Last updated on January 3, 2022
Content By: Dr. Nikita Toshi BDS, Assistant Manager (Medical Review) & Dr. Ritu Budania MBBS, MD (Pharmacology) Head, Medical Affairs
Last updated on January 3, 2022
After the brain, the human eye is one of the most complex organs in the body. Did you know your eye contains over 2 million working parts that allow you to see in perfect detail? While your eyes are also one of the fastest self-healing body parts, unfortunately, it is still prone to damage as an effect of other conditions such as Diabetic Retinopathy (DR).
A recent survey by the Union Health Ministry has revealed that diabetic retinopathy was present in almost 17% of the Indian population with 3.6% of it being sight-threatening. Specific to the rural population, a Shankar Nethralaya DR study identified that 10.4% had Diabetes, and around 10.3% had Diabetic Retinopathy. A WHO study further predicted that by 2030, the number of diabetics with Retinopathy is said to increase by more than 50%. Without proper diabetic retinopathy treatment, especially in the more severe cases, the individual is likely to suffer from complete vision loss.
Getting the right diabetic retinopathy treatment is important especially when it is caught at an early stage. In this article, we are going to look at what is diabetic retinopathy, the symptoms and causes and finally the treatment for diabetic retinopathy. Without further ado, let’s look at what is diabetic retinopathy.
After the brain, the human eye is one of the most complex organs in the body. Did you know your eye contains over 2 million working parts that allow you to see in perfect detail? While your eyes are also one of the fastest self-healing body parts, unfortunately, it is still prone to damage as an effect of other conditions such as Diabetic Retinopathy (DR).
A recent survey by the Union Health Ministry has revealed that diabetic retinopathy was present in almost 17% of the Indian population with 3.6% of it being sight-threatening. Specific to the rural population, a Shankar Nethralaya DR study identified that 10.4% had Diabetes, and around 10.3% had Diabetic Retinopathy. A WHO study further predicted that by 2030, the number of diabetics with Retinopathy is said to increase by more than 50%. Without proper diabetic retinopathy treatment, especially in the more severe cases, the individual is likely to suffer from complete vision loss.
Getting the right diabetic retinopathy treatment is important especially when it is caught at an early stage. In this article, we are going to look at what is diabetic retinopathy, the symptoms and causes and finally the treatment for diabetic retinopathy. Without further ado, let’s look at what is diabetic retinopathy.

Written by:
BDS, Assistant Manager (Medical Review)

Reviewed by:
MBBS, MD (Pharmacology) Head, Medical Affairs
Diabetic Retinopathy occurs when blood vessels in the retina (the light-sensitive tissue behind the eye) become damaged. Diabetic retinopathy is a common eye problem in diabetes that may occur in anyone with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Retinopathy generally occurs as a result of untreated, uncontrolled or undiagnosed diabetes. While diabetic retinopathy in India is more common in males than females, if you have been dealing with any form of diabetes for a long period of time, it is best to consult an eye doctor to check for diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic Retinopathy Types
There are two types of diabetic retinopathy – Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) and Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR).
Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) – In Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy, the eye does not create new blood vessels during the early diabetic retinopathy stages. In this type, blood vessels in the retina experience swelling and damage that cause blood and fluid to leak into the retina resulting in blurring of vision. NPDR has three stages – mild, moderate and severe. The condition may even progress to the 4th stage or another type – proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) – This stage is the 4th stage of diabetic retinopathy and the most advanced of the diabetic retinopathy stages. In proliferative diabetic retinopathy, the healthy blood vessels that supply blood to the retina get deformed and blocked and new blood vessels grow around the retina. However, these new blood vessels are abnormal and fragile. Patients in this stage usually require surgery.
These diabetic retinopathy types depend on how much the condition has advanced. We will explore these diabetic retinopathy stages in further detail in section 3.
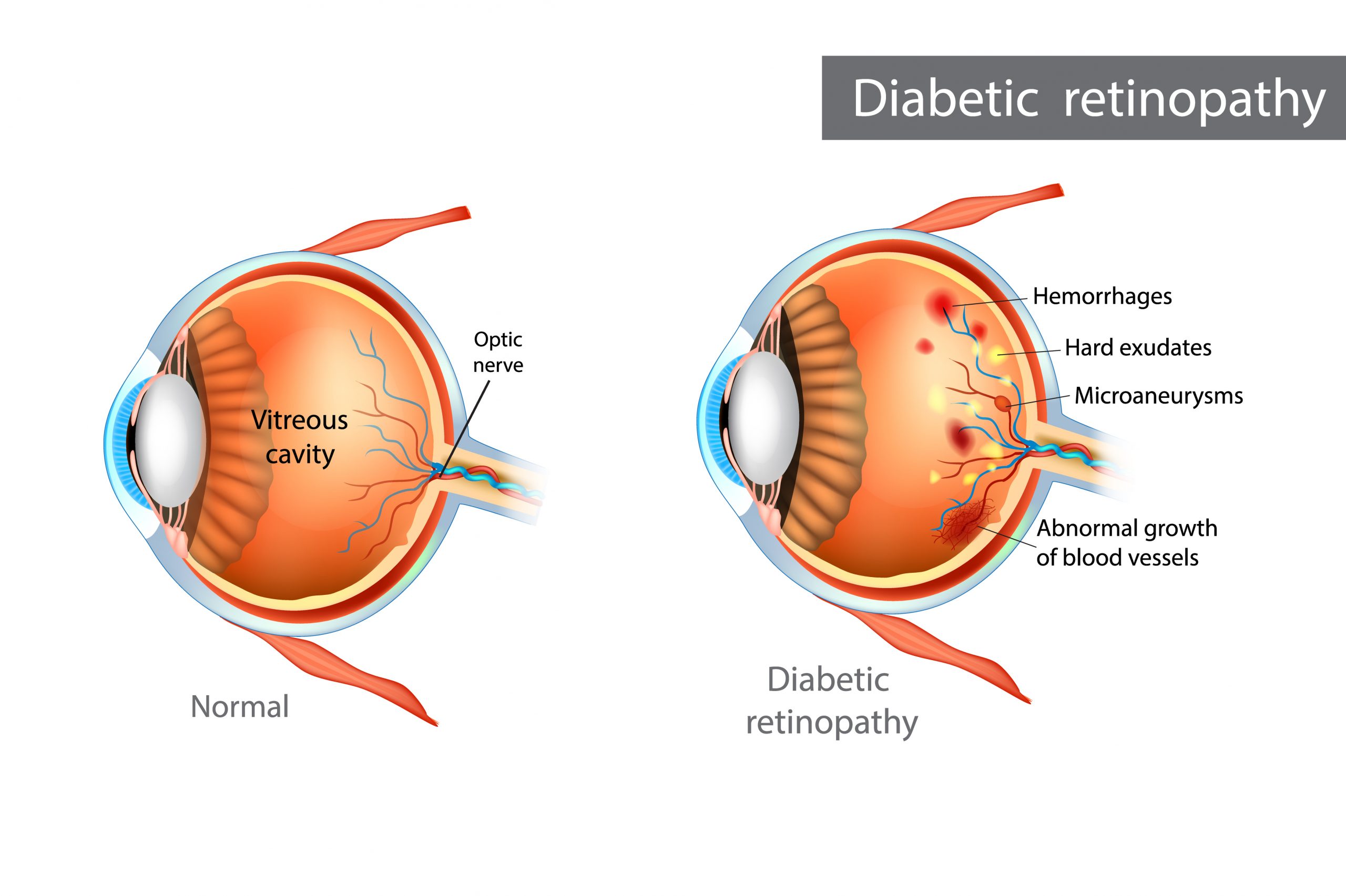
What are the causes of diabetic retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is an eye problem in diabetes that is usually caused by high blood sugar levels in the body over a long period of time. The excess sugar in the blood eventually causes damage to the very blood vessels that supply blood to the retina.
The retina as we know is a light-sensitive tissue in the back of the eye that functions to convert images into nerve impulses that the brain can process. In diabetic retinopathy, these blood vessels get blocked, in turn, weakening the blood supply to the retina. This decrease in blood flow can cause the growth of newer but abnormal blood vessels that can leak blood and fluid and create scar tissue in the retina causing it to tear or detach. This leads to vision impairment and eventually blindness if left untreated.
What are some of the diabetic retinopathy risk factors for Indian patients?
While prolonged Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes is one of the most commonly found diabetic retinopathy causes in India today, some other diabetic retinopathy risk factors include:
Keeping your blood sugar levels in check with a proper diabetes diet plan, exercises and doctor-prescribed medicines can help slow the development of the condition. In many cases, surgical or invasive treatment is needed only if your condition is severe.
What are some of the complications of diabetic retinopathy?
Abnormal blood vessel growth in the retina, if left untreated, can cause complications leading to serious vision problems. Some common complications of diabetic retinopathy include:
Bleeding in some areas of the eye – The new blood vessels that grow as a result of weakened blood supply to the retina may bleed into the clear jelly-like fluid that is present in the centre of the eye. If the bleeding is light, you may see only a few dark spots. However, severe bleeding can fill up the entire centre of the eye causing complete vision loss.
Detachment of the retina – The abnormal blood vessels may also cause scar tissue to develop that can pull the retina causing tears or detachment. In this case, initially, you may see a few spots that appear to be floating around in your vision or in other cases, flashes of light and eventually or complete vision loss if left untreated.
Glaucoma – The growth of new blood vessels may obstruct the natural outflow of fluid from the eye causing a build-up of pressure in the front region of the eye – a condition known as glaucoma. If left untreated, this pressure may cause damage to the optic nerve which is the primary nerve that carries image signals from the eye to the brain.
Complete vision loss – Untreated diabetic retinopathy can eventually lead to total vision loss for the individual.
Diabetic retinopathy in India although an increasingly common diabetes eye problem can be treated and prevented by getting regular eye tests, managing blood sugar levels and intervening early as soon as mild symptoms show up. It is advised to consult a good ophthalmologist from time to time who will be able to give you the right advice on diabetic retinopathy management and prevention.

Diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy?
Order your medicines online on PharmEasy
and get it home delivered with a click!
Diabetic retinopathy is a diabetic eye problem that is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina. Many may show little to no symptoms in the early stages of the condition. However, as the condition progresses some diabetic retinopathy symptoms emerge such as:


![]() Spots or dark coloured strings that appear to float in your vision (floaters)
Spots or dark coloured strings that appear to float in your vision (floaters)
![]() Blurry vision
Blurry vision
![]() Blank or dark spots in your vision
Blank or dark spots in your vision
![]() Colours may appear faded or washed off (Colour vision impairment)
Colours may appear faded or washed off (Colour vision impairment)
![]() Difficulty seeing at night time
Difficulty seeing at night time
![]() A complete loss of vision
A complete loss of vision
When to see a doctor?
When these diabetic retinopathy symptoms appear, they mostly appear in both the eyes and are a sign to take immediate action towards the right treatment. If you currently have diabetes, it is advised to schedule an annual eye exam irrespective of the state of your vision. If you notice any changes in your eyesight or anything unusual with your vision, please consult an eye specialist (ophthalmologist) without delay.
Screening recommendations for patients with diabetes with no complaint of eye problems
| Type of diabetes | Eye Examination by an Ophthalmologist |
|---|---|
| Type 1 diabetes | Within 5 years of onset of diabetes followed by annual routine eye check-ups. |
| Type 2 diabetes | At the time of diagnosis of diabetes followed by annual routine eye check-ups. |
| Women with preexisting diabetes planning pregnancy or if already pregnant. | Before planning a pregnancy or in the first trimester if already pregnant. |
| Women with gestational diabetes | An eye examination is not required during pregnancy if there is no problem with eyesight. |
However, if you do happen to experience common diabetic retinopathy signs like a sudden vision change, blurriness or dark spots in your vision, consult with your eye doctor at the earliest to prevent further complications.

Showing signs of diabetic retinopathy?
Book a screening test for diabetes on Pharmeasy to
confirm your symptoms today!
As briefly mentioned earlier, there are two types of diabetic retinopathy – nonproliferative and proliferative. Diabetic retinopathy tends to progress in 4 stages from a non-proliferative state to a proliferative state. This is also called grades of diabetic retinopathy. If not arrested with the treatment, it can be dangerous. Let’s explore the 4 stages in more detail:
Stage 1: Mild Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
This is the earliest diabetic retinopathy stage in which there is a balloon-like deformation in the blood vessels of the retina called microaneurysms.
Stage 2: Moderate Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
This is the second grade of diabetic retinopathy. As the condition begins to progress, the main blood vessels that provide blood supply to your retina start to swell and alter in shape. They become partially blocked and unable to function properly, affecting the appearance of the retina. Fluid can get leaked from blood vessels to the retina. Part of it (macula) is responsible for focussing images and can cause the macula to swell up due to fluid leakage and causes blurring or sometimes loss of vision.
| STAGES OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Frame in Years | 0 | 3 to 5 | 5 to 10 | 10 to 15 | More than 15 | ||
| Stages of DR | Normal Eye | Stage 1 Mild Non-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy |
Stage 2 Moderate Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy |
Stage 3 Severe Non-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy |
Stage 4 Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy |
||
| Onset of Diabetes | → | → | → | → | |||
| Changes in Retina |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Stage 3: Severe Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
In this third diabetic retinopathy stage, multiple retinal blood vessels get blocked cutting off blood supply to the retina which then signals the secretion of special proteins responsible for the formation of new blood vessels.
Stage 4: Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
This is the 4th and most advanced or critical diabetic retinopathy stage. In this stage, new blood vessels grow along the surface of the retina and then spill over into the vitreous humor, the clear, jelly-like substance in the eyeball. Blood and fluid can leak out of these fragile new blood vessels causing abnormalities in your vision (vitreous haemorrhage). Scar tissue begins to form that can cause retinal tears or detachment of the retina entirely. If left untreated, this can lead to permanent vision loss.
Patients may not even experience symptoms in the first two stages of this diabetic retinopathy classification. However, early detection is key in easy diabetic retinopathy management. By scheduling regular eye examinations with your eye doctor, you can closely monitor the progression of the condition and prevent it from worsening by medication or lifestyle changes. Pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy can be due to many factors and, if severe, your ophthalmologist will also be able to recommend the right treatment needed to reverse the damage.

Prevent the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
Explore PharmEasy’s diabetic care range to help manage
your blood sugar levels today!
Since the condition may start off small and then progress in severity, screening for diabetic retinopathy may involve a few basic tests; then, if needed, your doctor may move on to some more comprehensive eye exams. Here are few ways diabetic retinopathy is diagnosed in India:
Vision Test
This is usually the first test that a doctor may conduct as part of the diabetic retinopathy diagnosis. A vision test is conducted to check for any unusual changes in vision – both near vision and distance vision. Since diabetic retinopathy symptoms may be absent for many during the early stages of the condition, to rule out the presence of diabetic retinopathy, the doctor may suggest eye dilation.
Dilated Eye Exam
This diagnostic test is a common eye exam conducted to check for any abnormalities inside of the eye. As part of the dilated eye exam, your doctor will give you special eye drops and request that you keep your eyes closed for the recommended duration of time (usually 30 to 45 minutes). These eye drops make your pupils dilated or open wider allowing your eye doctor to get a clearer look of the inside of your eye with the help of their viewing instruments.
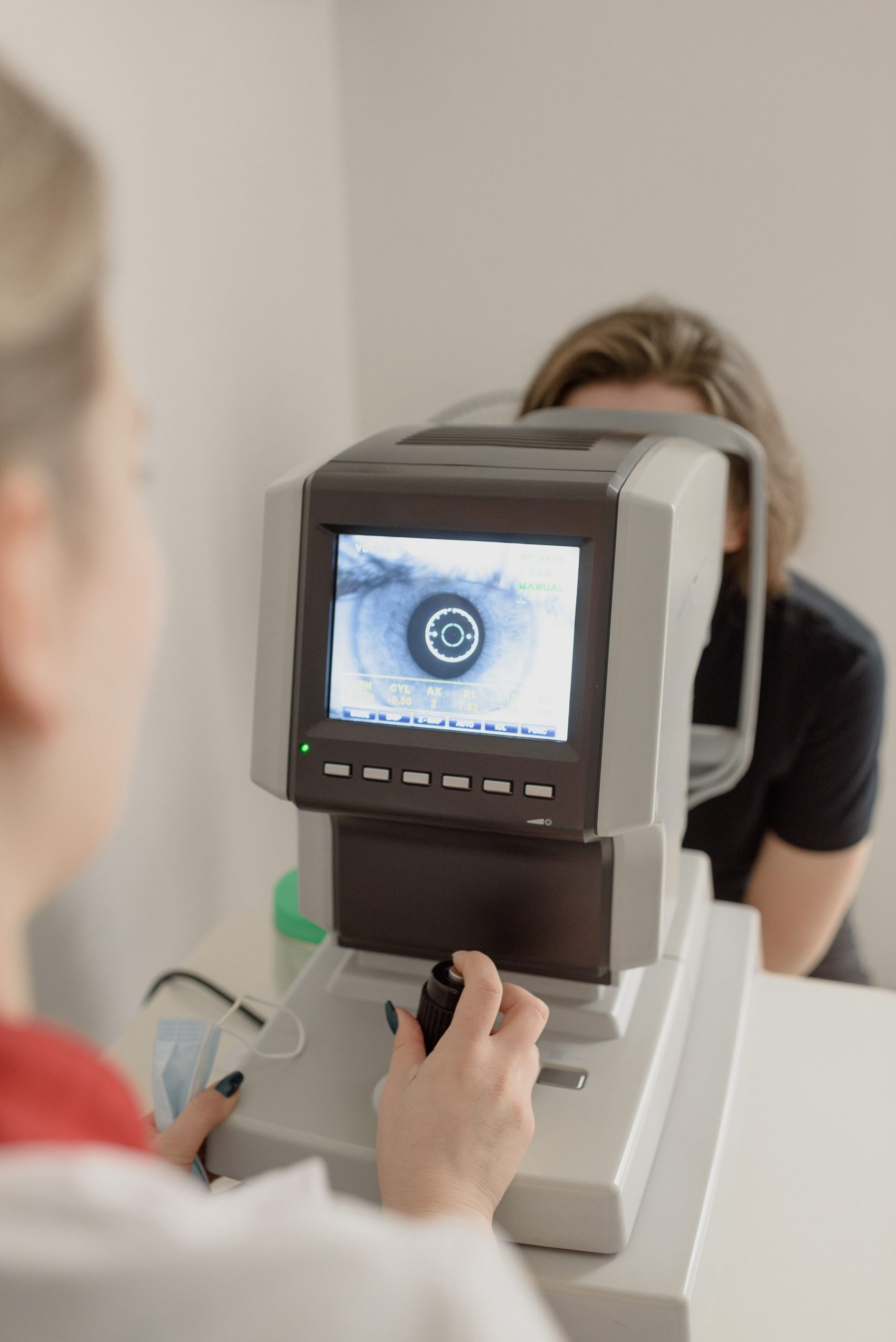
Fluorescein Angiography Test
In this diabetic retinopathy diagnosis test a special dye will be injected into a vein, usually in your arm. The dye travels along your blood vessels and reaches your eyes. It can be pictured through a special camera. This will allow your eye doctor to monitor how the blood flows in your eye. Then with the help of a special camera, photographs will be taken of your eye to determine if any vessels are showing blockage, tears or leaks. It can also help to identify the formation of abnormal blood vessels in that region.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
The Optical Coherence Tomography test is an imaging test that makes use of light waves to capture cross-section images of your retina. You will be asked to sit in front of the OCT device while resting your head on a support. The machine will then scan your eye and produce images of your retina. Screening for diabetic retinopathy using this process will take up to 10 minutes. If your eyes are dilated, it’s normal to experience light sensitivity for a few hours post-exam. Through this diagnostic test, your eye doctor will be able to see each of the layers of your retina and measure its thickness. Through the OCT test, doctors will be able to detect the presence of diabetic eye problems as well as glaucoma, swelling of the macula and other eye-related conditions.

Showing diabetic retinopathy symptoms?
Book a diagnostic test on PharmEasy today to
confirm your diagnosis!
Diabetic retinopathy treatment in India is prescribed by an ophthalmologist according to the stage and severity of the condition. Diabetic retinopathy, if left untreated, has the potential to cause irreversible vision loss and therefore early detection and diagnosis is key for a full recovery.
If doctors start to see some mild diabetic retinopathy signs, they may recommend medication such as special diabetic retinopathy eye drops or oral medication supplemented with lifestyle changes such as diet and physical exercise to manage your blood sugar. Some other treatments may be prescribed if the condition has developed to its 2nd or 3rd stage. They include:
Medications will be prescribed to keep your blood sugar, blood pressure and cholesterol levels in normal range.
Depending on the severity of diabetic retinopathy, your eye doctor may recommend steroid-based injections that help reduce inflammation and swelling. Another injection that helps in this condition is the anti-VEGF (anti-vascular endothelial growth factor) injection. This is a medicine that suppresses the action of the growth factor responsible for the formation of new blood vessels in your eyes. It thus, helps to reduce the worsening of the condition.
This diabetic retinopathy treatment has two types: focal laser surgery and scatter laser surgery.
Focal laser surgery – In this type of diabetic retinopathy, laser treatment will be used to make small burns on the areas of the blood vessels around the retina that are leaking. Many patients may also require anti-VEGF medication post-surgery.
Scatter laser surgery – In this type of treatment, a laser is used to make numerous small burns on a large area around the retina to treat the leaking blood vessels. Scatter laser surgery can also help shrink the abnormal blood vessels. Some patients require two or more sessions of this laser treatment. While it may help restore your central vision, it can weaken your peripheral, night or colour vision. For optimum outcomes, it is recommended that this diabetic retinopathy laser treatment be done before the new blood vessels start to leak fluid or bleed.
A vitrectomy, as the name suggests, is a type of invasive eye surgery that is done to remove blood that has leaked. This type of treatment is recommended when patients are in the proliferative or the most advanced stage of diabetic retinopathy. When blood from the new blood vessels leaks fluid or blood into the vitreous cavity, it can cloud your vision partially or even completely depending on the amount of leakage. This eye surgery works to remove the leaked blood as well as scar tissue and even some of the vitreous gel to help the patient see clearer. Simultaneously, any retinal movement, tears or detachment can also be corrected. After the procedure, it would normally take around 2 – 4 weeks for the patient to resume their day-to-day activities.

Diabetic medication is only a click away!
Order online on PharmEasy at great prices
and get it home delivered in a click!
Diabetic retinopathy prevention starts with managing diabetes or your blood sugar levels. If you have been diagnosed with diabetes, it is important that you consult an endocrinologist or a diabetes specialist to help you keep your blood glucose levels in check. While high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels may also risk your chances of developing diabetic retinopathy, your doctor may recommend these prevention tips and diabetic retinopathy home remedies to help keep the condition at bay:
Regular Monitoring of Blood Sugar Levels
It is important to keep a regular check on your blood sugar levels to assure that your medications, exercise and diet plan are working well and your diabetes is under control. In case you observe a rise or fall in your blood glucose levels beyond the normal range, you can consult your doctor immediately and the dose of your diabetes medications can be changed as per the need. Keeping an eye on your blood sugar levels will help reduce the chances of development of complications like diabetic retinopathy.
There are various devices called glucometers available in the market which can make it easy and convenient for you to check your blood sugar levels at home. One popular glucometer is the Accu-Check Active Glucometer Kit that you can purchase on PharmEasy.
It is important to take your diabetes medications timely as prescribed by your doctor. Lowering your blood sugar levels not only helps with preventing diabetic retinopathy but if you have diabetic retinopathy, it helps in drastically slowing down its progression.
Smoking should be avoided at all costs for diabetics in general. They pose overall harm to the body and directly impact one’s blood sugar levels.
Diabetes Diet that is low in sugar and simple carbohydrates
Consuming a diet for diabetes is one of the first and the most common diabetic retinopathy prevention tips that a doctor is likely to suggest if you have been diagnosed with diabetes. In your diet for diabetes, it is advised to exclude processed foods, fried foods, sweets, sugary drinks, high sugar-fruits and naturally starchy vegetables. These food elements generally tend to spike blood sugar levels instantly. Instead, include foods that have a low glycemic index such as oats, millet, leafy vegetables and legumes, lentils, foods rich in protein like paneer, chicken, eggs and fish and healthy fats like avocado, mixed nuts, etc.
Regular exercise or physical activity
A diabetes diet is only effective when it is supplemented with regular exercise for diabetes. Even 30 minutes of physical activity everyday has shown to work wonders for many diabetic patients in bringing their sugar levels down. Consult a doctor to find the right exercises for you.
Relaxation and meditation techniques to cope with stress and anxiety
Stress and anxiety is often linked to high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels that can put you at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. Therefore, if you are dealing with high stress and anxiety levels your doctor may suggest some meditation or relaxation techniques like breathing exercises or yoga for diabetes to help prevent diabetic retinopathy from developing in the long run.
Scheduling annual eye examinations
If you have diabetes, monitoring the condition of your eyes becomes essential in diabetic retinopathy prevention. Since it is easier to treat diabetic retinopathy, if it’s detected early, your doctor may recommend you schedule regular eye examinations to monitor your eye health closely.
A comprehensive eye exam in your first trimester if you are pregnant with diabetes
If you are pregnant with diabetes type 1 or type 2, your doctor may ask you to schedule a thorough eye examination in your first trimester to prevent any eye-related complications popping up during the course of your pregnancy. You can schedule an eye exam before planning pregnancy, if you are diabetic.
In case you are a non-diabetic woman and develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy, you are at minimal risk of developing diabetic retinopathy and do not require an eye exam during pregnancy unless you notice any changes or abnormality in your vision. You can get an eye exam after delivery if your diabetes remains uncontrolled.
No matter what stage you may be in, with the right treatment, abnormalities in the eye or vision can be improved to a great extent. By constantly monitoring your eye health and finding proactive ways of keeping your blood glucose levels under control, diabetic retinopathy can be prevented in the long run.

Prevent the occurrence of diabetic retinopathy!
Explore diabetic health products on Pharmeasy that help you
manage your blood sugar effectively.
What are the four stages of diabetic retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy classification depends on how much your condition has developed. The 4 diabetic retinopathy stages include:
What is the first stage of diabetic retinopathy?
The first stage of diabetic retinopathy is called mild nonproliferative retinopathy. It is also called background retinopathy. This is one of the earliest diabetic retinopathy stages where you may experience little-to-no symptoms. In this stage, the blood vessels in the retina start to change in shape. Some other small surrounding areas start to swell. In some cases, the swelling can result in some blood or fluid leaking into the retina. These are called microaneurysms and can cause mild vision changes. If you have been diagnosed with mild nonproliferative retinopathy, it is important to consult your doctor for ways or the recommended treatment with which you can prevent this condition from progressing. If you have been diagnosed with background retinopathy in both eyes then there is a 25% chance that you will progress to the next stage in around 3 – 4 years.
Can you reverse diabetic retinopathy?
With early detection and the right treatment, diabetic retinopathy can be reversed to an extent. The treatment outcome varies from person to person. It is advised to frequently follow up with your eye doctor, schedule regular diabetic retinopathy screening examinations and monitor your eye health closely to slow down its progression. Apart from this, maintaining normal blood sugar, blood pressure and cholesterol levels along with a healthy diet, exercise and sleep schedule for diabetes can help ensure your eyes as well as your overall body stays healthy in the long run.
How long does it take to go blind from diabetic retinopathy?
The progression of diabetic retinopathy depends on several factors such as the control of blood sugar levels, age, medical history, blood pressure readings, blood cholesterol levels, effect of medication or treatment, diet, exercise, etc. If diabetic retinopathy goes undiagnosed or untreated, it can progress faster than one that has been detected early and proactively managed. If you have been diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy in both eyes, there is a 25% likelihood (if left untreated) of the condition developing to the next stage in around 3 – 4 years. While it may take several years before diabetic retinopathy can dangerously threaten your vision, it is important that it is detected early in order to make a full recovery.
Is diabetic retinopathy curable?
Yes, in many cases if diabetic retinopathy is detected early enough, it can be cured. However, there is a variation in the response and treatment outcome from person to person. Diabetic retinopathy treatment options include diabetic medication, a low-sugar diet, physical exercise and in advanced stages, eye injections, laser treatments and eye surgery which can definitely help in improving the eye condition.
What precautions should a diabetic female take to avoid retinopathy before planning pregnancy?
Retinopathy may worsen during pregnancy, therefore, it is advisable that you should get a complete eye examination to check for any abnormalities indicating retinopathy, before planning pregnancy. In case, there are any signs of diabetic retinopathy, follow your doctor’s advice and start your treatment for the same. Plan your pregnancy, once your doctor considers it safe.
Can a pregnant patient diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy plan for a natural vaginal birth?
Diabetic retinopathy in a pregnant patient is not a contraindication for natural vaginal birth. However, there are many more factors that govern the selection of birth type. Ultimately your doctor is the best person to evaluate your condition and decide the type of birth suitable in your case.
What can I expect after a dilated eye examination?
The dilated eye examination is a simple procedure, which is performed routinely as a part of eye checkups. There is nothing to worry about but you may find the following tips useful. You may expect:
What can I expect from a focal laser treatment?
Also called photocoagulation, this treatment aims to stop the leakage of blood or fluids in the eye. It is treated with a laser that stops the leaks from abnormal blood vessels. This session usually takes place in just one sitting but doctor’s analysis is recommended based on your condition.
Is injecting medicine into the eye recommended?
A procedure to inject medications called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitors may be suggested by your doctor to improve your vision affected due to diabetic retinopathy. This treatment has shown good results in a number of patients. However, treatment options vary from patient to patient and your ophthalmologist will recommend the best available treatment depending on your condition.


Leave a Comment