Prediabetes Symptoms in Indian Patients
By Dr. Arpit Verma +2 more

Get,

to manage your symptom
Get your,


4 Cr+ families
benefitted

OTP sent to 9988776655



You’ve successfully subscribed to receive
doctor-approved tips on
Whatsapp

Get ready to feel your best.

Hi There,
Download the PharmEasy App now!!


Register to Avail the Offer
Send OTPBy continuing, you agree with our Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions

Hi There,
Sign up on PharmEasy now!!
Trusted by 4 crore+ families

OTP sent to 9988776655



You have unlocked 25% off on medicines




Code: NU25
By Dr. Arpit Verma +2 more
Table of Contents
Chronic illnesses such as diabetes, high blood pressure, cholesterol and other disorders are growing more common as the world develops and progresses. But sadly, diabetes a condition that presents very few symptoms in its early stage, leaving most people unaware of their increasing sugar levels.
Prediabetes is a condition where your blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough for it to be diagnosed as diabetes. Prediabetes symptoms are almost like a warning call. If you do not pay attention to these symptoms, unfortunately, you risk the chance of developing type 2 diabetes in the near future.
Prediabetes is a prevalent health condition in which blood sugar levels are more than usual but not high enough to be diagnosed as Type 2 diabetes.
According to a study published in the Lancet, the prevalence of prediabetes in India is estimated to be 15·3% [1] . The major concern that needs to be addressed is identifying these people so that early therapeutic intervention may be made.
If you have prediabetes, your pancreas still generates adequate insulin in response to consumed carbohydrates. However, because your body’s cells do not respond to insulin well, your blood sugar level remains high. Insulin resistance is the medical term for this condition.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), prediabetes is a condition that can be managed and potentially reversed[2]. Lifestyle changes, such as diet, exercise and medication, may be used to treat the condition. If you recognise prediabetes symptoms and don’t make positive lifestyle adjustments, you might develop Type 2 diabetes within the next few years.
To Summarize
Prediabetes is almost like a warning of what’s to come. Prediabetes increases the risk of Type 2 diabetes by 5 to 15 times compared to people with normal blood sugar levels.
Unfortunately, those odds will only grow higher if you don’t make any healthy adjustments to your diet or activity habits. Adults with prediabetes usually have no symptoms at all, or the signs are so subtle that they go undiagnosed for years. There are, however, warning signs from time to time.
If you’ve got a family history of diabetes, you should see your doctor if you’ve any of the following symptoms:
Monitoring blood sugar levels can help your doctor screen you for prediabetes.
To Summarize
How likely are you to develop prediabetes?
Prediabetes happens due to certain causes and risk factors that raise the chances of developing it. If not detected in time, it can eventually lead to Type 2 diabetes. Some of these factors include:
Here are some other health conditions that are linked to prediabetes:
But don’t worry, it’s not as grim a picture as it seems. There are ways to manage prediabetes, as we’ll see in the following sections. Prediabetes does not signal a life sentence, and it’s very possible to live happy, fulfilling lives with prediabetes.
To Summarize
Also Read: Mounjaro vs Zepbound: Differences, Uses, Side Effects & More
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, your doctor will ask you to get a simple blood sugar test done to check for prediabetes. This entails taking a blood sample and sending it to a lab for analysis.
Depending on the type of test, the results may differ. Consult a doctor for the interpretation of lab tests and diagnosis.

Your doctor will ask you to fast for eight hours or overnight before the fasting plasma glucose test. A phlebotomist will collect a blood sample for testing before you eat.
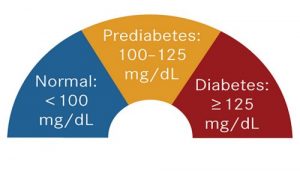
Normal fasting blood sugar levels are less than 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) – 5.6 millimoles per litre (mmol/L).
Prediabetes is defined as a fasting blood sugar level of 100 mg/dL to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 7.0 mmol/L)[3]. Impaired fasting glucose is a term used to describe this outcome.
Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed by a fasting blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or greater.
Fasting is also required for an OGTT. Your doctor will check your blood glucose levels twice – first at the start of the visit and again two hours later after you’ve consumed a sugary drink.
After two hours, normal blood sugar levels are considered as levels lower than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L).
A blood sugar level of 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL (7.8 to 11.0 mmol/L) is considered prediabetic. Impaired glucose tolerance is the term used to describe this condition[3].
Type 2 diabetes is defined as a blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or greater[3].
If you’ve been diagnosed with prediabetes, your doctor will examine your blood sugar levels at least once a year.
The haemoglobin A1c test, commonly known as the A1c test, is a blood sugar test that evaluates your average blood sugar level over the past two to three months. This test requires no fasting and can be performed at any time.
HbA1c score of 5.7% to 6.4% indicates prediabetes (in undiagnosed people) [3]. However, to validate the results, a second HbA1c test and other tests like FBS and PPBS are recommended. The higher your HbA1c value is, the more likely your prediabetes will develop into Type 2 diabetes.
Generally speaking:
You can regulate your blood sugar levels by making lifestyle adjustments. Emphasise reducing sugary and processed foods, which quickly break down into glucose and raise blood sugar levels quicker than the body’s ability to create enough insulin. Consult a doctor and understand the dietary and lifestyle changes that are required.
According to ICMR guidelines[4], screening should be performed in all individuals >30 years of age and earlier if the person has any of the following risk factors:
If your doctor detects any of these risk factors, he or she may suggest that you undergo a blood glucose test. Doctors recommend conducting screening tests every year.
To Summarize
What happens when prediabetes is left undiagnosed? Prediabetes is a condition that can be managed effectively if you identify the symptoms, get diagnosed early and take the necessary steps. However, if left undiagnosed, complications can arise. Fear of the disease is one reason that many people don’t get tested for prediabetes. However, late diagnosis or leaving the disease undiagnosed will only worsenthe condition in the future. So, it’s recommended that you get your screening test done as soon as possible. By diagnosing prediabetes, you can considerably delay the onset of Type 2 diabetes.
Consider prediabetes as a warning sign – ignore it, and your chances of developing Type 2 diabetes increase. On the other hand, if you lose a little weight or fat, to be precise and engage in regular physical activity, your risk of developing Type 2 diabetes decreases. For a 90 kg person, modest weight reduction is losing 5% to 7% of their body weight or 4.5 kg to 6 kg[5]. Regular physical exercise is defined as at least 150 minutes of brisk walking or other comparable activities each week[6]. That’s all you need to do to control your prediabetes – dietary changes + exercise + stress management. Always consult a doctor and do as advised.

To Summarize
Also Read: Mounjaro (Injection): Uses, Side Effects, Dosage, and How It Works
Managing prediabetes can also be viewed as an attempt to prevent or delay the onset of Type 2 diabetes. If you’ve got prediabetes, your doctor will advise you to make certain lifestyle adjustments. People who meticulously followed these modifications for the long term saw a 58% reduction in their risk of diabetes, according to the Diabetes Prevention Program[7].
The following are the most frequent strategies to control prediabetes:
Some people with diabetes choose to opt for complementary and alternative medicine therapies to help them control their condition. Supplements, meditation and acupuncture are examples of complementary and alternative medicine therapies. However, always consult with your doctor before beginning any complementary and alternative medical therapies since they may interfere with your medications.
To Summarize
Also Read: Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment in India
Yes, though it’s a common condition, it’s reversible in many cases. If you’ve got prediabetes, with the help of simple, proven lifestyle modifications, you can avoid or delay the onset of Type 2 diabetes.
Though it might be difficult to know if you’ve got prediabetes, there are some subtle signs to watch for. It is not necessary to experience one of these symptoms to have prediabetes. However, if you experience any of these symptoms, you must discuss them with your doctor.
-Vision is blurry
-Hands and feet feel cold often
-Urinary tract infections become more common
-Dry mouth
-Excessive thirst
-Frequent urination
-Irritability, anxiousness or worry have increased
-Itchy skin
-Strange feelings in your extremities, such as tingling, numbness, pain or burning
-Infections that recur
-Sudden weight loss
-Extreme fatigue
-Wounds that don’t heal quickly
Screening tests for prediabetes can help detect it early on.
Three to six years is the window of opportunity to prevent or delay the progression of prediabetes to Type 2 diabetes. However, this duration may vary from person to person depending on the individual’s risk factors, dietary habits and lifestyle.
Make sure you follow the diet and lifestyle modifications as advised by your doctor to stay on track in your fight against prediabetes and reduce your blood sugar levels.
When you’re trying to reverse prediabetes, your doctor will tell you how often you should have blood tests done, generally every three months. But this could vary from one patient to the next, so make sure you consult with your doctor as well.
The body has a hard time reducing blood sugar levels after meals for people with prediabetes. Keeping a close eye on your carbohydrate and fat consumption might help you avoid blood sugar rises.
When you consume more calories than your body requires, the excess calories are stored as fat. You may gain weight as a result of this. Insulin resistance is connected to body fat, particularly around the abdomen. So, avoid fried, processed, packaged and sugary foods.
Staying active helps burn calories, manage weight, and improve blood sugar control. A brisk 30-minute walk five times a week is recommended. Strength training (weight lifting, pushups, pull-ups), yoga, and aerobic exercises like walking, swimming, and dancing are all beneficial. A combination of both strength and cardio works best. Exercising with a friend or joining a gym can help you stay motivated. If you’re new to working out, start under expert supervision for safe and effective results.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.

Leave your comment...
Comments