fruits like oranges, grapefruits, and lemons, and their juices may cause irritation leading to worsening of GERD symptoms in some people.

Tomato products like tomato sauce, canned tomatoes and ketchup are highly acidic. So, these can worsen GERD symptoms too.

Caffeine boosts stomach acid levels and may relax the lower oesophageal muscles (LES). This can trigger GERD symptoms. Decaf options or herbal drinks can be helpful instead3,4.

Spicy foods have materials like chili peppers, curry powder, hot sauces etc in them. These all can cause irritation to the oesophagus and fire up stomach acid, causing more heartburn2,3.

High-fat foods can slow digestion and induce acid reflux by relaxing LES. Some examples of high-fat foods to avoid are2,3:

Food items such as chicken chunks, onion rings, and potato chips could make GERD symptoms worse.

High-fat dairy like cream, cheese, butter, and whole milk might worsen GERD symptoms. Try low-fat dairy or other alternatives instead.

Bubbly drinks like soda and sparkling water can exacerbate GERD symptoms. The bubbles push up pressure in the stomach, spurring stomach contents to flow into the oesophagus3.

Alcohol use can worsen GERD symptoms by relaxing the LES which allows acid to reflux into the oesophagus and worsen GERD symptoms. It also delays gastric emptying, and can irritate the gastric mucosa, all of which exacerbate GERD symptoms. Cutting down on alcohol intake is advised when on pantoprazole. If needed, ask your healthcare provider about what safe levels of drinking are while on this medication5.
When on pantoprazole, it’s vital to know about potential drug and nutrient interactions. Always talk with your healthcare provider before starting any new medicines or supplements.
Pantoprazole could interact with certain medications affecting their usefulness or causing unwanted side effects. Let’s see what these are:
Examples and Effects
Always tell your healthcare provider about the medicines you’re currently on. This can help avoid harmful drug interactions.
Like other PPIs, long-term use of pantoprazole could interfere with the absorption of specific nutrients. This might lead to deficiencies. Here are some examples:
Discuss with your healthcare provider any concerns over potential nutrient interactions. Regular blood tests might be needed to monitor nutrient levels for those using pantoprazole long-term.
To boost overall digestive health and help manage GERD symptoms, a Mediterranean diet or low carbohydrate diet is preferred8. These foods can be included in your diet while on pantoprazole:
Foods with a neutral or slightly alkaline pH help strike a balance in stomach acid levels. They alleviate GERD symptoms. Some examples are:
Foods rich in fibre can boost digestion health and help prevent acid reflux. Some high-fibre options are:
Incorporate lean protein sources in your meal plan. These include:
Also Read: Foods to Avoid While Taking Duloxetine
Certain precautions need to be kept in mind while on pantoprazole to assure both safety and effectiveness. Keep the following points in mind:
Stay alert to side effects, both minor and serious ones like diarrhoea, nausea, headaches and allergic reactions. Always inform your healthcare provider of any long-lasting or severe symptoms.
Severe or persistent diarrhoea could signal Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhoea, a rare but serious complication of long-term PPI use1.
Acute interstitial nephritis (AIN), a condition affecting the kidney, is also a rare but documented adverse effect of PPIs including pantoprazole.
Also Read: Best Summer Foods to Keep Your Body Cool
Correct dosage, duration of treatment and precautionary measures vary as per the specific populations:
Also Read: What To Eat During Food Poisoning?
Knowing which foods and drinks to avoid, how to monitor medicine interactions, and adopting healthy eating habits are essential when on pantoprazole for maximum benefits and safety. Always work together with healthcare providers to get personalized advice and recommendations, ensuring that pantoprazole remains an effective and well-tolerated treatment for your needs.
How long you are on pantoprazole treatment hinges on your specific health problem and how well you respond to therapy. Always stick to the duration of your treatment as advised by your doctor.
Weight gain is not listed as a common side effect in pantoprazole studies. But everyone’s body reacts differently. If you see great changes in your weight, talk to your healthcare provider.
The right pantoprazole dosage varies based on the individual and the condition treated. Always follow your doctor’s advice on dosage.
Take pantoprazole as directed by your doctor. Usually, it is taken once in the morning 45 minutes before breakfast. Do not break, crush, or chew the tablet/capsule as this can impact its effectiveness.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Next Page »