Three medicinal herbs make up Triphala (in Sanskrit, “tri” means “three” and “phala” means “fruits”). It is an antioxidant-rich herbal preparation described as a Rasayana (rejuvenator) medicine by Ayurvedic practitioners. Combining the three fruits is said to be responsible for Triphala’s numerous health benefits1.
Triphala is made from the dried fruits of:
The spring-harvested fruits of Terminalia chebula are high in tannins such as gallic acid, ellagic acid, chebulic acid, chebulinic acid, chebulagic acid, neochebulinic acid, corilagin, terchebin, punicalagin, terfavin, flavonoids (rutins, luteolin and quercetin), starches, amino acids (glutamic acid, aspartic acid, lysine, arginine and proline), β-sitosterol, succinic acid, fructose and fatty acids2.
The fruits of Terminalia bellerica consist of proteins and oils that include omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids (linoleic acid). Because of its high fatty acid content, this plant can impact cholesterol levels, increasing high-density lipoprotein levels (good cholesterol) while decreasing low-density lipoprotein levels (bad cholesterol), making it effective in treating coronary artery disease.
Phyllanthus emblica (amla) fruits are high in ascorbic acid, i.e. vitamin C2. The high density of tannins may contribute to the overall bitterness of amla. These fruits also include punicafolin and phyllanemblinin A, phyllemblin, and other polyphenols such as gallic acid, ellagic acid, flavonoids and kaempferol2.
Based on my experience, I have come across evidence suggesting that Amalaki, which is a component of Triphala, may possess properties to manage diseases of the sense organs and enhance memory. It is believed that the active compounds present in Amalaki exert beneficial effects on the central nervous system, potentially improving sensory function and memory.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Triphala is described as a tridoshic Rasayana in Ayurveda, capable of balancing and rejuvenating the three doshas that regulate human life: Vata, Pitta and Kapha. It is widely used in several disease conditions owing to its following properties1,3:
Triphala is used to treat fatigue, oxidative stress, and infectious disorders like tuberculosis, pneumonia, AIDS and periodontal disease, among others. It’s also used for headaches, dyspepsia, ascites and leukorrhea3.
In my experience, I have observed that Triphala, a herbal formulation, may have the ability to increase the number of red blood cells and improve haemoglobin content in the body, making it potentially beneficial for managing anaemia. The active compounds in Triphala are believed to stimulate the production of red blood cells, leading to an increase in haemoglobin levels and overall improvement in anaemic conditions.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Over the years, I have observed that Triphala, a herbal formulation, might have growth inhibitory activities against certain bacterial strains commonly found in HIV-infected patients. Studies have indicated that the aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Triphala, as well as its individual plant components, have shown potential antibacterial effects against these bacterial isolates.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
Haritaki, bibitaki, and amlaki are powdered to make Triphala churna (powder). As per research, it is advisable to take it with ghee, honey, or milk1.
It is made by combining the powder with water and boiling it. The decoction is then filtered through a clean cloth, and the filtrate can be used to treat skin conditions like erysipelas, eruptions, scrotal enlargement, colic pain, worm infestation, and urinary diseases. It is applied directly to open wounds and eyes, as well as gargled during pharyngitis1.
It is made by boiling Triphala powder with oil. It is used as a gargle, snuff, an enema, and orally to treat obesity and itching1.
It’s made by heating Triphala powder for a long time at a low temperature in a controlled setting. Mashi/Masi is an intermediate product containing organic and inorganic ingredients. The mashi is black and has a high carbon and oxide content. Triphala Mashi, when mixed with honey, can be used to treat soft chancres and wounds1.
It is made by cooking the paste of Triphala, trikatu (a herbal compound of Indian Long Pepper (Piper longum), Black Pepper (Piper nigrum), and Ginger (Zingiber officinale) in ghee and milk, as well as grapes (Vitis vinifera), Yestamadhu (Glycyrrhiza glabra), Kutki (Picrorhiza korroa), and cardamom (Elettaria cardamom). It is frequently used to treat eye conditions like conjunctivitis, blindness, and cataracts. Triphala gritha is also used to treat jaundice, leucorrhoea, tumours, greying, and hair loss1.
Terminalia chebula: It should not be used if you have an acute cough, diarrhoea, or early-stage dysentery5.
Triphala is an ayurvedic herbal formulation made up of dried fruits from three different plants: Terminalia chebula (black myrobalan), Terminalia bellerica (bastard myrobalan), and Phyllantus emblica (emblic myrobalan)2.
It is suggested that Triphala churna can be taken with ghee, honey, or milk1.
Yes, we can take Triphala churna with milk1.
The Triphala gritha is made by boiling the Triphala paste in ghee and milk. It is frequently used to treat eye conditions like conjunctivitis, blindness, and cataracts1.
Triphala churna has analgesic, antibacterial, anti-arthritic, hypoglycemic, antiaging, antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties. It helps with headaches, dyspepsia, fatigue, oxidative stress reduction, and infectious disorders like tuberculosis and periodontal disease3. It is also used for eye problems such as infections, blindness, myopia, and cataractogenesis1.
Yes, Triphala is good for the liver as it reduces pro-inflammatory chemicals, restores the levels of antioxidant enzymes, and reduces liver damage, as seen by lower serum enzyme values1.
It is made by grinding haritaki, bibitaki, and amlaki1.
Triphala is an ayurvedic herbal formulation made up of dried fruits from three different plants: Terminalia chebula (black myrobalan), Terminalia bellerica (bastard myrobalan), and Phyllantus emblica (emblic myrobalan or Indian gooseberry)2.
Triphala restores antioxidant enzyme levels in experimental animals, resulting in an 80% reduction in cataract formation1. Thus, it might be helpful in improving eyesight in humans, but more studies are needed to prove the same.
Yes, Triphala is good for hair. It is considered to help with hair greying and hair loss1.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Almonds are said to be one of the world’s most loved tree nuts, which are highly nutritious and filled with fats, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Most people are aware that almonds are good for your health, but the question lies, what are their health benefits?
Whether you’re enjoying ice cream topped with almonds or sipping on a glass of almond milk, this nut not only delights your taste buds but also supports a healthy diet. How can something this small offer so many nutritional benefits? Let’s see how.
Almonds are considered healthy, but how exactly do they support you in the long run? Here are some essential facts about almonds and how they can benefit you1.
Almonds are known to offer several health benefits, so what happens when you add them to your daily diet? Here are some advantages and uses of almonds.
According to a recent study2, almonds had high amounts of vitamin E and also reduced the risk of high LDL cholesterol. By boosting the levels of vitamin E in your bloodstream, antioxidants are generated that prevent the clogging of your cells. Thus consuming a handful of almonds daily can generate more vitamin E into your bloodstream, which can effectively reduce your risk of high cholesterol levels.
Eating almonds and other nuts is considered to be good for your heart. As per a recent study3, researchers found that almonds may reduce the risk of heart disease by regulating blood pressure and reducing inflammation. In fact, the Mediterranean diet, which includes a lot of nuts has been recommended for the prevention of cardiovascular disease as per American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) guidelines.
Almonds may help regulate blood sugar levels, especially in people with type 2 diabetes, as they have a low glycaemic index. They also contain magnesium, which supports insulin function and may improve insulin sensitivity. The consumption of a handful of almonds regularly may help lower fasting blood glucose and HbA1c levels3.
Low magnesium levels may be associated with high blood pressure, which may eventually lead to heart attacks, strokes or kidney failure. Almonds contain magnesium, which may help regulate blood pressure. If your body lacks magnesium, you must add almonds to your diet3.
Almonds are said to contain high levels of vitamin E, an antioxidant that protects your cells from damage. Higher vitamin E intake may help reduce the risk of conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, or heart disease. However, it is essential to consume vitamin E in moderation as the excessive intake of vitamin E may carry health risks1,2.
Almonds are high in protein and fibre, which help you feel full for a longer duration. This may help weight management by regulating your caloric intake2,3.
Almonds are nutrient-rich edible seeds and contain a healthy amount of carbohydrates, protein, fibre, fat, vitamin E, manganese, and magnesium3.
Almonds are a high source of vitamin E, which protects your eyes and may help reduce age-related changes to the lens of your eye. However, it is important to consume them in moderation as they can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excessive amounts4.
Almonds are a rich source of antioxidants that may help protect against oxidative stress, a factor associated with inflammation, cancer, ageing, and other health concerns. As per a study3, consuming about 84 grams of almonds per day can increase antioxidants in your body and may protect your body against inflammation, ageing, and other effects of oxidative stress2.
Almonds are often included in most skincare products as they have several benefits for your skin. They contain a flavonoid (that is also found in green tea and broccoli), which nourishes the skin and offers anti-ageing properties5.
Almonds may be used to make bones stronger. I strongly recommend the consumption of almonds regularly in your diet. Almonds are known for being rich in calcium and phosphorus, which may help build stronger bones9.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Almonds are high in fibre, proteins, vitamins, minerals, phytochemicals, and unsaturated fats. All these may have anti-cancer properties. Fibre supports digestion by helping the food move through the digestive system more easily, which may be a factor in reducing the risk of colon cancer. They also contain vitamin E and flavonoids that may help against breast cancer6.
Almonds contain nutrients like L-carnitine and riboflavin7, which play a role in supporting the growth of brain cells and many cognitive processes. They also contain phenylalanine, which helps cognitive function. Consuming just five almonds every morning can help you boost your brain function.
Anaemia is usually caused when red blood cells do not carry enough oxygen to the body’s tissues. Almonds contain nutrients like copper, iron and certain vitamins that support the production of haemoglobin and, as a result, may be helpful in reducing the risk of anaemia.
Almonds contain magnesium, a mineral that supports the nervous system and helps maintain a healthy metabolic rate. Magnesium is involved in keeping the bones healthy. The benefits of almonds surpass those of peanut butter.
Almonds are considered to be helpful in managing and avoiding acne, blackheads and whiteheads by regulating the oil balance of the skin due to the fatty acids in them. Applying almond oil to your skin also helps in reducing skin rashes.
Almond oil nourishes and moisturises the skin and may be useful in the management of stretch marks. You can warm up the oil, apply it to the stretch marks twice a day, and leave it on for an hour each time. Many people notice a visible difference in the appearance of your stretch marks over time with this oil.
Almond oil is commonly used as a hair care product to nourish the scalp and hair. It may reduce common hair concerns, such as hair fall and premature greying. Almond oil also supports the management of dandruff as it nourishes the scalp. Over time, it can give your hair a silkier and shinier appearance.
Almonds are a source of magnesium, a mineral that is important for many functions in the body, including hair growth. Magnesium deficiency can lead to hair loss. Including almonds in your diet can reduce hair thinning caused by low magnesium levels and boost hair growth8.
Bitter almond oil is useful in the management of joint pain, haemorrhoids, hair loss, and acne. The compound amygdalin in bitter almonds, has an anti-cancer effect. However, it is also toxic and should not be consumed in large amounts as it may cause poisoning due to its cyanide content8.
Almonds and milk both contain potassium. When combined, almonds and milk offer a potassium boost, which may support improved memory and cognitive performance7.
Almonds contain folic acid, which is essential for the growth and development of the unborn baby. Folic acid also plays a role in supporting foetal nervous system and brain development, and may help reduce the risk of neural tube defects. Thus, consuming almonds in moderation can help support healthy foetal development10.
Although almonds have a lot of calories, they may lower your risk of weight gain and obesity, provided you pay attention to portion control in your daily food intake. As a result of the good quality of protein and fibre in the nuts, you feel fuller more quickly, allowing you to consume fewer calories while still satiating your appetite. I recommend including almonds in your daily routine11.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Although almonds are good for your health, they should not be consumed excessively. Here are some of the risks associated with over-consumption of almonds.
Note: Do not consume almonds if you are allergic to them.
If you are allergic to almonds or other nuts, it is essential to educate yourself on how to manage your allergy. Here are a few basic precautions to keep in mind:
It is important to reach out to a medical professional as early as possible when faced with an allergic reaction.
Also Read: Sunflower Seeds: Nutrition, Benefits, Side Effects & More!
Almonds are a nutritious addition to a balanced diet, offering numerous health benefits when consumed in moderation. They support overall well-being but should be enjoyed with awareness of possible allergies and individual dietary needs.
Like any food, almonds should also be consumed in moderation. Eating too many almonds may lead to health issues, such as:
-Weight gain
-Digestive problems
-Kidney stones
-Nut allergies
-Symptoms of toxicity
Although almonds are considered healthy, the amount you eat should match your health goals. For example, if you want to gain weight, you can eat up to 40 almonds a day, spread throughout the day. However, if you want to manage or lose weight, just 5 almonds with a glass of milk for breakfast should suffice for you.
Almond skin contains tannin, which affects the absorption of nutrients. Soaking almonds in lukewarm water helps soften the skin, making it easier to peel and improving nutrient absorption. Soaked and peeled almonds can also be blended to make homemade almond milk.
There are two types of almonds, sweet and bitter. Sweet almonds are commonly used in everyday diet. Bitter almonds contain glycoside amygdalin, which is toxic and may even be fatal as it can release hydrogen cyanide. While almonds have many health benefits, they should be eaten in moderation. Excessive consumption, especially of bitter almonds, can be fatal. For a healthy lifestyle, you can add sweet almonds to your regular diet.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Few things feel worse than falling ill after enjoying your favourite meal. Unfortunately, this is sometimes the reality when food is not prepared or stored properly. Discomfort such as abdominal discomfort, nausea, or general digestive upset can follow, leaving you feeling unwell and drained.
While there is no instant fix for this kind of discomfort, there are simple, everyday habits that may help support your recovery and overall well-being during such times.
What many people do not realise is that some of the ingredients commonly found in their kitchen might be helpful in managing mild digestive discomfort. For example, cumin seeds, often used in cooking, may have properties that support digestion and soothe the stomach when included as part of a balanced routine1.

Apple cider vinegar is known to have antibacterial properties and may support digestive health. Some people include it as part of their home routine during periods of digestive discomfort2.
Tips on How to Consume: Add two tablespoons of apple cider vinegar to a glass of lukewarm water and drink it away. This may help stabilise the body as you recuperate from the condition.

Rich in potassium and fibre, bananas are easy to digest and make for a reliable, quick, healthy option for food poisoning3.
Tips on How to Consume: Consume one whole, ripe banana daily, or prepare a banana shake and consume the same twice every day.

Basil has several health benefits. Its antimicrobial properties can alleviate the discomfort caused by food poisoning4.
Tips on How to Consume: Consume the juice of basil mixed with a teaspoon of honey, or chew on some basil leaves along with cardamom. The combination of cardamom and basil help to ease food poisoning symptoms.
I recommend including toast in your diet if you’re dealing with food poisoning. Toast is a low-fibre food option that may help firm up your stool, making it easier on your digestive system11.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.

The seeds of this flavourful herb can help reduce stomach inflammation and ease abdominal discomfort caused due to food poisoning5.
Tips on How to Consume: Add one teaspoon of cumin seeds to a cup of boiling water. Additionally, add some freshly extracted coriander juice to it with a pinch of salt. Allow it to cool down until it is lukewarm and then drink it.

Packed with antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral properties, garlic is certainly one of the most nutritive ingredients available. One of the many benefits of garlic is that it helps detoxify your system, thus contributing to digestive wellness6.
Tips On How to Consume: Chew on a fresh garlic clove or mix the crushed cloves of garlic with a teaspoon of honey before consuming.

Lemons are a great source of Vitamin C. It helps to keep you hydrated and relieves discomfort in the digestive system. Moreover, lemon helps in detoxification, which in turn, keeps your system clean and healthy from within7.
Tips On How to Consume: Squeeze out half a lemon into a glass of lukewarm water. Add a teaspoon of honey to it and consume. Drinking this water 2-3 times a day can speed up recovery from food poisoning.

The antimicrobial and antibacterial properties of yoghurt make it an ideal food to eat. Consuming yoghurt helps to combat bacteria, which causes food poisoning. When combined with fenugreek seeds, it has a soothing effect on your stomach, the concoction provides prompt relief from abdominal discomfort8,9.
Based on my observations, when dealing with food poisoning, opting for a nourishing choice like broth and whole-wheat crackers might be highly beneficial. Broth, with its sodium and water content, may aid in rehydration, helping to replenish lost fluids. Meanwhile, the crackers might provide some bulk to your stools, easing your digestive discomfort13.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
After experiencing food poisoning, it is important to give your body the care and support it needs to recover. In addition to choosing gentle foods, here are some steps that may help speed up your recovery:
As a doctor, I highly recommend that you always check for the word ‘pasteurised’ on the containers of milk, yoghurt, cheese, and other dairy products. Pasteurisation is a crucial process that may help eliminate harmful bacteria and pathogens, ensuring the safety of these products10.
Dr. Anuja Bodhare, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Now that you know which foods may support your recovery from food poisoning, it’s equally important to avoid those that could make your symptoms worse. Start by eliminating the food that initially caused the discomfort. Then, focus on consuming food that is hygienic and safely prepared. It is advisable to avoid fried, spicy, or heavily seasoned foods, including junk food, as well as caffeinated drinks, alcohol, dairy products, and nicotine. Additionally, avoid of fruit juices, as they may irritate the stomach. While fibre is an essential part of a healthy diet, it is best to limit high-fibre foods during recovery, as they can put extra strain on your digestive system.
Adding oatmeal to your diet might be really helpful. Oatmeal is low in fibre, making it a suitable choice when you are recovering from an upset stomach12.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Food poisoning often occurs after consuming food that may be contaminated or handled improperly. During such times, it may be helpful to avoid certain types of foods that are more difficult to digest or may irritate the stomach. Items such as dairy products, spicy or heavily processed foods, fried snacks, and raw or unwashed fruits and vegetables are best limited while experiencing digestive discomfort. Opting for lighter, well-cooked meals may support overall digestive comfort. It is always advisable to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate dietary guidance, especially if symptoms continue or worsen.
Recovering from food poisoning requires both careful food choices and adequate rest for your digestive system. By opting for easily digestible, hydrating, and bland foods, you can help support your recovery. Additionally, it is crucial to avoid foods and drinks that could further irritate your stomach or prolong discomfort. While natural remedies and home care can offer relief, it is always important to consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen. Taking these steps can help you recover more comfortably and return to your regular routine when you’re ready.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Pineapple is said to have originated from South America and is rich in nutrients and antioxidants that can fight inflammation. Also, known as Ananas comosus, this healthy fruit is said to have a lot of health benefits. It contains vitamin A, vitamin K, phosphorus, calcium, and zinc that can work wonders in fighting many diseases. It’s a rich source of vitamin C that helps in maintaining a healthy immune system while its content of manganese can help regulate the metabolic rate and aid digestion. This fruit may also have several benefits for your hair, skin, and bones. This blog will give you a detailed account of its proposed health benefits and any potential side effects. It will also cover some ways in which you can use pineapple to achieve healthy skin and hair. But before that’s have a look at some interesting facts about this fruit!
Here are some interesting facts that you should know about pineapple.
Pineapple is a low-calorie fruit (83 kcal per 165 g) rich in essential nutrients. It provides 21.6 g of carbohydrates (including 16.3 g of natural sugars) and 2.3 g of dietary fiber. It is an excellent source of vitamin C (79 mg, 88% DV) and manganese (1.5 mg, 67% DV), and also contains vitamin B6, thiamin, copper, folate, and potassium in moderate amounts1. This nutrient-dense profile makes pineapple a healthy and refreshing fruit choice.
Here are some proposed health benefits of pineapple that you need to know.
Pineapple may benefit if you are suffering from a bad cold and cough. This is because this healthy fruit contains bromelain, which is an enzyme that has anti-inflammatory properties and can help fight infections2. Eating it regularly can help build your immunity and avoid cough and cold.
Pineapple is rich in manganese, which helps in strengthening your bones3. Along with manganese, it also has other nutrients like zinc, copper and calcium which can support bone health. Thus, adding this fruit to your everyday diet can help you keep your bones strong and healthy.
Pineapple is said to strengthen your gums and keep your teeth strong. Studies4 have shown that bromelain found in pineapple helps fight harmful bacteria that cause gum disease. Plus, pineapple also has a good calcium and manganese content that help in strengthening the teeth. Consuming pineapple regularly can help you achieve healthy gums and teeth.
Pineapple is also proposed to keep cancer away. This fruit has loads of antioxidants in it that can protect you from a wide range of diseases and help avoid some types of cancers from occurring. Pineapple may also have the potential to damage cancer cells, although further research is needed in this regard5.
Pineapple is a rich source of bromelain, dietary fibre, and vitamin C that help in good digestion. Bromelain consists of proteolytic enzymes that help in proper break down and absorption of food, thereby aiding in digestion. Drinking some pineapple juice or eating it every day can thus help you get rid of stomach issues.
Regular consumption of 100% pineapple juice may help reduce your risk of macular degeneration which is a condition that affects the eye as you get older6. As this healthy fruit is a good source of vitamin C and several antioxidants, it can aid in keeping your vision intact.
Arthritis involves severe pain in the joints which is primarily caused due to inflammation7. Pineapple contains bromelain which is said to have a major anti-inflammatory property and all you need to do is to make pineapple juice and drink it. This will ease joint pain and prevent you from arthritis.
If you have potential risk factors for developing cardiovascular disease such as high cholesterol levels, then eating pineapples regularly can help. This fruit has high amounts of healthy nutrients and phytochemicals that can lower lipids and reduce inflammation8. This can be a good natural way to control your cholesterol levels.
Bromelain being the major substance in pineapples may help reduce your risks of blood clots, which can avoid plaque from building in the arteries3. There, incorporating pineapple in your routine diet can be beneficial for your blood circulation and heart.
Pineapple contains enzymes that can soothe the feeling of vomitting9. This is because of its bromelain content particularly, which can help deal with nausea, motion sickness and morning sickness of pregnancy. However, it’s important to discuss with your gynaecologist before incorporating anything to your diet, especially pineapple, during pregnancy.
Pineapple contains valine and leucine which are two substances that are very important for the growth and repair of muscle tissue. Drinking one glass of pineapple juice may benefit in overcoming fatigue and boosts your stamina to keep you running the whole day. The best thing about this fruit is that it can keep you hydrated the entire day and provide all the energy you would need to run yourself.
Pineapple has tryptophan, which helps in the production of serotonin which is a natural stress buster that keeps your hormones and nerves relaxed10. Thus, including pineapple in your routine diet can help beat the stress and keep your mood elevated.
Pineapples are rich in nutrients and antioxidants that have the ability to prevent diseases that your body is prone to. Aging and oxidative damage to the body can cause chronic inflammation and weaken your immune system. Pineapple has antioxidants that can boost your immune system and protect you from many diseases3.
According to some studies11, bromelain in pineapple has demonstrated positive effects on muscle fatigue due to exercise. It can help protect muscle from damage and inflammation and is, therefore, a great way to promote muscle recovery after a workout.
Similarly, the bromelain in pineapple has also been seen to be helpful to the body when it is recovering from surgical intervention12. Bromelain is a potent anti-inflammatory compound and was also approved in some European countries for both internal and topical use on surgical wounds to facilitate faster healing.
A recent study13 on rats has proven that pineapple does have an anti-obesity effect. According to the results of this study, raw pineapple juice has been seen to prevent the deposition of fat in rats that were put on a specific diet. Thus, pineapple may have a promising role in supporting weight loss by providing a delicious and nutritious food option with low calorie content and presence of digestion-promoting enzymes.
While studies13 have shown beneficial health effects of pineapple, further large-scale human trials are needed to confirm these. Nonetheless, studies of initial research seem promising and there is a good chance that consuming pineapple routinely can show several positive effects on health as discussed.
As discussed, pineapple is good for your overall health and similarly, it is also good for your skin and hair too. Pineapple extracts can help rejuvenate your skin. It may be helpful for conditions like skin rashes or skin damage, and make you skin look clean and fresh. It also helps keep your hair and scalp healthy.
Here are some potential benefits of pineapple for your skin and hair.
Pineapple extracts may help fight acne and other skin infections. Studies14 have shown that application of bromelain extracted from pineapple skin can be beneficial in fighting microorganisms causing skin infections and manging acne.
The older you get your skin begins to lose its glow and you will begin to develop wrinkles. Pineapple is a rich source of antioxidants and vitamin C that are said to boost skin elasticity and hydrate your skin15. Alpha-hydroxy acid in pineapple helps delay the death of cells, thus aiding in anti-ageing capabilities.
Pineapple has loads of vitamin C and antioxidants that can help deal with sun damage and uneven skin toning. Pineapple extracts can help exfoliate dead skin and flush away the toxins from your face, thus making your skin look vibrant and clean.
Pineapple may help reduce black spots on your face by rubbing it over the spots. A study16 involving long term application of pineapple extract cream showed that it helped in reducing pigmentation and dealing with conditions like dermatitis and greasy skin.
Pineapple contains antioxidants that are responsible for softer and shinier hair. Its vitamin C content deal with brittle and dull hair and also aids in improving the thickness and elasticity of your hair. Thus, pineapple can help in promoting strong, healthy and lustrous hair.
Pineapple ranks high in the list of foods rich in vitamin and mineral content. Vitamin C, that promotes the growth and repair of tissues, is present in pineapple in nearly one-third of the daily required quantity. Studies10 show people taking vitamin C regularly may be able to fight cancer, heart disease, and arthritis. Vitamin C is known to possibly strengthen your immune system as well.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Pineapple has vitamin C that helps build collagen and makes your hair strong, potentially avoiding hair fall. The enzymes present in this fruit can also help improve blood circulation and enrich the hair follicles, thereby helping in new hair growth.
Pineapple extracts can help ease inflammation in your scalp. If you are suffering from severe itching on the scalp, applying this can give you instant relief. It may help deal with dandruff or inflammatory skin conditions such as dermatitis affecting the scalp and promote its health17.
Although natural remedies like applying pineapple and its extracts can help promote skin and hair health, if you’re suffering from any skin conditions or have symptoms such as itchy scalp or extensive hair fall, it’s ideal to consult a dermatologist first. They can help diagnose the underlying cause of your condition and suggest appropriate management strategy.
Here are a few preparations that use pineapple to help you take care of your skin and hair.
Mash half a medium-sized pineapple with 2-3 tablespoons of yoghurt and olive oil until a smooth paste is achieved. Apply the mask by massaging it into your hair and leaving it in for about 20 minutes. The pineapple enzymes will help to nourish your follicles and give you with thick strong hair while the mix of olive oil and yoghurt can give your hair shine and help manage scalp irritation.
In a blender, mix gram flour, pineapple, and oatmeal till it reaches a grainy consistency, then apply to your face gently while slowly massaging in a circular motion. Do not leave the face mask on for more than 10 minutes. The mixture of pineapple for skin is an all-round facial care scrub. Pineapple and gram flour have been known be great for complexion, helping reduce dark spots and evening out the skin tone. The gram flour and oatmeal also work together to absorb excess facial oils while cleansing the skin surface.
Make a mash of pineapple and turmeric and apply to zits, pimples, and cuts on your skin. Due to Bromelain in pineapple, it helps in wound repair while turmeric helps reduce inflammation and aids in wound healing. Together ,these two ingredients can help your skin recover quickly while using natural ingredients.
Researchers believe pineapple provides a healthy serving of the vitamin B complex including thiamin, niacin, B6, and folate. These vitamins and minerals may assist your body in converting food into usable energy. Additionally, they are essential for the production of new red blood cells that carry oxygen to your organs and tissues3.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Also Read: 12 Incredible Health Benefits of Bananas
While pineapple has many potential health benefits, it may have some side effects too. These include:
Also Read: Best Home Remedies for Hair Growth
Pineapple is a nutrient-dense, multipurpose fruit, full of essential nutrients and antioxidants.
There are numerous proposed health advantages of pineapple, including improved digestion, increased immunity, and even lowering risks of certain cancers. It is found to be great for the skin and hair too! Although further studies are needed to confirm its health benefits, pineapple seems to show promising results and can be incorporated in routine diet. However, despite the benefits, consumption in moderation is key to prevent any side effects of pineapple. Also, if you have any medical conditions or are on certain medications, it’s best to discuss with your healthcare provider before including pineapple or any other food item in your routine diet.
Also Read: Health Benefits of Garlic (Lahsun)
Of course, consuming pineapples are good for your overall health, but this fruit must not be consumed in excess as it can lead to several health problems such as:
-Diarrhoea
-Vomiting and nausea
-Skin Rashes
-Excess menstrual flow
-Swelling in your cheeks and mouth
Note: Bromelain is a major substance that is found in pineapples and this has its merits and demerits probably if you do not consume this fruit in excess. So, make sure that you drink only one glass of pineapple juice every day and this will do you good.
Well, the answer is no because this can make you feel very uncomfortable if you do not have the habit of consuming pineapples for every breakfast. Make sure that you complete your breakfast and then consume some fresh pineapple juice and this would do you good. Consuming it on an empty stomach can result in acidity.
Pineapple may offer relief during periods due to its anti-inflammatory properties and bromelain content, which could help alleviate menstrual cramps. However, individual responses vary, and it’s essential to consider personal health and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Pineapple can be included in a diabetic diet in moderation due to its low glycaemic index and high fibre content, which may help regulate blood sugar levels. However, it’s crucial for individuals with diabetes to monitor their carbohydrate intake and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized dietary recommendations.
No, pineapple thorns are not poisonous. The outer skin of a pineapple may have sharp spines, but they are not harmful if handled carefully.
Pineapple can be included in a kidney-friendly diet as it is low in sodium and provides essential nutrients. However, individuals with kidney issues should consult their healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate amount based on their specific dietary needs.
While there’s no direct evidence that pineapple increases sex drive, its nutritional content, including vitamin C and manganese, can contribute to overall well-being, potentially indirectly supporting aspects of sexual health. However, individual responses vary, and lifestyle factors play a significant role in libido.
Yes, you can freeze pineapple. Cut it into bite-sized pieces, spread them on a tray to freeze individually, then transfer to a sealed bag or container for convenient, frozen pineapple whenever needed.
To determine if a pineapple is ripe, look for vibrant green leaves at the crown, a sweet aroma at the base, and a slightly firm texture with a little give when gently squeezed. Additionally, the golden colour at the base of the fruit can indicate ripeness.
While some believe pineapple may induce labour due to the enzyme bromelain, there is limited scientific evidence to support this claim. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before attempting any natural methods to induce labour during pregnancy.
Pineapple juice may help reduce swelling due to its bromelain content, which has anti-inflammatory properties. However, it’s essential to consume it in moderation, and consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable for personalized advice on managing swelling.
No, pineapple leaves are generally not considered poisonous, but they are tough and indigestible. It’s crucial to avoid consuming them. For personalized health advice, consult with a healthcare professional.
No, pineapple eyes are not edible as they are tough and fibrous. It’s advisable to discard them before consumption. For personalized health advice, consult with a healthcare professional.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
The liver is one of the most hardworking but undervalued organs in the body. While much attention is given to heart health, weight loss, and glowing skin, it is the liver that performs approximately hundreds of essential functions. These include storing nutrients like sugar, minerals, and vitamins to fuel the body; controlling the production and excretion of cholesterol; producing bile, which is stored in the gallbladder and helps break down fats1; and filtering out harmful substances, such as alcohol, medicines, and environmental factors2.
Just like the heart, the liver can also be stressed; however, unlike heart problems that may show early signs, the symptoms of a distressed liver show up very late. The liver is stressed when it is overworked and becomes sluggish.
So, how do you understand if the liver is in distress? Here are 17 symptoms that may indicate your liver is under stress:
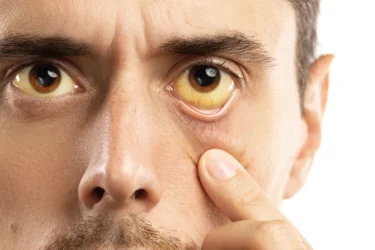
Skin discolouration may sometimes be linked to liver problems. If your skin colour changes to jaundice yellow or pale with a blue tinge, your nails or fingertips turn yellow, or you have yellowing of the eyes, it is advisable to visit a doctor. This change in colour occurs because the body is unable to flush out the toxins, which leads to bilirubin accumulating under the skin, causing skin discolouration3.

Feel bloated frequently and have constipation too? Frequent indigestion may be associated with liver issues. With bloating, you may experience stomach pain as well4. This happens because the bile is unable to break down the food during digestion.
Another important sign is Spider naevi. Spider naevi or angiomas are small clusters of blood vessels that form just beneath the skin, often spreading outward like a spider’s legs. Angiomas typically appear red or purple in colour. These are often present in excessive numbers in people with liver disease.
Dr. M.G. Kartheeka, MBBS, MD (Pediatrics)
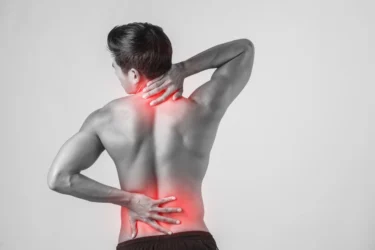
The liver plays an essential role in filtering blood and supports the synthesis of many nutrients needed for good health. However, when the liver is stressed, it may affect the synthesis and delivery of nutrients to muscles, tissues and tendons. This may lead to symptoms such as muscle cramps, weakness, and fatigue5.

Do you feel tired all the time? Persistent fatigue may occur when the liver isn’t functioning efficiently. When the body is under continuous strain, it may place additional pressure on the liver and other organs, leading to persistent tiredness. It is best to get your liver checked at this point5.
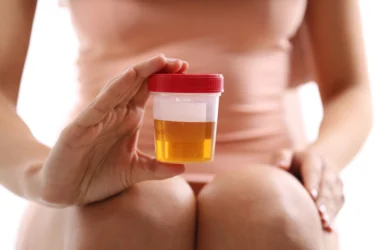
Is your urine darker than usual? It is possible that this may be due to inadequate water intake, which may cause your stools to be darker too. If you start drinking enough water and the colour of your urine and stool lightens, all may be well. However, if your urine and stool colour are still dark, you should seek medical help as this may be caused by liver problems5.
The culture of fast foods these days is slowly damaging the liver due to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Avoiding refined sugar and fast foods and eating before dusk helps a lot in prevention of fat accumulation in the liver, which can allay liver stress symptoms (by promoting weight loss).
Dr. Nikhil Yadav, MBBS MD, CCEBDM

When the liver is stressed, some individuals may experience mood changes or emotional disturbances, such as irritability, anxiety, mood swings, and depression, and some may even experience cognitive impairment, meaning their memory, attention span, and decision-making may be affected6.

Another potential liver distress symptom is little-to-no interest in food. A reduced desire to eat is often caused by an underlying health issue and should be taken seriously5.

Although irregular sleep pattern is a common occurrence amongst millennials due to a stressed lifestyle, a study7 found that liver cirrhosis was responsible for unusual sleep patterns in many patients.

When you have liver problems, the liver may not be able to purify your blood adequately. When toxins are not removed from the blood, it may lead to symptoms like memory loss, difficulty thinking, and confusion5.

Abnormal skin itchiness may be a symptom of liver cirrhosis3.

Liver disease tends to develop over time, slowly replacing healthy liver tissue with scarred or damaged tissue. This affects liver function and changes the metabolism, hormonal balance, and many other factors, which may lead to weight gain8.
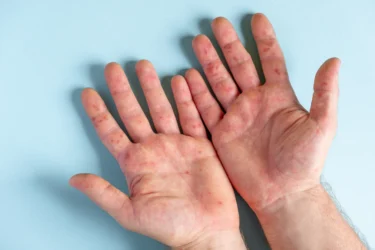
Experts believe that when you develop nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (liver disease not associated with alcohol), your palms start to turn reddish, an outward indicator of liver dysfunction3.

Another probable symptom of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is the enlargement of breasts in men. Although the exact cause of this is unclear, it is speculated that this may occur due to excess production of the female hormone, oestrogen, in this condition9.

Liver damage also manifests in the form of easy and sudden skin bruises and even bleeding5.
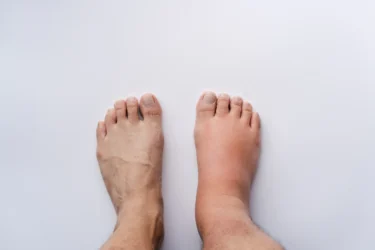
Swelling in the ankles and feet may also be associated with liver dysfunction. There may also be abdominal swelling due to the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen5.
Liver function tests are commonly recommended blood tests for measuring different enzymes, proteins and other substances made by the liver. Changes noticed in liver function tests should be reviewed by a physician to find the cause and manage the condition.
Dr. Ashish Bajaj, M.B.B.S., M.D., in Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology

Experiencing chills is often a natural response of the body when the mercury drops or when you are developing a fever. However, if none of this fits the bill, it could indicate cholestasis (blocked or reduced bile flow) associated with liver disease10.

When the liver is under stress, it can disrupt many bodily functions and may be associated with symptoms such as ringing in the ears, sleep disturbances, dizziness, blurry vision, allergic reactions, gastrointestinal bleeding, reduced sex drive, unexplained weight changes, sensitivity to chemicals, and the appearance of spider veins11,5.
Also Read: Natural Home Remedies for Fatty Liver
A healthy liver is important for overall well-being, as it supports many essential functions like the storage of nutrients, digestion, and filtering blood. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms mentioned in this article, it is advisable to consult your doctor or a liver specialist today to identify the cause of your symptoms and support the timely management of liver issues.
Also Read: What is Hepatitis A? Causes, Symptoms, and How It Spreads
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
It is well known that fruits are a valuable part of a balanced diet. They have great nutritional value and are packed with vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fibre. However, simply eating several fruits at random times may not always offer the full range of nutritional benefits.

If you are unsure about what to include in your breakfast, fruits are always a simple and nutritious choice.
Research suggests that due to the high fructose content in fruits, the best time to eat fruits is in the morning after your body has rested through the night and needs a quick boost of energy1.
Fruits are generally easy to digest and may be suitable to consume on an empty stomach for some individuals. Including them early in the day can be a convenient way to support your daily intake of vitamins and minerals.

If you enjoy snacking between meals, fruits can be a wholesome and refreshing option. Mid-morning or mid-afternoon is often a suitable time to enjoy fruits, especially when you’re looking for a light and natural choice of snack until your next meal.
Fruits are naturally rich in fibre, which can help you feel satisfied. When paired with a small serving of nuts or seeds, they can make for a balanced and enjoyable snack.
Including fruits between meals may also help support your daily intake of essential nutrients without relying on processed alternatives2.
According to the research, women reported that the intensity of pain due to irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) was decreased by including bananas before meals daily. In my experience, kiwi fruit may be useful as well and from my knowledge, bananas and kiwis are well known for their antioxidant properties which may help some individuals with IBS feel better and have better digestion.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S M.D (Ayu)
While fruits are a healthy part of a balanced diet, there may be times when it’s better to be mindful of when you consume them.
Eating fruits just before going to bed might not be suitable for everyone. Consuming fruits right before bedtime can spike your blood sugar levels which may not align with the body’s need to wind down at night. Some individuals find that eating late at night, including fruits, may affect their sleep routine.
It is generally advised not to combine fruits with heavy meals, as it may slow down the process of digestion. Allowing at least an hour or two after between eating fruits and having a full meal may help with comfortable digestion3.
While all fruits have their unique benefits, certain types are particularly rich in important nutrients such as vitamin C, folate, potassium, and small amounts of other vitamins like E, K, B5, and B64.
The following are commonly recognised for their natural nutrient content5:
These fruits provide a combination of vitamins, minerals, fibre, and natural sugars. Incorporating a variety throughout the day, at times suitable to your routine and digestion, may help you meet your daily nutritional needs6.
Certain fruits, when consumed in moderation prior to a meal, may help support digestion and provide a soothing and cooling effect. I recommend having small pieces of amla at the beginning, middle, and end of your meals8.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
Fruits are a versatile and naturally flavourful addition to your diet. While they can be eaten raw, juiced, pulped, or added to smoothies, eating fruits in their raw form retains their natural fibres, which may support digestion and also provides texture and freshness7.
Here are a few simple and delicious fruit-based snack recipes. These combinations offer a balance of sweet and tangy flavours, making them enjoyable at any time of day.
Preparation:
Preparation:
It is ideal to refuel with nutritious carbohydrates minutes before working out. I suggest eating an apple or a banana preferably five to ten minutes before your workout. This will help your muscles to replenish the fuel you’ve used. Of course, you should also drink water to replenish the fluids you lost while perspiring.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Including a variety of fruits in your daily diet is a simple and enjoyable way to support overall wellbeing. When consumed mindfully and at the right times, fruits can enhance both flavour and nutrition in your meals. Ensure to consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your diet.
1. Lesani A, Mohammadpoorasl A, Javadi M, Esfeh JM, Fakhari A. Eating breakfast, fruit and vegetable intake and their relation with happiness in college students. Eating and Weight Disorders – Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity [Internet]. 2016 Feb 29 [cited 2025 May 21];21(4):645–51. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/296475425_Eating_breakfast_fruit_and_vegetable_intake_and_their_relation_with_happiness_in_college_students
2. Potter M, Vlassopoulos A, Lehmann U. Snacking Recommendations Worldwide: A Scoping Review. Advances in Nutrition [Internet]. 2018 Mar 1 [cited 2025 May 21];9(2):86–98. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5962965/
3. Visvanathan R, Williamson G. Effect of citrus fruit and juice consumption on risk of developing type 2 diabetes: Evidence on polyphenols from epidemiological and intervention studies. Trends in Food Science & Technology [Internet]. 2021 Sep [cited 2025 May 21];115:133–46. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/352556999_Effect_of_citrus_fruit_and_juice_consumption_on_risk_of_developing_type_2_diabetes_Evidence_on_polyphenols_from_epidemiological_and_intervention_studies
4. Slavin JL, Lloyd B. Health Benefits of Fruits and Vegetables. Advances in Nutrition [Internet]. 2012 Jul 6 [cited 2025 May 21];3(4):506–16. Available from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3649719/
5. (PDF) Fruits and Vegetables and its Nutritional Benefits [Internet]. ResearchGate. [cited 2025 May 21]. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343846823_Fruits_and_Vegetables_and_its_Nutritional_Benefits
6. Harris J, de Steenhuijsen Piters B, McMullin S, Bajwa B, de Jager I, Brouwer ID. Fruits and Vegetables for Healthy Diets: Priorities for Food System Research and Action. Science and Innovations for Food Systems Transformation [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2025 May 21];87–104. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/366786007_Fruits_and_Vegetables_for_Healthy_Diets_Priorities_for_Food_System_Research_and_Action
7. Fardet A, Richonnet C. Nutrient density and bioaccessibility, and the antioxidant, satiety, glycemic, and alkalinizing potentials of fruit-based foods according to the degree of processing: a narrative review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition [Internet]. 2019 Nov 1 [cited 2025 May 21];60(19):3233–58. Available from: https://hal.science/hal-02373211
8. S D, N R V, Mishra A. Traditional methods of food habits and dietary preparations in Ayurveda—the Indian system of medicine. Journal of Ethnic Foods. 2019 [cited 2025 Jun 12]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42779-019-0016-4
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
People these-days are getting very particular about their health and are focusing on natural ways to build their immunity. Their attention is diverting towards consuming a good diet rich in essential nutrients which helps strengthen the immune system, and the mineral zinc plays a crucial role when it comes to boosting immunity and improving health.
Zinc is a trace mineral that plays an important role in many body functions. About 60% of zinc is present in the muscles, 30% in bone, hair, skin and plasma, and some in organs like pancreas, liver, kidney and brain. Zinc is essential for healthy immunity because of its role in the activation of T lymphocytes and enhancing functioning of natural killer cells (major components of your immune system). It is also vital for over several enzymes in the body, and plays a role in protein synthesis, wound healing, DNA synthesis, and is necessary for a proper sense of taste and smell1.
Zinc deficiency is a common issue because your body doesn’t store it, so you need to get enough zinc from your daily diet. Knowing the right food items to choose can help boost your zinc levels and maintain proper functioning of the body including immune support. In this blog, we will discuss about some food sources that are rich in zinc and can keep your health in good shape.
Before we move onto the sources, let’s understand the daily requirement of zinc by our body.
Actually, only a small amount of zinc is needed to maintain good health. According to ICMR 2020, the recommended daily allowance of zinc for women is 13.2 mg and for men is 17mg. For pregnant women, the recommended daily intake of zinc is 14.5 mg, and for breastfeeding women, it is 14.1 mg2.
Though the requirement of zinc by the body is minimal, it is essential for proper functioning. Low levels of zinc may cause diarrhoea, stunted growth, hair fall, eye, and skin lesions, loss of libido, and suppressed immunity.
I may suggest a fantastic option for all the veggie lovers out there who want to ensure they’re getting enough zinc: raw green peas! These vibrant little green gems might not only be delicious but are also packed with this essential mineral. In fact, 100 g of raw green peas may provide you with approximately 1.24 mg of zinc19.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Animal foods are considered to be the best sources of zinc. Since there are lesser plant-based sources of zinc available, vegetarians are more likely to fall short on this mineral. However, there are some best plant-based sources of zinc available for vegetarians. These include the following –

Indians commonly use chickpeas in their meals. If you want to fill your zinc requirement without eating meat, then chickpeas are the best option. A small cup containing 100g of raw chickpea will provide 2.7 mg zinc3. You can use chickpeas in curries, salads, or snacks.
I would recommend boiled lima beans if you’re looking to boost your zinc intake. These mighty legumes might not only provide a burst of flavour but may also offer a valuable source of this essential mineral. They boast an impressive 1mg of zinc per 100 g of boiled lima beans18!
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS

Lentils are the best source of zinc. They are also low in fat and calories, and contain essential nutrients like proteins and fiber. A cup of approximately 100gms contains zinc about 3.31 mg in whole and 3.6 mg of in dal lentil4. Use them in regular meals in the form of curries.

Pumpkin seeds are super versatile and easy to add to countless meals. 100gm of pumpkin seeds contain 7.8 mg of Zinc5. Consuming a diet rich in pumpkin seeds could increase immunity and fight inflammation in the body.

While having fresh watermelon juice, don’t throw its seeds. Believe it or not, watermelon seeds are highly nutritious, containing zinc and other micronutrients. 100gm of watermelon seeds contain 10.13 mg to 10.24 mg of zinc6, you can dry them and eat them as a daily snack. These seeds help enhance immunity and may aid in keeping your heart healthy.

Sunflower seeds are a rich source of zinc. About 100g of sunflower seeds contain 5mg of zinc7. These can also be healthy for your heart and boost energy levels. Sunflower seeds can be consumed raw or roasted. You can add them to seed trail mix or oatmeal porridge for a tasty and healthy snack.

Hemp seeds are loaded with unsaturated fats and zinc. 100g of chia seed gives 7mg of zinc9. Hemp seeds are also rich in amino acids arginine, which may help to reduce the risk of heart diseases. Try sprinkling them on yoghurt or salads.
Based on my experience, if you’re on the lookout for a zinc-rich food, look no further than chia seeds. These tiny seeds might not only be versatile but also packed with nutrients, including zinc. Just 100 g of chia seeds may contain 4.58 μg of zinc8, making them an excellent option for all the veg folks out there.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.

Beans are another excellent source of zinc, especially kidney and black beans. These beans are also high in soluble and insoluble fibers, proteins, iron, phosphorus, and calcium that support overall health. A cup of black beans (100g of raw rajmah) contains 3.08 mg of zinc, and a half cup of cooked kidney beans contains 0.9 mg of zinc. While 100g raw Cowpea (chawali) and moog dal will give 3.57 mg and 2.49mg of zinc, respectively.

Oats are the classic breakfast because it is a nutrient-dense food item. Oatmeal is loaded with zinc, fibers, folate, vitamin B6 and beta-glucan. About half a cup of oats contains 1.3 mg of zinc10. Oats can also help regulate cholesterol levels and keep your heart healthy.

Cashews are one of the delicious options to get natural, plant-based zinc. Whether you eat them raw or roasted, you will get about 5.34 mg of zinc from 100g of cashew nuts (approx. 6 number (14.5g) will provide 0.77mg of zinc). They are rich in vitamin A, vitamin K, copper, folate, and healthy unsaturated fat. Eating cashews may also be healthy for the heart by promoting good cholesterol11.
I may have a great recommendation for all the vegetarians. Did you know that pecans might be an awesome choice to get your zinc fix? These tasty nuts might not only make a delightful snack but may also pack a punch when it comes to getting your zinc dosage. Only 100 g of pecans may contain a whopping 4.53 mg of zinc17!
Dr. Anuja Bodhare, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)

Almonds are not just excellent sources of energy they’re also jam-packed with nutrients. Almonds are great sources of zinc, protein, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus and fiber. A handful of almonds can be a healthy, energy-rich snack as well as an easy way to boost your zinc levels. 100g of almond gives 3.5mg of zinc (12 number or 14g will give 0.49mg of zinc). Almonds can also be added to a variety of dishes, from desserts to Mughlai cuisine.

A low-fat curd or yoghurt gives us good bacteria for a healthy gut and also provides enough amount of zinc. A cup of curd or yoghurt contains 1.5 mg of zinc. It is best for digestion and for boosting your immunity13.

Dark chocolate is loaded with zinc. A hundred grams of dark chocolate contains 3.5 mg of zinc12. But dark chocolate is also rich in calories and sugar, therefore consume it in moderation.
I may advise incorporating flax seeds in your diet if you’re looking to up your zinc game. These tiny wonders are not only packed with goodness but also happen to be a fantastic source of zinc. With a generous 4.34 mg of zinc per 100 g, they may be an excellent choice to fulfill your nutritional requirements16.
Dr. Ashok Pal, BAMS

Soyabean is a popular vegetarian as well as vegan food option that offers a good amount of zinc per serving. About 100 grams of this can contain about 4.01mg of zinc14. Moreover, Soyabean can be used for several different kinds of recipes, making it a versatile source of zinc Tofu prepared from soyabean can be a good option suitable for several recipes.

Any type of unprocessed rice, be it brown, red or black is a good source of zinc for vegetarians. This type of rice is also known as wild rice and it provides 1.6 mg of zinc in every 100 grams. You can sauté them with veggies to make a wholesome meal.

This list is incomplete without this green leafy vegetable that is often considered the best source of vitamins and minerals for vegetarians15. It provides about 4 mg of zinc in every 100 gms of serving, making it one of the healthiest foods on this list.

Last but not least, button mushrooms and shiitake mushrooms are also high sources of zinc. In a 100-calorie serving of white button mushrooms, there is about 8 mg of zinc. In a similar 200-calorie serving of shiitake mushroom, there is 5 mg of zinc. Along with an attractive umami flavour, these mushrooms can also be considered a great vegetarian source of zinc.

The cover or top part of grains is usually one of the most mineral-rich parts of the seed. Typically, during the production of refined flours, the germ is removed, lowering the nutrient value. Apart from having a good amount of zinc, these also contain numerous vitamins, minerals, and ample fiber making it a healthy food choice.
100g of whole wheat gives 2.85 mg of zinc, which means one medium size chapatti (25g of wheat flour), gives 0.71mg of zinc.
Other whole grains like samolina (rawa) 100gm gives 2.13 mg of zinc, 2 tbs gives 0.63 mg of zinc (around ¾ cup of upama /sheera ).
Bajara is also good source giving about 2.76 mg of zinc /100g.

Moong is a type of bean also called moong dal and is consumed widely across India. It can be eaten raw, boiled, sprouted or whole. Moong has a zinc content of about 2.6mg per 100g. This makes it an excellent source of zinc, a daily serving can provide up to 24% of your daily requirement. Sprouted moong is the healthier option as it offers better absorption of minerals like zinc.
Moreover, Indian spices like ajawain (5.67mg ), mustard seeds (4.03mg ), khus khus seed ( 6.38mg ) / 100g are also good source of zinc. Adding these to your favourite dishes doesn’t only enhance the taste but also adds on the health benefits.
Zinc is an essential mineral required by the body for proper functioning. Zinc is present in many natural sources such as meat, seafood, beans, legumes, seeds, and nuts. If you are vegetarian or vegan, then you need to increase your intake by eating plant-based sources like cereals. These foods are easily available and delicious addition to your routine diet. Adding zinc-rich foods to your diet is a natural way to support your immune system and keep infections at bay. However, if you feel you have a low immunity, consult your doctor to understand the underlying cause and appropriate management.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
In a bid to lead a healthy life, we keep trying different hacks and healthy concoctions. Besides promising countless health benefits, they also claim to detoxify the body and help in weight loss. Although many of these remedies may not work well enough to match-up to the claims, there are some which have proven benefits! And one such drink is cumin or jeera water.
Jeera’s health benefits are well documented in the traditional ayurvedic texts, and a significant part of these has been verified by modern science as well. Jeera seeds have been used in most Indian kitchens since ancient times. This spice adds a nutty and earthy flavour to foods and is said to be packed with several health benefits. One of the easiest way to experience the benefits of this wonder spice is to consume the jeera seeds soaked in water.
In this blog, we will discuss in detail about the potential benefits of jeera water, how and when to consume it and if there are any precautions and risks you must be wary of when considering jeera water in your routine diet. So, let’s get started!
Before we move onto the benefits, let’s first see how to prepare jeera water.
To prepare jeera water, all you need to do is soak a handful of cumin seeds in water and let it rest overnight. Being soaked for that long, the seeds swell up and release bioactive compounds into the water. Consuming this concoction in the morning everyday can help support your overall health in several ways.
Here is how it can help and why it is an ultimate detox drink:
Jeera is naturally low in calories. One teaspoon of jeera seeds contains only about eight calories1! That’s very low compared to other beverages.
Cumin seeds are loaded with antioxidants that play a significant role in fighting oxidative stress. Extracts of cumin seeds are rich in polyphenols and numerous other compounds, which help detoxify the body by eliminating toxins from the system but also help boost immunity2.
Drinking jeera water regularly helps keep the digestive system healthy, which in turn, keeps the overall body functioning on track. It helps to break down complex nutrients like proteins, fat, and sugar to keep your gut healthy, and may keep digestive issues such as bloating, indigestion, diarrhoea, and nausea at bay. Jeera seeds have been found to be helpful in relieving symptoms in digestive issues like Irritable Bowel Syndrome3.
Jeera or cumin is believed to lower appetite and accelerate body metabolism to promote fat burning, aiding in weight loss efforts2.
A daily exercise routine, however simple it is, keeps the body fit and helps in fat-loss. Jeera water can add to the calorie-burning effects of following a regular exercise regime, not to forget a balanced diet to complete the overall health benefit!
Studies have shown that cumin seeds have anti-inflammatory properties due to the presence of bioactive compounds. These can help regulate the mediators of pain and inflammation in body and prove to be helpful in managing symptoms and alleviating conditions like arthritis and kidney disease2,4.
Jeera water is proposed to have anti-cancer properties. It reduces the risk of a variety of cancers and helps avoid metastasis, which is the spreading of cancer to other parts of the body5.
Jeera water can help improve insulin sensitivity, that is the utilization of blood sugars by body cells. It also helps enhance insulin secretion and avoid sudden spikes in blood sugar levels, thus aiding in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus6.
Jeera water helps in hydrating the body. The water content also helps to flush out toxins from the body.
Cumin seeds are said to be gastro-protective. They contain compounds which help neutralise stomach acids and are effective in reducing acidity and mitigating its symptoms like heartburn, pain, nausea, bloating, constipation, etc2.
Cumin seeds are rich in iron. Iron is required for the formation of haemoglobin in the blood, which is further essential for the transport of oxygen in the body. Drinking jeera water regularly helps to reduce the risk of and deal with the symptoms of anaemia such as fatigue and breathlessness7.
Jeera water helps in regulating blood pressure, triglycerides, and cholesterol levels in the body. These are essential to keep the heart heathy. Moreover, jeera seeds are rich in antioxidants that can help keep the heart protected from various disorders8.
Jeera water is proposed to contain antioxidants and antimicrobial compounds which can help detoxify the body. It lowers acne risk and protects the skin from infections, thus supporting a healthy and glowing skin.
Jeera water is good for the hair as well. It strengthens hair and helps avoid hair loss, dandruff issues and premature greying of hair. However, these could be signs of an underlying medical condition and should be examined by a dermatologist before resorting to home remedies.
Many women face discomfort during their menstrual cycles having symptoms such as backache, fatigue and cramps. It is found that drinking jeera-infused water can beneficial in relieving these symptoms. Traditionally, cumin seeds were also believed to regularise menstrual blood flow by stimulating the uterus to contract and releasing any trapped blood, although there is no scientific evidence to these claims9.
Also, jeera is also believed to support milk production in lactating women. It is enriched with iron, which is healthy for consumption by lactating women.
Cumin water when drunk with a teaspoon of honey and black pepper works is believed to work as a great aphrodisiac tonic in traditional medicine.
Although studies have shown potential benefits of jeera water, further large-scale human research is needed to prove these claims. Also remember, if you have any medical condition or are any facing symptoms, always consult your doctor before initiating any home remedies.
A good source of dietary fibre is found in jeera (cumin) water, which may aid with piles and constipation. Studies10 have revealed that constipation, combined with infections in the anal tract, which are also brought on by constipation, is the primary cause of piles. Jeera has carminative, stimulant, anti-fungal, and anti-microbial qualities due to the presence of essential oils that contain cuminaldehyde and various pyrazines. Thus, jeera water may promote natural urination, aid in the recovery of infections or wounds in the digestive and excretory systems, and quicken digestion.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)
Consumption of jeera water at the beginning of the day, after waking up, is the optimal time to do so. The benefits of jeera water on an empty stomach early in the morning include aiding in digestion, reducing any bloating and potentially being beneficial for weight loss. The drink can be consumed any time throughout the day, but the maximum benefits of jeera water can be availed when consumed early in the day.
Since cumin or jeera water has a bland taste, you can try having it with a pinch of lemon juice or cinnamon powder. This will make the detox water appealing to your taste buds, as well as your health goals.
Jeera water may have several health benefits, yet excess consumption can be harmful and may lead to side effects like:
The consumption of jeera increases the release of more gas in the gastrointestinal tract. The excessive release of gas is attributed to causing heartburn in some individuals.
People who are susceptible to hypoglycaemia should be wary of the consumption of cumin water. Cumin has the tendency to reduce blood sugar levels. The consumption of cumin water can reduce blood sugar levels to a great extent which can offset hypoglycaemia. Thus, if you have diabetes, kindly check with your doctor or nutritionist before starting the same.
High levels of jeera water consumption during pregnancy may have the possibility of increasing the chances of a miscarriage or inducement during labour. Pregnant women should limit their consumption of jeera water and discuss with their gynaecologist before consuming the same.
Cumin has the possibility of slowing down the process of blood clotting in the body. This can increase the bleeding time from cuts and bruises. If you are consuming blood thinning medication, then its best to avoid cumin water.
Jeera is an amazing condiment that has a host of health benefits, yet consumption in moderation is the best way to see its effects on the body. Jeera water may work wonders for the body, however, a healthy lifestyle goes a long way in keeping you healthy and fit.
It is believed that jeera simultaneously acts as a stimulant and a relaxing agent. Research10 indicates that a healthy diet, adequate vitamin intake—particularly B complexes—and excellent digestion, with jeera supplementation contribute to restful sleep. In ancient Ayurvedic medicine, jeera water is consumed before bed to promote restful sleep.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Also Read: Top Health Benefits of Buttermilk
In conclusion, jeera water is a remarkable drink packed with numerous health benefits, making it an excellent addition to a healthy lifestyle. From aiding in weight loss and improving digestion to boosting metabolism and reducing inflammation, this simple concoction potentially offers a range of advantages. Incorporating jeera water into your daily routine, along with a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help contribute to your overall well-being. However, it is essential to consume jeera water in moderation to avoid potential side effects. Also, if you have any medical condition, it is always advised to consult your healthcare provider before incorporating jeera water or any other home remedies in your routine.
Also Read: 10 Benefits Of Drinking Water From Copper Bottle Vessels
Jeera water itself is very low in calories. The main calorie content would come from the cumin seeds (jeera) used to make the water. Typically, 1 teaspoon of cumin seeds contains around 8 calories. However, the number of calories in jeera water as a drink is negligible unless large quantities of seeds are used.
Jeera water is believed to have a warming effect on the body according to ayurveda. Jeera seeds contain compounds that can stimulate digestion and metabolism, which may lead to a slight increase in body heat. This warming effect is often associated with improved digestion and circulation, but individual reactions may vary.
Yes, jeera water can be consumed at night. It is often recommended to drink jeera water before bedtime to aid digestion, promote better sleep, and potentially boost metabolism. However, moderation is key, as consuming too much liquid before bed could disrupt sleep by causing frequent urination.
Yes, jeera water can be consumed daily as part of a balanced diet. It offers various potential health benefits, including improved digestion, metabolism, and potential weight management support. However, like any dietary supplement, moderation is advised, and individual tolerance should be considered to avoid any adverse effects. Its best to consult a doctor if you have any medical conditions.
There is no scientific evidence to suggest that jeera water can induce periods. While cumin seeds are known for their potential benefits in digestion and overall health, they do not possess properties that can regulate menstrual cycles or induce periods.
Jeera water may be beneficial for fatty liver. Cumin seeds contain antioxidants and compounds that can support liver health by promoting digestion, reducing inflammation, and potentially aiding in fat metabolism. However, it should be consumed as part of a balanced diet and lifestyle changes recommended by a healthcare provider for managing fatty liver disease.
Jeera water may have some beneficial effects on uric acid levels. Cumin seeds (jeera) contain antioxidants and compounds that can help in reducing inflammation and improving digestion, which may indirectly contribute to managing uric acid levels. However, specific scientific evidence regarding jeera water’s direct impact on uric acid levels is limited, so it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
There is no direct evidence to suggest that jeera water causes acne. In fact, cumin seeds (jeera) contain antioxidants and antimicrobial properties that may help in reducing inflammation and promoting clear skin. However, individual reactions to foods and drinks can vary, so if you notice any adverse effects, it’s best to discontinue use and consult a dermatologist if necessary.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
When your blood sugar levels are higher than normal, carbohydrates such as cereals, pasta, certain fruits, desserts and bread are usually responsible. When one is diabetic, a meal plan is very important because it guides you on what kind of foods to eat. It should be good enough to fit in with your eating habits and also your schedule. A good meal plan should include consideration and optimization of the following:
Foods with low glycemic index values are better choices for stabilizing blood sugar than foods with high glycemic index values. The glycemic index basically depends on the physiological ability of dietary carbohydrates to lower or increase the level of blood sugar in reference to the type of food consumed by the diabetic patient. Relatively high glycemic index foods have ratings above 50, and often between 75-100. Check out the Glycemic Index Food Chart to find out the glycemic index values of foods that you can include in your Diabetes Diet Plan.
The purpose of a good meal plan is to help keep your weight on track, improve your cholesterol level, blood sugars and also blood pressure. According to past research[1] & health educators from the American Diabetes Association (ADA), a healthy diet along with a healthy lifestyle of exercising to maintain a healthy weight can help to reduce diabetes type 2. You can check healthy, mouth-watering recipes for diabetes that can help you lower your blood sugar levels, without compromising on taste and variety!

These are rich in fibres & help you feel full for longer periods. Beans, including black beans, do contain carbohydrates, but they also contain a significant amount of dietary fibre, protein, and other nutrients that result in a relatively low glycemic index rating[2]. Consequently, they secure a prominent position in the Diabetes Food Chart.

This is an all-season vegetable that is a very good source of dietary fibres, vitamins, folate, chlorophyll, manganese, calcium, potassium, zinc, phosphorus, protein and carotene. Spinach’s glycemic index is very low and which is why it is very helpful for diabetic patients for stabilizing blood glucose levels[3].

These are a part of the cruciferous vegetable family and include kale, rutabaga, brussel, broccoli, sprouts, cabbage, turnips, etc. They provide a lot of nutrients at low calories & are known to lower the blood glucose level in patients with type 1 diabetes and stabilize the lipids, insulin and blood glucose level type 2 diabetics.
I suggest kale if you’re looking to keep your blood sugar under control. It contains a mere 0.8 g of sugar. Packed with essential nutrients and fibre, kale may offer a powerhouse of benefits for your overall health.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS

Leaf-mustard is very low in calories (27 calories per 100g raw leaves) and fats[4]. However, its dark-green leaves carry ample amounts of phytonutrients, vitamins, and minerals. Additionally, it contains a very good amount of dietary fibre that helps control cholesterol levels by interfering with its absorption in the gut.

Best amongst the potato family, boiled sweet potatoes have a glycemic index of 44 which is why they are considered a superfood for diabetics. According to the American Journal[5] of Clinical Nutrition, eating sweet potatoes in moderate amounts as compared to other potatoes, is likely to give lesser troubles with sugar control.

Berries contain a natural sugar called fructose which does not need to be metabolized; hence, the fruit is well tolerated in the body. It’s advisable to take two servings but always monitor what works best for you.

Fresh tomatoes, when consumed in moderation, are not a problem for managing your blood sugar levels. For example, 1 cup of cherry tomatoes contains 5.8 g of carbohydrates and 1.8 g of fibre, which is the equivalent of 4 g of net carbs, while 1 medium whole tomato has 4.8 g of carbohydrates and 1.5 g of fibre, or the equivalent of 3.3 g of net carbs. Its estimated glycemic index is 2 to 4.

Studies[6] have confirmed that eating whole grains and high-fibre foods helps in reducing the risk of diabetes by almost 35 to 42%. Oatmeal consists of high fibre and whole grains. In addition, it consists of soluble fibre that slows down the rate of glucose absorption in the GIT(gastrointestinal tract) thus ensuring the blood-sugar levels are kept at the right levels.

According to research[7] from St. Michael’s Hospital and the University of Toronto, eating nuts every day could help control diabetes type 2. It is important to note that nuts have a much lower glycemic index which ranges from 14 to 21. They contain relatively minimal amounts of carbohydrates in comparison to the favourite snacks consumed by most people such as crackers.

Depending on the kind of mushroom you go for, the glycemic index might fluctuate although it is always considered as low. With their unique line of nutritional benefits, it also has the benefit of adding a whole new flavour to a meal. Portabella mushrooms are used as a meat replacement because of their beefy texture and nutritional value. It contains 22 calories per 100g.

Cruciferous vegetables such as cauliflower are very beneficial in terms of glycemic load. These vegetables are often seen in the health news since they are known for their heart disease and anti-cancer characteristics. If taken regularly, this unique blend of phytonutrients is very healthy and absorbed well in the body. One can rotate this kind of vegetables so as to avoid eating the same kind every day[8].

This fruit ranks pretty low when it comes to the glycemic index. Though not as low as some vegetables, it’s considered healthy for diabetic people. It’s definitely a fruit to consider when making a listing of a low glycemic index food diet.

Coconut ranks highly in saturated fats, but if used sparingly, it is not a big threat to your blood glucose levels. Coconuts are used to flavour different types of dishes. Its different parts can be used, be it, coconut milk, coconut flour, its flesh and also coconut water. However, it’s important to know which part you are using to determine the glycemic index as well as nutritional benefits.

They say, an apple a day keeps the doctor away. This is because apples provide you with fibre, vitamins and minerals and a wide range of nutritional benefits while having a low glycemic index of 39. It requires very little preparation and no special storage, and it is also easy to carry[9].
Let me share a delicious and healthy fruit recommendation with you: passion fruit! If you’re looking to control your blood sugar levels, passion fruit might be a great addition to your diet. Just 100 g of this tropical fruit contains approximately 11.2 g of sugar. Given that the type of sugar is 100% natural, it is advisable as a natural source to keep your blood sugar levels normal. Do consume in a small to moderate amount.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)

Peaches are a great food to stock in the season. You can enjoy the natural sweetness in them, and when eaten in moderation, they can keep the levels of blood sugars in check. Though the GI changes when peaches are used as a part of a dessert, eating fresh peaches shouldn’t raise concerns. Its GI ranking is 28.

Whole wheat bread has gained popularity in recent years. This is because white bread is regarded as unhealthy. However, wheat bread is ranked 49 in terms of GI. This is because it’s processed differently from white bread and hence, has more nutritional benefits[10].

Beta carotene in carrots is known to help with eyesight and is also high in vitamin A. When mixed with peas, they can make a very delicious meal and still keep low glycemic content. Carrots have a glycemic index of 19[11].

Broccoli is a superfood often seen in almost every healthy food listing. They are known for providing fibre, minerals, vitamins and nutritional value. They have a very low value of 10 on GI scales and therefore, the body can handle it very well[12].

These contain 81 calories in every 100g serving. They also have high amounts of fibre and a fair amount of potassium. Also, it is a source of vitamin c and protein. Its glycemic index is 39.

Milk is known for providing calcium and vitamin D as well as high protein. Having a glass of milk when you are diabetic is totally acceptable since it falls under the low GI foods with a glycemic index of 31[13].

Yoghurt is known because of its active and live cultures which help in the digestive issues by providing good bacteria. Whether you are eating unsweetened yoghurt or one with artificial sugars, it will still fall under low GI foods. However, low-fat yoghurt is recommended. Its glycemic index is 33. Also, it is advisable to consume natural flavoured yoghurt that is free of any type of artificial sweeteners[14].
Another excellent option for managing blood sugar levels is tofu. If you’re looking for a protein-rich and low-sugar food, tofu might be a great choice. Only 0.62 g of sugar is included in 100 g of tofu.
Dr. Anuja Bodhare, B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu)

Lentils are very rich in fibre, minerals and vitamins. They are slowly gaining popularity and are often overlooked when it comes to a blood sugar conscious diet. Their Glycemic index rank is 30[15].

Grapes are very sweet and many mistakenly believe they should be avoided when it comes to diabetics dieting. There are various types of grapes one can enjoy eating, be it red or white. Whichever kind you love the glycemic index is considered low & lies between 43 to 53 depending on the kind.

These are often compared to apples but they contain different nutrients as well as taste. They are a great choice when one is considering a low glycemic index food. Their glycemic index rank is 41.

Brown rice is one of the common foods that most diabetic people consume. This is because, compared to white rice, a serving is considered to have a glycemic rank of 87 whereas that of brown rice is 55.

Peanuts can either be enjoyed as a snack, with butter or even sauce. They are considered legumes and are very good at keeping someone alert. They are also very good at stabilizing blood sugars. Their glycemic index rank is 6[16].

Hummus is made up of chickpeas but ranks lower than them. This is due to other ingredients in them such as lemons, tahini, and olive oil. Their GI is virtually zero but you still need to watch portions so as to avoid gastrointestinal discomfort. The glycemic index is 6[17].

These are healthy nuts and can be taken as desired. They act to help the health of polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats. It’s also a great source of magnesium and iron. Cashew nut butter is also healthy if one opts for an organic variety. They have a very low GI of 2[18].

Green beans are one of the most popular foods often consumed as a side dish. They are relatively low when subjected to the GI scale and are also an excellent source of fibre, vitamin c, and minerals. They help strengthen the immune system and also provide antioxidants that help battle free radicals so as to help avoid inflammation. Their Glycemic index rank is 15.

Oranges are known for their vitamin C content and it’s a great fruit to eat to boost your immune system when you notice early symptoms of a cold. They can be used as a smoothie, morning fruit or an all-time top-up. Its glycemic rank is 40.

These are considered to be low glycemic foods. Though they may vary in scale, they have a considerable amount of nutrition. The glycemic index for plums is 24 and 29 for prunes.

Fish are good for diabetic patients since it’s an excellent source of low proteins. They are known to be rich in omega 3, a kind of fat that strengthens the heart and potentially helps with management of diabetes. Including seafood in your diet and having at least two or more servings a week will help a great deal in blood sugar levels reduction[19].

Although many sprinkle this in our drinks every morning, you might be surprised to realize the health benefits of this wonderful spice. Other than lowering the bad cholesterol, and raising the good cholesterol, cinnamon has been proven to lower blood sugars modestly.

Many people tend to fear garlic due to bad breath. But garlic extract is known to increase the levels of insulin available for diabetics. It has thereby been proven to reduce the levels of blood sugars[20].

These are foods such as avocados, nuts, and salmon, tuna, trout and olive oil. They all contain monounsaturated fats that help lower insulin resistance.

Chia seeds are minute dark, seeds with nutty flavours. They are rich in healthy fats, vitamins, fibre, and antioxidants. One of the studies[21] published in ‘Diabetes Care’ found out that Chia seeds play a role in improving blood sugar. Also, it reduces the chances of heart diseases occurring in type-2-diabetic patients.

Capsicum is known to be cultivated for thousands of years and used for food, medicine and also for decorative purposes. The effectiveness of chilli peppers as medicine is that they can activate the transient receptor vanillin. This receptor is associated with neuropathic and inflammatory pain, anxiety and how our bodies process fats. It’s also an important insulin regulator. This study has led to the production of extracts aiming at pharmacological strategies to treat medical conditions such as diabetes[22].

Vinegar has been used for centuries for a variety of health problems, including glucose management, dandruff, excessive sweating, fungal infections, and even heartburn. In a study[23] published in Diabetes Care, two tablespoons of ACV at bedtime helped to regulate fasting blood glucose levels in patients with type II diabetes.

Protein foods are an important part of a diet plan. They include; fish, chicken, meats, soy products, and cheese. The difference between these foods is how much fat they contain and protein.

Although dried figs are available throughout the year, there is nothing more refreshing than the unique texture and taste of fresh figs. The leaves of fig have been known to contain anti-diabetic properties and can reduce the level of insulin needed by persons with diabetes.

Dates, along with other healthy but relatively unsafe foods for diabetes like peanuts and honey, often get a bad rap. These foods are, however, good for reducing bad cholesterol or LDL. For diabetics, in particular, portion control of these foods becomes very important.

A cup of cooked whole-grain barley consists of 14 grams of fibre. The fibre is 3g soluble and 11g insoluble. 1 cup of cooked pearl barley consists of 6g fibre which is 2g soluble and 4g insoluble. Diabetic patients experience alterations in blood glucose levels after consuming carbohydrate-rich foods. Barley consists of a GI of 25.

Unlike white bread or potatoes, pasta is pretty low in terms of its glycemic impact. Many diabetics fear pasta because of its infamously high carbohydrate nutrients. However, with proper proportions, pasta can be safely indulged in a diabetic diet. Limiting portion size and choosing high-fibre whole grain pasta is the key to keeping the blood sugars low.

Quinoa is an excellent item to control your blood sugar. Whole grain with a low glycemic index to support even blood sugar, is packed with protein, fibre, vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals. Quinoa is easy to cook and flavorful, and you can incorporate it into a healthy diabetic diet in a variety of ways[24].

Apricots are sweet and have a delicate flavour. They have a wide range of nutrients and this makes them worthwhile to be added to a diabetic diet. Apricots can help you satisfy your sweet tooth without worrying about your blood sugars due to their low glycemic index. Dried apricots are also a great alternative when eaten in small amounts.
Let me share with you another fantastic option for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels: arugula! If you’re looking for a nutritious leafy green that won’t spike your blood sugar, arugula is a great choice. In just 100 g of raw arugula, you’ll find only 2 g of sugar.
Dr. Smita Barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
Apart from the above list of foods to eat to lower blood sugar, there are other dietary and lifestyle changes you can use. Here are a few tips on diabetes control to get you started:
Weight management will be a major factor in your fight against diabetes, so be sure to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
Apart from lowering the blood sugar within a short duration the foods also offer the body other benefits that include boosting body immunity, repairing worn-out cells and checking on most of the lifestyle diseases. However, this is not an exhaustive list of food items that can be eaten to control blood sugars. This list is meant to guide you on some of the locally available foods that have a low GI and which can be considered when regulating the blood sugar in the body. For those who are suffering from very high blood sugar levels, it is advisable that they seek the advice of a dietitian, clinical nutritionist and their family doctors so as to come up with the best treatment plan besides healthy eating.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
The very mention of diabetes can strike fear in the heart of the bravest. It is known to adversely affect several organs in the body, like the eyes, kidneys, nerves, heart and many more. If not diagnosed and treated on time, it can lead to several complications.
You may have read plenty of blogs on how you can manage diabetes or about the measures you can adopt to prevent the onset of this disorder. But are you aware that there is a test that can predict your chances of developing diabetes? It’s called the HOMA-IR (Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance) test. This test may help you prevent diabetes.
Besides HOMA-IR, several other diagnostic tests are used to diagnose diabetes. Contact your doctor to determine which test is best for you and how to prepare for it. Remember, the earlier the diagnosis, the easier and more effective the treatment will be.
To understand how HOMA IR may help you, you have to understand a thing or two about diabetes.
Diabetes is classically understood as two major types– Type 1 (your body produces less insulin) and Type 2 (associated with insulin resistance and less insulin production)2.
Glucose, also known as blood sugar, provides energy to the cells in our body. It acts as fuel, driving our cells, tissues, muscles and organs to perform their respective tasks. Our pancreas produces a hormone called insulin. Insulin sends signals to your cells to pick up glucose from your bloodstream. But sometimes, your cells are unable to process the signals that insulin sends and fail to absorb sugar from the blood. This is a case of insulin resistance. And when this happens, the sugar level in your blood begins to soar. So, we can say that insulin resistance is the precursor to diabetes.
Abdominal fat increases insulin resistance. Cardio exercises combined with strength training not only decrease insulin resistance(via weight loss) but also increase insulin receptor density in muscles.
Dr. Nikhil Yadav, MBBS MD,CCEBDM
Insulin resistance not only paves the way for type 2 diabetes but also other diseases like hypertension, dyslipidemia, cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Strangely enough, people with normal blood sugar levels may be insulin resistant. And this is exactly where HOMA IR can help. This test measures how resistant your cells are to insulin. Higher Insulin resistance, even if the sugar content in your blood is within acceptable levels, suggests that your blood sugar may spike in the future. This is how the HOMA-IR goes a step further than a normal blood sugar test, which can only monitor your sugar level and cannot detect any issues until high blood sugar develops1.
HOMA IR, on the other hand, might ring the warning bells as the resistance to insulin increases in the pre-diabetes stage, so that you can take the necessary steps to prevent a full-blown attack of diabetes.
Acute illness and stress are the two clinically often neglected conditions where the fasting plasma glucose test is more sensitive than HbA1C, which is also known as glycated haemoglobin test, for detecting blood sugar levels. One should always do the Fasting plasma glucose along with HbA1C to get a correct diagnosis.
Dr. Ashish Bajaj, M.B.B.S., M.D. in Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology
Also Read: Mounjaro (Injection): Uses, Side Effects, Dosage, and How It Works
Your results from the HOMA-IR test are displayed against a scale or range that determines the level of your insulin resistance. Low HOMA-IR implies you are sensitive to insulin, and higher levels indicate insulin resistance and a higher chance of you developing diabetes mellitus.
To properly address the rising insulin resistance in your body, it’s necessary to make changes to your lifestyle and habits. There are two ways in which this could be achieved:
Initial diagnosis of diabetes should always be made by fasting blood sugar and postprandial blood sugar. For monitoring, you can use HbA1c.
Dr. M.G. Kartheeka, MBBS, MD(Pediatrics)
You should consult a doctor who can advise you on appropriate lifestyle modifications or prescribe the right medication. You will also need to follow a special diet of fresh vegetables, fruits, whole grains, fish, eggs, and soy products. Seek a dietician’s help to draw up a diet chart and don’t forget to exercise regularly. Workout is known to decrease insulin resistance. Get at least 7 hours of sleep.
HOMA-IR is a groundbreaking new method of diagnosing diabetes before it develops. With appropriate care, you can avert diabetes.
Also Read: Your Ultimate Guide To A Balanced Diet For Diabetes
It is crucial to understand that diabetes doesn’t develop overnight; it builds silently over time. The HOMA-IR test offers a way to evaluate your risk before the diabetes symptoms even appear. By identifying insulin resistance early, you can take preventive measures such as making lifestyle changes, seeking medical guidance, and developing better habits3. If you or a loved one is at risk, talk to a healthcare professional about whether this test is suitable for you. Take control of your health today, because beating diabetes beforehand is always better than managing it later.
Also Read: 45 Food Items That May Help To Control Blood Sugar!
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
« Previous Page