Table of Contents
Introduction:
Bhumi Amla (Phyllanthus niruri) is a tiny erect annual herb native to the Amazon rainforest and other tropical areas such as South East Asia, Southern India, and China. It grows up to 30-40 cm in height. It has alternate, sessile and oblong leaves, 7-12 cm long. Its flowers are tiny, solitary, apetalous, auxiliary, pedicellate, monoecious and white-greenish.1
This herb belongs to the Euphorbiaceae family and has a wide range of therapeutic characteristics. It is widely used around the world. Bronchitis, urinary problems, anaemia, leprosy, asthma, and other conditions are treated using Phyllanthus niruri plant extract.2
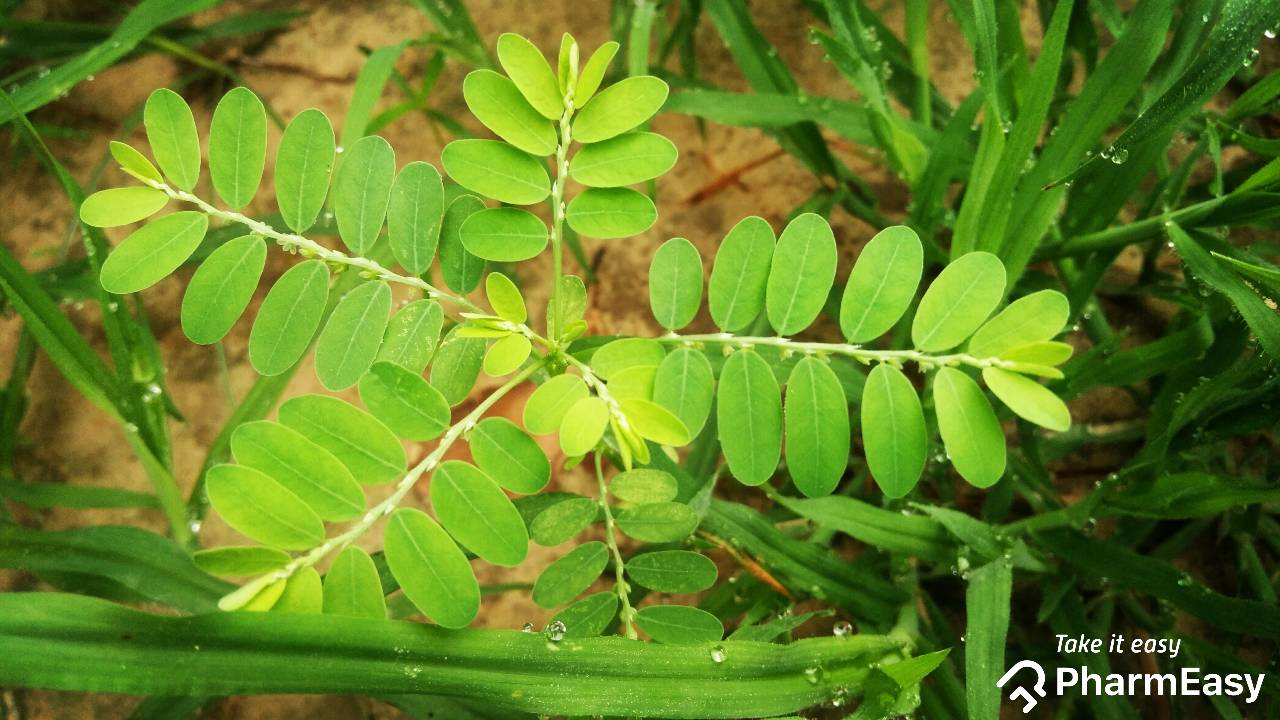

Nutritional Value of Bhumi Amla:
Bhumi amla has the following nutritional value:
- Crude Protein (% dry matter): 14.74%
- Sodium: 1947 ppm
- Ferric: 665 ppm
- Phosphorus: 6978 ppm
- Potassium: 18252 ppm
- Calcium: 2911 ppm
- Magnesium: 2914 ppm
- Manganese: 94 ppm
- Copper: 12 ppm
- Zinc: 37 ppm
- Vitamin A: 812.78 µg/100g
- Vitamin B6: 0.234 mg/100g
- Vitamin D: 34.79 µg/100g
- Vitamin E: 57.18 mg/100g
- Vitamin K: 19.83 mg/100g
Therapeutic Uses of Bhumi Amla:
- For jaundice, whole plant juice is advised. Fresh milk combined with powdered roots can also be taken for quick treatment of jaundice.
- The leaves can be mashed with salt and used as a topical treatment for skin ailments.
- For diabetes and chest pain, plant decoction proves quite beneficial.
- Ulcers are treated with a decoction of leaves or roots.
- Wounds and ulcers are treated using a mixture of the plant’s dried powder and gruel water.
- For treating leucorrhoea, gonorrhoea, menorrhoea, and other urinary problems, whole plant juice is used.
This plant’s extract can effectively treat hepatitis and may also treat human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
In addition, P.niruri has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-fungal, anti-viral, anti-oxidant, antibacterial, hypoglycemic, hypotensive, hepatoprotective, inhibitory effects on renal stone formation, and other properties.
It is used as an ingredient in nearly 175 ayurvedic formulations, and the fruits of this plant are usually used to treat haemorrhages and diarrhoea.
It’s also used to make chavanprash, face lotion, hair oil dye, and tooth powder, among other health and beauty products.2
Benefits of Bhumi Amla:
1. Benefits of Bhumi Amla Against HIV & Hepatitis B:
- Phyllanthus niruri may stop the hepatitis B virus (HBV) from multiplying by preventing the virus’s genetic material from being replicated.
- An aqueous extract of P. niruri can block HBV’s endogenous DNA polymerase by attaching to the virus’s surface antigen.
- By attaching to the virus’s surface antigen, the extract was discovered to block woodchuck (Marmotamonax) hepatitis virus (WHV) DNA polymerase.
- Surface antigen titer and DNA polymerase activity in serum were significantly decreased and abolished by the extract.
- In addition, the alkaloidal extract of P. niruri showed inhibitory action against the cytopathic effects of both HIV strains on human MT-4 cells at the doses tested.4,5
Read more: Nutmeg – Uses, Benefits & Precautions
2. Bhumi Amla For Kidney Stones & Excess Uric Acid:
- The creation, nucleation, development, and aggregation of calcium oxalate crystals in the kidney is a prevalent condition that causes urinary calculi (stone) formation.
- The extract of Phyllanthus niruri inhibits the growth and aggregation of calcium oxalate [CaOx] crystals in calculi.
- The extract inhibits calculi formation while also altering their shape and texture.
- It can produce a matrix-like material on the surface of prepared calculi, and it can change the appearance and texture of the calculus.
- The extract is also given to hypercalcemic patients, as it lowers urine calcium levels and lowers excess uric acid in hyperuricemic individuals.4
Also Read: Safed Musli – Uses, Nutritional Value & Benefits
3. Anti-cancer Activity of Bhumi Amla:
- Phyllanthus niruri has a strong potential for inhibiting cancer cell development and growth.
- However, because it prolongs cancer formation in the skin and reduces its multiplicity and yield, Phyllanthus niruri intensifies two-stage skin carcinogenesis.
- The combination of P. niruri’s cytoprotective impact on normal cells and cytotoxic effect on pre-neoplastic or neoplastic cells resulted in this action.
- In addition, potent phytochemicals, such as quercetin and rutin were responsible for a significant reduction in the prevalence of skin papillomas.4,5
Also Read: Anjeer – Uses, Benefits & Nutritional Value
4. Wound-healing & Anti-ulcer Properties of Bhumi Amla:
- According to a rat study, the development of indomethacin-induced ulcers was significantly slowed when ethanolic preparations of the herb were given orally.
- Gallic acid, beta-sitosterol, ellagic acid, and the alkaloids-4-methoxy-securinine have been linked to its anti-ulcer action.
- P. niruri extracts also prevent ethanol-induced stomach mucosal ulceration in rats and reverse dexamethasone-suppressed burn wound healing. To date, no precise mechanisms have been stated.6
Based on some research and my observations, Bhumi amla (Phyllanthus niruri) might aid in improving antioxidant levels along with stimulant activity in mild to moderate alcoholic patients.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
How to Use Bhumi Amla?
Bhumi Amla can be used in many forms such as juice, decoction, powder, paste (topical application), etc.2
According to some studies, Phyallanthus niruri (Bhumi amla) along with Emblica officinalis (Amla) and Tinospora cordifolia (Giloy) have certain bioactive compounds (around 96) that might be potential COVID-19 microbial inhibitors.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Also Read: Isabgol – Uses, Benefits & Side Effects
Side Effects of Bhumi Amla:
In general, no adverse side effects were noted in human studies. When consumed under the supervision of a healthcare practitioner, Phyllanthus niruri is likely safe.
- Phyllanthus niruri is a plant that may help to reduce blood sugar levels. However, people with diabetes or hypoglycaemia and those taking blood sugar-altering medicines, herbs, or supplements should exercise caution. Your blood glucose levels may need to be checked.
- Phyllanthus niruri has been linked to an increased risk of bleeding. People with bleeding disorders or those taking medicines that may enhance the risk of bleeding should exercise caution. You may need to modify your dosage.
- Phyllanthus niruri has been linked to a drop in blood pressure. Therefore, people who are using blood pressure-lowering medications should exercise caution.4
Precautions to Take With Bhumi Amla:
- Sedation or drowsiness may occur-exercise caution when driving or operating big machinery.
- Use it cautiously if you have liver illness.
- Use it cautiously if you’re taking diuretics, cholesterol-lowering medications, or immuno-modulators.
- Do not use if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or attempting to conceive.
- Avoid Phyllanthus niruri or members of the Euphorbiaceae family if you have a known allergy or intolerance to them.
- Phyllanthus niruri can also cause anorexia, chills, diarrhoea, disturbed sleep, fatigue, dizziness, enlarged lymph nodes, hives, fever, headache, increased sodium, potassium, and chloride in the urine, increased urine volume, lung disease, joint pain, malaise (discomfort), skin prickling, muscle pain, nausea, rash, and sore mouth.4
Also Read: Castor Oil – Uses, Benefits & Precautions
Interaction With Other Drugs:
Drug interactions of Bhumi Amla:
- Phyllanthus niruri is a plant that may help to reduce blood sugar levels. Exercise caution when taking drugs that may drop blood sugar. People who take diabetes medications or insulin by mouth should be closely monitored by a skilled healthcare professional. You may need to adjust your medicine.
- When combined with medications that raise the risk of bleeding, Bhumi Amla may increase the risk of bleeding.
- Phyllanthus niruri may lower blood pressure. Therefore, people who are using blood pressure-lowering medications should exercise caution.
- Phyllanthus niruri may exacerbate the sleepiness caused by some medications and alcohol. Driving or operating machinery should be done with caution.
- Phyllanthus niruri may interact with drugs used to treat inflammation, pain, or wounds; drugs that affect immune function; drugs that harm the liver; drugs that increase urine output; drugs that inhibit angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), angiotensin-converting enzyme receptor, or endothelin; drugs that mimic acetylcholine (a neurotransmitter); drugs that protect against radiation; drugs that treat cancer.4
Also Read: Shikakai – Uses, Benefits, Side Effects & Precautions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Bhumi Amla has various therapeutic effects like antimicrobial, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-cancer, anti-viral, anti-plasmodial and diuretic.4
Bhumyamalaki in Indian Ayurveda, dukong anak in Indonesia, chanca piedra or stone breaker in Spanish, sampa-sampalukan in Tagalog, and quebra-pedra in Portuguese are all names for Phyllanthus niruri. It’s also called gale of wind. P. niruri is known by a variety of names in India, including bahupatra, bhudhatra, ksetramali, or suksmaphala in Sanskrit, keezhar nelli in Malayalam, bhuianvala/ray avail in Marathi, bhui amla/noe in Bengali, nela nelli in Kannada, bhui avalae in Konka and Chalmeri in Hindi.5
After the first monsoon showers, Phyllanthus niruri is an annual herb that grows in the wild in Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Bihar, and other Indian states. It has, however, been observed to grow abundantly in coastal locations. It grows in Indian states during the second week of June and bears fruit until mid-July or August. It can be found in the wild till the rainy season is over. However, it can grow and live until mid-winter under safe conditions.4
References:
- Bagalkotkar G, Sagineedu S, Saad M, Stanslas J. Phytochemicals from Phyllanthus niruri Linn. and their pharmacological properties: a review. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 2006;58(12):1559-1570.
- Satya, A. & Narendra, Kumara & swathi, j & sowjanya, k.m. (2012). Phyllanthus niruri: A Review on its Ethno Botanical, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Profile. journal of pharmacy research. 5. 4681.
- Olufayo O, Tayo G, Olumide M. Assessment of the nutritive value of Phyllanthus niruri Linn. (stonebreaker) leaves [Internet]. Ajol.info. 2022 [cited 8 February 2022]. Available from: https://www.ajol.info/index.php/tjas/article/view/220739#:~:text=Phytochemical%20evaluation%20revealed%20that%20Phyllanthus,(1.40g%2F100g).
- Kamruzzaman HM, Hoq O. A review on ethnomedicinal, phytochemical and pharmacological properties of Phyllanthus niruri. Journal of Medicinal Plants Studies. 2016;4(6):173-80.
- Kaur N, Kaur B, Sirhindi G. Phytochemistry and Pharmacology ofPhyllanthus niruriL.: A Review. Phytotherapy Research. 2017;31(7):980-1004.
- Lee N, Khoo W, Adnan M, Mahalingam T, Fernandez A, Jeevaratnam K. The pharmacological potential of Phyllanthus niruri. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 2016;68(8):953-969.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.



 By
By 


















Comments