At PharmEasy, our customers are at the heart of everything we do. As your healthcare and wellness partner, your health and well-being matter the most to us. To help you take it easy with your healthcare needs and enjoy guaranteed savings – the idea of ‘Lucky Hour’ was born.
During our ‘Lucky Hours,’ the lucky 200 users stand a chance to get their medicine orders for FREE. How can you participate? By making your purchase within the designated Lucky Hours each month.
But wait, there’s more excitement—drumrolls—as we have a surprise cashback for everyone who places an order during the ‘Lucky Hours’!
Let’s welcome our lucky winners to our winner’s room.
Heartiest congratulations and a big applause *clap clap* for them.
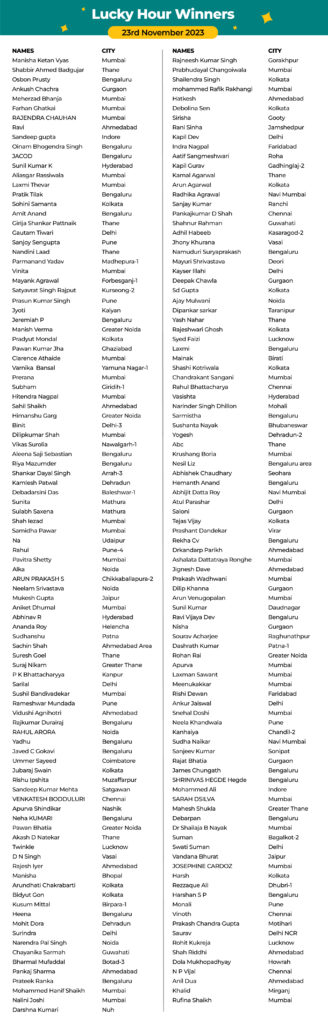
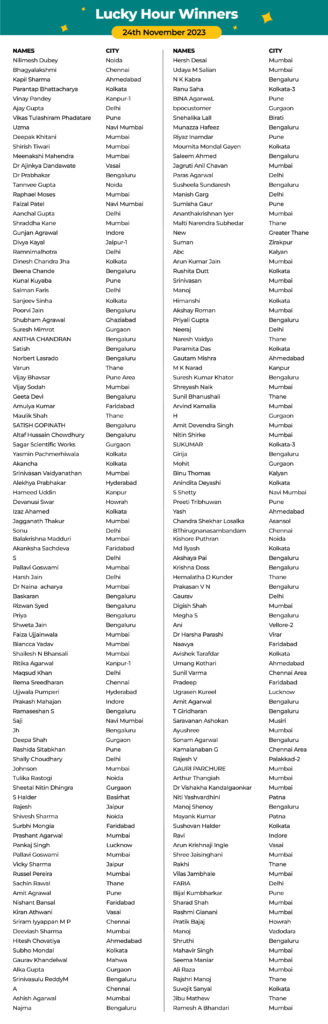
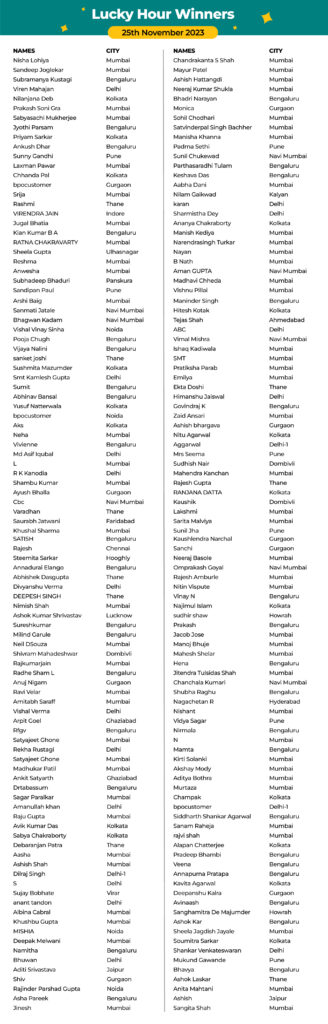
Stay tuned, and don’t forget to participate during our next ‘Lucky Hours’.
Who knows, the next winner might just be YOU.
Team PharmEasy
Do you love adding extra jalapenos on your pizza? Of course you do! This variety of chili pepper can really enhance the taste of pizzas, burgers, subs and everything else! That’s largely because of its spicy flavor! Jalapeno peppers are loved worldwide because of their fiery spice and many health perks. These spicy veggies offer rich tastes in various foods. Enjoy them in chips and dips, as well as main course meals. But they are not only tasteful. Scientists have also looked into the health upsides of eating these peppers. So in this chat, we’ll delve into the history and growth of jalapenos and their varied types, sum up their healthful parts, and underline the well-researched health perks of this well-known chilli pepper. Let’s dive in!
Did you know?
“Jalapeno” comes from a place named, Xalapa (or Jalapa), Veracruz, in Mexico. This is where these peppers were first grown. They hold a high spot in Mexican food, used by Aztecs in plenty of dishes and even as a spice. Over time, jalapeno use spread across the earth. Today, they remain a top ingredient in many global foods. Their wide appeal is clear. Jalapeno peppers are the top chili peppers picked and eaten around the globe.
Jalapeno peppers do well in different soils and temperatures. This makes them handy for food use and farm use. Even so, these peppers still need special care to give the top yields and the best quality.
The key to a good jalapeno crop is proper early planting. Start your plants indoors about 2-3 months before moving them outside. This can greatly boost their growth and outcomes. It’s also important to water the young soil and budding plants often but not too much. Why? To keep your jalapeno garden healthy.
The whole life of the jalapeno plant needs careful attention. This includes giving it enough sun (no less than 6-8 hours a day) and making sure the soil drains well. Right pH levels of 4.5 to 7.0 are best for jalapeno growth. Also, keeping an eye on water and sunlight helps lessen any possible stresses on the plant, such as uneven watering or heat changes.
Even though jalapeno peppers are usually green, these adjustable plants come in lots of types and flavors, suited for any taste.
Over time, growers have bred a big mix of jalapeno blends and sub-types. Each shows its own traits and tastes. These changes often focus on disease resistance, softer heat levels, quick ripening, better looks, and higher yields. Some F1 blend types include Mitla, Perfecto, Tula, and Grande. Each is fit in its own way for different food or farm uses.
Apart from the usual jalapeno types, crosse owners have also made blends with a sweeter taste. These lack heat but are full of flavour. These sweet jalapeno peppers are a nice choice for those who want less heat but still crave the traditional jalapeno taste and smell.
Having a full understanding of jalapeno peppers requires knowing their make-up. These parts add to the overall spice, taste, and look of jalapeno peppers.
With a medium range of spiciness, jalapenos have their own place when compared to other chili peppers.
The Scoville scale measures pepper spice by checking its capsaicin amount. Jalapeno peppers rank between 2,500 and 8,000 Scoville Heat Units (SHU), placing them as medium hot. This is when compared to other chilli peppers. Even so, each jalapeno pepper can vary in heat. So it’s key to test them before adding them to your foods.
Many things impact the overall spice of jalapeno peppers. This includes growing settings, ripeness levels, and individual plants. Fast-growing and well-watered jalapenos usually taste milder. But jalapenos left longer on the plant or exposed to tough conditions may be hotter.
See what changes jalapeno pepper heat levels:
| Factor | Effect on Jalapeno Spice |
| Growing conditions | Heat levels can change |
| Maturity level | More ripeness means more heat |
| Individual plants | Uneven spice levels |
Jalapeno peppers not only spice up your meals but they’re also filled with needed healthful bits and tested health gains.
High in vitamins and minerals, jalapeno peppers hold large amounts of vital healthful bits like vitamins A, C, K, and B6, magnesium, fibre, folate, carotene (an antioxidant), and an active ingredient known as capsaicin, which offers several health benefits. These healthful bits help give the many health gains linked to eating jalapeno peppers.
Check out some vital bits inside jalapeno peppers:
| Healthful Bit | How It Helps in Jalapeno Pepper |
| Vitamin C | Antioxidant, helps boost immune system, may help fight cancer |
| Vitamin E | Antioxidant, helps skin health |
| Capsaicin | Helps soothe inflammation, helps pain relief |
One raw jalapeno contains the following:
Like most fruits and vegetables, jalapeno peppers are a good source of fibre. One pepper provides 2% of the RDI for a person consuming 2,000 calories per day.
Jalapeno peppers have been studied a lot for their possible health gains. Here are a few of the health upsides backed by research that are linked with eating jalapenos:
In my understanding, when applied externally, capsaicin from jalapeno peppers may relieve pain. By momentarily blocking pain receptors in the affected area, it may reduce pain. One may initially experience burning, which is followed by numbness and lack of pain. Capsaicin lotions and patches are commonly used to ease chronic muscular and joint pain, diabetic nerve pain, and shingles-related pain. You can talk to your doctor to check if one might be helpful for you.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Here are some ideas to include the health arms of jalapeno peppers in your everyday meals:
With a wide range of flavours, jalapeno peppers make an excellent choice for many food creations.
Jalapeno peppers have a bright, vegetable taste and some heat that can be added to loads of dishes. They can be eaten fresh or cooked, adding lots of tastes to varied recipes.
Enjoy the taste of jalapeno peppers:
| Eating Trait | Description |
| Fresh | Bright, vegetable taste, mild heat |
| Cooked | Richer, a bit smoky, earthy, hotter heat level |
Jalapenos pack a punch. So it’s needed to handle and cook them with care. Right jalapeno prep can help lessen their heat and prevent irritation while cooking and eating.
Try these food prep tips for jalapenos:
| Food Prep Issue | Solution |
| Handling irritation | Wear gloves when dealing with jalapenos. Avoid touching eyes or sensitive skin. |
| Changing how hot it is | Take out the seeds and soft parts to lower heat |
| Too hot of a heat | Balance the jalapeno spice with milder items in the recipe |
With their nice taste and wide use, jalapeno peppers can be added to lots of well-liked dishes. For example:
I recently came across an article which says that by raising your metabolism, increasing fat burn, and decreasing appetite, jalapeños may aid in weight loss. According to a number of studies, capsaicin and other related substances known as capsaicinoids might increase metabolism by 4-5 per cent daily, which may facilitate weight loss. However, they can definitely not serve as an alternative to exercise and mindful eating.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, MD
Also Read: Is Cayenne Pepper Good For You? Understanding Its Health Benefits and Uses
Jalapeno peppers offer a unique mix of flavour, heat, and lots of health perks. With a deep history in Mexico, these peppers have found their way into kitchens and hearts everywhere. As we’ve seen, jalapeno peppers provide key healthful parts, such as vitamins C and E and capsaicin. These help give many health upsides, including soothing swelling, digestive help, and antioxidant perks. Including jalapeno peppers in your meals can uplift your culinary creations and improve your overall well-being.
So, do you want a tasty first course, a zesty dip, or looking to pump up your everyday nutrient intake? Remember, don’t look past the power and wide use of the humble jalapeno pepper. A little bit of heat can go a long way in improving your health and raising your food experience.
Jalapeno peppers rank between 2,500 and 8,000 Scoville Heat Units. This puts them at a middle-spice level when compared to other chilli peppers. Even though jalapenos have a clear spice, they tend to be softer than other chilli peppers.
Green jalapenos are not ripe yet, while red jalapenos are fully ripe. As jalapenos ripen, they tend to get hotter and become a bit sweeter. Both green and red jalapenos can be used as you wish in meals, based on personal heat and flavor likes.
One way to see the heat level of jalapeno is the presence of scars or “stretch marks” on the skin. Peppers with more stretch marks are likely to be spicier, while those with smooth, perfect skin are likely to be milder.
You can include jalapeno peppers in many recipes. From first courses like jalapeno poppers to spicy cornbreads and salsas to mixing jalapenos in mixed drinks for a flavour and heat layer. Cooking them raises their depth and complexity in soups, stews, and covered dishes.
Contaminated jalapeños have caused outbreaks of illnesses, including salmonella. It’s important to wash all produce before you eat it. Talk to your doctor if you’re pregnant or have a problem with your immune system, your body’s defence against germs.
Jalapenos are usually picked green and have a bold, grassy flavour and mildly bitter taste when they are unripened. As they turn red and ripen, they do not get any hotter, but the taste becomes somewhat fruitier and less grassy.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
For ages, people have turned to bladderwrack (also known as Fucus vesiculosus, a type of brown seaweed that grows in the Baltic Sea, Atlantic Ocean, and North Pacific Ocean. The whole plant is used as medicine), which is rich in nutrients. Planning to eat it? There could be health benefits waiting for you. But we still need to dive into what science says about these benefits and side effects. That’s what this blog post will cover.
What’s the nutritional breakdown of bladderwrack? What are its possible health perks? Are there known side effects? How about safe doses and forms you can use? We discuss all of these in this detailed post. Ready to become an expert on bladderwrack? Let’s jump in.
Wondering what makes bladderwrack tick? It houses various vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. All these give it potential health powers. So, what’s inside bladderwrack?
Did you know there’s more? Bladderwrack also houses plant compounds like phlorotannins, fucoxanthin, alginic acid, and fucoidans. These help amplify its health benefits.
You hear “bladderwrack”, think “high iodine content”. Why is iodine crucial? It supports thyroid health and aids in forming thyroid hormones T3 and T4. These hormones manage metabolism and foster proper growth and brain development.
Not eating enough iodine? You might be at risk of hypothyroidism. You’ll see signs such as weight gain, fatigue, dry skin, and being sensitive to cold. Can bladderwrack help some people with an iodine lack? It could. However, too much iodine can also cause issues. Therefore, it’s crucial to talk to a healthcare professional before taking bladderwrack.
Apart from thyroid disorders, it holds potential use in obesity, ageing skin, joint pain, digestive issues, especially constipation, urinary tract infection, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
Don’t confuse Fucus vesiculosus with algin, bladderwort, blue-green algae, ecklonia cava, or laminaria. These are not the same.
Look out for this table that gives an overview of key nutrients and their roles in our bodies:
| Key Nutrient | Role in the Body |
| Iodine | Supports healthy thyroid function and hormone production |
| Calcium | Contributes to strong bones, teeth, muscle, and nerve function |
| Magnesium | Supports healthy muscles, nerves, and immune system |
| Potassium | Regulates fluid balance, muscle contractions, and nerve signals |
| Sodium | Aids in fluid balance, and muscle and nerve function |
| Vitamins A and C | Act as powerful antioxidants, protecting cells and supporting immune function |
Preparations of bladderwrack are used for diseases of the thyroid, obesity, arteriosclerosis, and digestive disorders, as well as for “cleansing the blood”. I recommend the use of bladderwrack only after getting a green signal from your doctor.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, MD
The iodine in bladderwrack is important for maintaining good thyroid function. It’s especially crucial for folks who lack iodine. But keep this in mind. Too much iodine can cause thyroid issues. So don’t start using Bladderwrack for thyroid support without asking your healthcare provider first.
The alginic acid in bladderwrack, in combination with magnesium carbonate, treats heartburn and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) by creating a barrier between the sensitive stomach lining and irritants, such as stomach acids and lowering inflammation.
Iodine scarcity can trigger hypothyroidism. This is when your thyroid hormone levels dip too low. Its effects include weight gain, fatigue, and feeling colder than usual. bladderwrack might help manage these symptoms, but we need more research to confirm this.
Thyroid hormones help keep metabolism balanced. Therefore, the iodine in bladderwrack could boost your metabolism. However, we need more research to confirm if iodine helps support human metabolism.
Bladderwrack has plenty of antioxidants. Think phlorotannins and fucoxanthin. What do they do? They combat free radicals. By lowering oxidative stress, these helpers might reduce body inflammation. Is that beneficial for health? It very well could be.
Recent studies show bladderwrack extracts have anti-inflammatory effects. But note that it’s only been tested in labs and on animals. So, we need more research to verify these effects in humans.
What if bladderwrack could ease your arthritis and joint pain? It might be possible. By cutting down inflammation, this seaweed may help improve joint comfort and flexibility. But again, more human studies are needed to confirm this.
Did you know bladderwrack possibly holds skin benefits? Topical use of this seaweed extract might boost skin bounce, lower cellulite look, and aid wound healing. Early research points at bladderwrack antioxidants, like fucoidan, as the secret. These promote collagen production in the skin. This could improve the skin’s overall look, increase healing and delay early skin ageing.
Still, we need more studies to confirm these effects and whether eating bladderwrack or supplementing with it benefits the skin.
Some people say using bladderwrack on the skin helps relieve acne and eczema. It alludes to its possible anti-inflammatory powers and skin-friendly properties. However, there’s little research to back this claim. So, we need more studies.
A study found that putting on a gel with 1% bladderwrack extract increased collagen production. It resulted in better skin elasticity than a product without bladderwrack extract. Another study reported similar findings when it used bladderwrack extract with other seaweed extracts. Despite these promising findings, more research is needed to verify bladderwrack’s potential skin benefits.
10. Menstrual cycle regulation in premenopausal women
Products of bladderwrack are sold as over-the-counter weight loss aids in the market. Bladderwrack’s iodine is thought to enhance thyroid hormone synthesis, which in turn may help boost metabolism. Weight loss may begin as a result of this accelerated metabolism without requiring dieters to alter their eating patterns. However, this is not necessarily safe and one should not skip exercise and mindful eating when trying to lose weight.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Just like any other supplement, bladderwrack could cause side effects. Some might find its use harmful. Here are some side effects and cautionary advice about using bladderwrack:
Though high iodine content can be a pro for some, it can harm others. Too much iodine might trigger thyroid problems and worsen hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism symptoms. So, it’s wise to talk with a healthcare provider before using bladderwrack, especially if you have thyroid issues.
High sodium content in bladderwrack might make it harmful for those with high blood pressure or on low-sodium diets.
People on blood thinners and antiarrhythmic medications: Bladderwrack may interfere with certain medications, such as blood thinners (heparin, warfarin), antiarrhythmic medications (amiodarone), and thyroid medications.
Applying bladderwrack to the skin is likely safe. However, avoid applying it to open wounds and cuts, and discontinue use if you experience any adverse reactions, such as a skin rash. Some people might show an allergy to bladderwrack, especially if they’re allergic to iodine. Signs of a reaction include itching, skin rashes, and trouble breathing. Seek immediate medical help if the reaction seems serious.
Bladderwrack could interfere with medications such as blood thinners, heart rhythm drugs, and thyroid medicines. Always ask your healthcare provider before starting new supplements or treatments. It’s especially important if you’re currently on any prescribed medicines.
Here’s a transition statement about the following table – Have a glance at potential side effects and precautions to consider when using bladderwrack:
| Potential Side Effects/Precaution | What to Consider |
| Iodine excess and thyroid issues | Excessive iodine intake from bladderwrack may negatively affect individuals with thyroid disorders |
| Blood pressure concerns | Bladderwrack’s high sodium content may not be suitable for those with high blood pressure or on a sodium-restricted diet |
| Allergic reactions | Some people may experience allergic reactions to bladderwrack, particularly if they are allergic to iodine |
| Drug interactions | Bladderwrack may interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners, antiarrhythmic medications, and thyroid medications |
In premenopausal women, eating bladderwrack may extend the menstrual cycle due to its anti-estrogenic properties. Studies have revealed that menstrual cycle lengths may increase significantly when bladderwrack is consumed; ranging from 5.5 to 14 days. However, since not too many large scale human studies are available on this, we cannot be too sure. You should not rely on bladderwracck alone to delay your menstrual cycle.
Dr. Smita barode, BAMS
Bladderwrack can come in several forms. These include capsules, tablets, tinctures, liquid extracts, and dried bladderwrack for tea making. A typical supplement dose is 500 mg, but there’s no hard-and-fast rule. Don’t forget to ask your healthcare provider about which form and dose would be best.
Capsules and tablets make bladderwrack easy to use. No clue how much to take? Just follow the package instructions or ask your healthcare provider.
You can add bladderwrack tinctures or liquid extracts to water, juice, or tea. They absorb easily in the body. To know how much to use, follow the package instructions or ask your healthcare provider.
Want to make tea? Use dried bladderwrack. Just steep it in hot water. For bladderwrack tea, let one tea bag sit in 8 ounces (236 mL) of hot water for 4–5 minutes. Or simmer 1 teaspoon (5 mL) of dried bladderwrack in boiling water for 10–15 minutes. Stick to at most 2 cups (500 mL) per day. Don’t forget to ask your healthcare provider about the right dose.
Without a standard recommended dose, it’s key to ask your healthcare provider what works best. This is based on your needs and any current health issues or medicines you might be taking.
Bladderwrack does offer potential health benefits. But everything good usually has a ‘but’ attached. It’s the same for bladderwrack – its high iodine content, risk of reacting with medications, and the chance it negatively affects your health condition. So, weigh the pros and cons before you dive in.
Before jumping into bladderwrack or any other supplement use, talk to a healthcare professional. They can check your needs, explain possible risks and gains, and guide you on the right form and dose.
Taking bladderwrack has been a traditional practice for a long time. There are possible health benefits to gain, such as thyroid function, skin health, or anti-inflammatory effects. Yet, more research is needed to back these benefits. Check with your healthcare provider before trying bladderwrack, especially if you have thyroid issues, are pregnant or nursing, or take any medicines.
There’s some evidence that bladderwrack might help boost a healthy metabolism due to its iodine content. But can it promote weight loss? More studies are needed to confirm this.
We lack safety data. So, bladderwrack is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women. Still unsure? Check with your healthcare provider.
The time to see the benefits from bladderwrack might vary. It depends on you as an individual and the specific health issue you’re targeting. Ask your healthcare provider for advice on how long it might take for you to see results.
It’s possible that bladderwrack might react with certain medications such as blood thinners, heart rhythm medicines, and thyroid medicines. Is it important to check with a healthcare provider before using bladderwrack with other supplements or medicines? Absolutely.
Marfan Syndrome is a complex condition that can affect multiple body systems. In the following sections, we will discuss in detail what Marfan Syndrome is, explore its causes, delve into its various symptoms, and illuminate on the available treatment and management options. As the intricacies of this condition unfold, prepare to enhance your understanding of Marfan Syndrome and how it can impact the lives of those affected by it.
In my experience, the majority of those who have Marfan syndrome are able to engage in some kind of leisure or physical activity. You should probably stay away from contact sports, high-intensity team sports, and isometric activities (like weightlifting) if you has an enlarged aorta. You can get an echocardiogram to check for the same.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, MD
A genetic disorder, Marfan Syndrome, affects the body’s connective tissues. Most notably, it impacts the cardiovascular, skeletal, ocular, and pulmonary systems. Let’s discuss this syndrome, its commonness, and the genetics behind it, shall we?
So, Marfan Syndrome results from a change in the FBN1 (fibrillin-1) gene. This change messes up the formation and function of connective tissue. Connective tissue supports various organs and structures in the body. With a rate of about 1 in every 5,000 people, anyone can get it, regardless of race, ethnicity, or gender.
Due to medical advancements, some individuals with Marfan syndrome are now able to live until the age of 72!
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Marfan Syndrome is often passed down the family tree, with a child having a 50% chance to get it. However, in about a quarter of cases, new mutations occur without any family history. That’s called a sporadic case. Even though the direct cause is the genetic mutation, the severity of the syndrome changes greatly from one person to another.
Marfan Syndrome can cause many different symptoms because it affects the connective tissue in the body. The signs and symptoms of Marfan syndrome can vary greatly, even among members of the same family, because the disorder can affect so many different areas of the body. Some people experience only mild effects, but others develop life-threatening complications.
Studies have revealed that a leak in the valve that separates two of the heart’s four chambers (mitral valve prolapse) or the valve that controls blood flow from the heart into the aorta (aortic valve regurgitation) are among the several cardiac issues that many individuals with Marfan syndrome experience. Breathlessness, exhaustion, and palpitations—an irregular pulse that feels like extra or skipped beats—can all be symptoms of leaks in these valves. Early diagnosis can help with timely treatment and prevent fatal complications.
Dr. Smita barode, BAMS
Now, Marfan Syndrome often shows various abnormalities in the bones, such as:
People with this condition might have very long fingers, stretching beyond the edge of their hands when making a fist.
Longer arms and legs are also common, sometimes with an arm span longer than the person’s height.
Another symptom could be scoliosis, causing a bent spine that can result in pain and difficulty breathing.
Heart-related issues can be some of the most risky effects of Marfan Syndrome.
The first worry is the aorta, the big blood vessel taking blood from the heart, getting weak and stretched. This may lead to an aortic aneurysm and, if it gets worse, an aortic dissection. An aortic dissection is a tear inside the aortic wall – and it’s a big health threat.
Another risk lies in the weakening of the heart valves. This could cause regurgitation or not closing enough or may cause heart murmurs If this is not treated, it can lead to heart failure.
Marfan Syndrome could also cause issues with the eyes, such as:
The lens in the eye, supported by other parts, may move out of place due to weak tissue. This can happen in over half the people with Marfan Syndrome. This is called ectopia lentis.
The retina, or the light-sensing part in the back of the eye, could tear or detach. This may mess up the vision or even cause vision loss if left untreated.
It’s critical to recognise the symptoms of Marfan syndrome in order to prevent and treat severe, perhaps fatal consequences. Certain individuals with Marfan syndrome may not exhibit any symptoms until much later in childhood or maturity.
Dr. Anuja Bodhare, MD
Marfan Syndrome can also affect the chest and lungs, causing:
Abnormal growth of the ribs may cause chest deformities such as a sticking-out or sunken breastbone.
In some situations, air might build up near the top of the lungs. This can lead to a collapsed lung, which we call spontaneous pneumothorax.
A high, arched palate and crowded teeth are commonly seen in patients with Marfan’s syndrome.
In my experience, the majority of those who have Marfan syndrome are able to engage in some kind of leisure or physical activity. You should probably stay away from contact sports, high-intensity team sports, and isometric activities (like weightlifting) if you has an enlarged aorta. You can get an echocardiogram to check for the same.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D
The main cause of Marfan Syndrome is a change in the FBN1 gene. Marfan syndrome affects men and women equally and occurs among all races and ethnic groups. The incidence of Marfan syndrome is approximately 1 in 5,000 worldwide. But there are factors that may influence how bad it is or if you’ll get it from your parents.
The cause of Marfan Syndrome is changes in the FBN1 gene. This gene makes fibrillin, a protein needed for normal connective tissue. Not enough fibrillin weakens connective tissue, causing the different symptoms of the syndrome.
Even though Marfan Syndrome is often inherited, sometimes new mutations happen without any family history. This is the case in about a quarter of all cases, and we haven’t found out why these spontaneous mutations occur.
Our genes play a big role in this disorder. The biggest risk of getting Marfan Syndrome is if your parent has the gene change causing it. Each child of a parent with this changed gene may get it with a 50% chance.
Being pregnant could increase the risk of severe heart complications in those with Marfan Syndrome and an enlarged aorta. This is why medical check-ups are very important during pregnancy.
Due to medical advancements, some individuals with Marfan syndrome are now able to live until the age of 72!
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
There’s not a single confirmatory test for Marfan Syndrome, but the way to diagnose it usually involves a physical check-up, genetic testing, and medical imaging.
A doctor will check things that could tell them if you might have Marfan Syndrome, like being very tall, having long limbs and fingers, and any bone abnormalities.
Tests could be done on the FBN1 gene, but these tests often can’t say for sure if you have the syndrome.
Several imaging techniques such as echocardiograms, X-rays, and CT scans can be used to watch the heart valves, the aorta, and the skeleton for any abnormalities.
Eye exams that may be needed include:
Slit-lamp exam: This test checks for lens dislocation, cataracts or a detached retina. Your eyes will need to be completely dilated with drops for this exam.
Eye pressure test: To check for glaucoma, your eye doctor may measure the pressure inside your eyeball by touching it with a special tool. Numbing eyedrops are usually used before this test.
Genetic testing is often used to confirm the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome. If a Marfan mutation is found, family members can be tested to see if they are also affected. You may want to talk to a genetic counselor before starting a family, to see what your chances are of passing on Marfan syndrome to your future children.
Studies have revealed that a leak in the valve that separates two of the heart’s four chambers (mitral valve prolapse) or the valve that controls blood flow from the heart into the aorta (aortic valve regurgitation) are among the several cardiac issues that many individuals with Marfan syndrome experience. Breathlessness, exhaustion, and palpitations—an irregular pulse that feels like extra or skipped beats—can all be symptoms of leaks in these valves. Early diagnosis can help with timely treatment and prevent fatal complications.
Dr. Smita barode, B.A.M.S, M.S.
Even though we can’t cure Marfan Syndrome, multiple treatments and lifestyle changes can help control symptoms and avoid complications.
Your doctor may prescribe beta-blockers or ACE inhibitors. These help control blood pressure and heart rate, which reduces stress on the aorta. It also lessens the risk of further complications.
In some cases, surgeries like aortic root replacement or heart valve repair or replacement may be needed to fix heart issues.
Orthotics, braces, or surgeries to fix scoliosis or chest deformities can help manage bone problems.
Eyeglasses or surgeries to replace the lens may be needed to help you see well and to keep watch for retinal detachment.
Regular doctor visits, avoiding high-impact activities, and sticking to diets and exercise can help manage Marfan Syndrome and its related complications. Less intense activities — such as brisk walking, bowling, doubles tennis or golf — are generally safer.
It’s critical to recognise the symptoms of Marfan syndrome in order to prevent and treat severe, perhaps fatal consequences. Certain individuals with Marfan syndrome may not exhibit any symptoms until much later in childhood or maturity.
Dr. Anuja Bodhare, B.A.M.S, M.D
To sum up, Marfan Syndrome is a genetic disorder that greatly affects those who have it. It may impact many body systems, with symptoms from mild to severe. Even though there’s no cure, managing the syndrome, getting treatment, and changing your lifestyle can vastly improve the quality of life for those living with Marfan Syndrome. It’s very important to diagnose and start treatment early to manage this disorder and keep it from causing life-threatening complications.
With the right management and treatment, most people with Marfan Syndrome can live a full life, often living into their 70s or beyond.
While risky activities and contact sports may have to be skipped, those with Marfan Syndrome can still do lower-impact exercises and sports, with guidance from their healthcare provider.
Marfan Syndrome is passed down in an autosomal dominant pattern. This means there may be a 50% chance of a child getting the gene change from an affected parent.
Yes, the symptoms of Marfan Syndrome can range from mild to severe, with some people only seeing minor signs and mild impacts on their daily lives.
Yes, groups such as The Marfan Foundation give support, resources, and facts to those with Marfan Syndrome and their families.
Are you curious about skincare? Are you looking for a natural fix for hair and skin troubles? If so, you might have stumbled upon rosehip oil! In this blog post, we’ll dig into what rosehip oil is. We’ll learn where it comes from. We’ll cover its many benefits for your skin, hair, and overall health. Plus, we’ll explore how to use rosehip oil, its risks, and side effects, and how it measures up to other face oils.
Did you know?
Rosehip oil, often called rosehip seed oil, hails from the seeds of the wild rose bush (Rosa rubiginosa). It’s mainly found in Chile and other parts of the globe. The oil is packed with essential fatty acids like linoleic, alpha-linolenic, and oleic acid. Plus, it’s full of nutrients like tocopherol (Vitamin E), carotenoids, and vitamins A and C.
Both the Mayans and Native Americans treasured this oil for its wonderful healing abilities. Today, modern science is astounded by the many skin care benefits it offers.
Rosehip oil is usually extracted through a process called cold-pressing. In this process, they mechanically press oil from the seeds and fruit of the rose plant. This method makes sure we get as many nutrients as possible in the final oil.
In my experience, rose hip oil may help keep your skin hydrated because it is rich in fatty acids. So, you may want to avoid this one if you have oily skin.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, MD
The essential fatty acids in rosehip oil can hydrate your skin? Regular use can help your skin stay moisturized. It does this by strengthening the cell walls which leads to lesser water loss.
Sounds good, right? Here are some of its key hydration benefits:
Besides hydration, rosehip oil also boosts skin moisturization. The linoleic acid in the oil is crucial for keeping the skin’s moisture intact. Plus, the vitamin E present in it enhances its moisturizing effects.
What other moisturization benefits does it offer? Check these out:
Bet you didn’t know that rosehip oil can exfoliate and brighten your skin! The vitamin A and C content in the oil boosts skin cell turnover. This helps promote a smooth texture and a glowing complexion.
Interested in the brightening benefits? Here’s what it has to offer:
The vitamin C content in rosehip oil is very high. Vitamin C is believed to aid in shielding skin cells from the ageing effects of exposure to sunlight. I suggest one might consider using rosehip oil for healthy skin after consulting their skin specialist.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
How about anti-aging effects? Thanks to its high vitamin C content, rosehip oil helps collagen production. This helps reduce the signs of aging like wrinkles and fine lines. The carotenoids in rosehip oil help regulate skin turnover for healthier-looking skin
Want to know more about the benefits of collagen?
Rosehip oil is rich in polyphenols and anthocyanin. This gives it strong anti-inflammatory abilities. It works well in calming skin irritation and inflammation due to eczema, rosacea, and dermatitis.
Here are its anti-inflammatory benefits:
Rosehip oil comes with a unique perk – may help to protect against sun damage! It’s loaded with vitamin C, which shields the skin from harmful UV rays. This may be helpful to lower the risk of skin cancer. Plus, its antioxidant properties may aid in repairing sun-damaged skin and keeping future damage at bay.
Interested in knowing more about its sun damage protection perks? Here they are:
Still not convinced about rosehip oil? It has been found effective in lessening hyperpigmentation and brightening the skin in some cases. The vitamin A (retinoids form) and vitamin C in the oil may help in reducing dark spots, age spots, and other skin discolouration.
Does this ring a bell? Here are the hyperpigmentation reduction benefits:
Rosehip oil’s a high content of essential fatty acids and antioxidants that may aid in the regrowth of tissue and cells. This makes it very useful in reducing scars and fine lines. Studies have shown that regular use of rosehip oil can help fade scars and minimize fine lines, promoting the overall look of your skin.
Curious to know about its benefits in soothing scars?
In my experience, rose hip oil may help keep your skin hydrated because it is rich in fatty acids. So, you may want to avoid this one if you have oily skin.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, B.A.M.S, M.D
The essential fatty acids in rosehip oil may help boost hair growth. They do this by nourishing hair follicles and scalp tissues. The oil also hydrates and fights dryness, contributing to the good health of your hair.
Want to learn more about its hair growth benefits?
Rosehip oil or cream may help tackle acne caused by clogged skin pores. Rosehips contain trans-retinoic acid, a retinoid that helps your body regulate the production of new skin cells. When new cells are produced more often, it is less likely that your pores will become clogged. The retinoids in rosehip oil can help brighten your skin, fight blackheads, and help reduce inflammation.
Doesn’t shiny, vibrant hair sound appealing? Using rosehip oil can enhance the shine, softness, and texture of your hair. It can also help rid you of frizz, leaving your hair looking smooth and perfect.
Curious about the lustre and texture benefits it offers?
Suffering from a dry, itchy scalp and dandruff? Rosehip oil’s moisturizing abilities make it a good choice for managing these issues. It can soothe scalp irritation and help reduce dandruff thanks to its anti-inflammatory properties.
Excited to try out its dandruff and flaking reduction benefits?
The vitamin C content in rosehip oil is very high. Vitamin C is believed to aid in shielding skin cells from the ageing effects of exposure to sunlight. I suggest one might consider using roeship oil for healthy skin after consulting their skin specialist.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Rosehip oil has been a popular remedy for joint pain for years. Research shows that it might provide relief from osteoarthritis. The polyphenols and anthocyanin in the oil can reduce inflammation and provide pain relief. This oil can be useful for people who can’t take NSAIDs or other pain meds.
Want to learn about its osteoarthritis relief benefits?
Rosehip oil is rich in lycopene, a strong antioxidant. It protects the skin from harmful free radicals. This nutrient can also give your immune system a boost, shielding your body from infections and diseases.
Excited to know more about its lycopene and immunity benefits?
Besides relieving osteoarthritis, the oil’s anti-inflammatory properties may provide relief from different forms of joint pains. Applying the oil to painful joints several times a day can provide comfort and ease inflammation.
Curious about its joint pain relief benefits?
Also Read: Cottonseed Oil: Health Benefits, Uses, Side Effects & More!
You can apply rosehip oil to the skin or hair to reap its benefits. It sinks into the skin easily and isn’t sticky. This makes it suitable for all skin types. To include rosehip oil in your skincare routine, put a few drops on your face or body and gently massage. You can also mix rosehip oil with other oils or moisturizers for better results.
For your hair, put a few drops of rosehip oil in your hands and spread it through your hair from root to tip. Want to promote blood flow and boost hair growth? Try massaging the oil into your scalp!
There’s no fixed dosage for rosehip oil. But, applying it to the skin twice daily is generally safe. If you’re a newbie, start with a small amount. Then gradually work your way up based on your needs.
For haircare, toy with the amount that suits your hair type and needs. If you have dry or damaged hair, you might want to apply more. Unsure? Ask your healthcare provider or a hair expert for personalized advice.
Though rare, rosehip oil might cause allergies in some people. Symptoms can go from mild skin irritation to severe anaphylaxis. Before using rosehip oil in your beauty routine, do a patch test. If you see any bad reactions, stop using the oil and consult a healthcare professional.
We don’t have much info on the safety of rosehip oil for pregnant and breastfeeding people. It’s best to avoid the oil during this time or ask your doctor for advice.
Rosehip oil might mess with blood clotting, raise the risk of kidney stones, and even cause blood clots. This can lead to heart trouble and stroke. Do you have any lingering health issues or taking meds that might interact with rosehip oil? Make sure to ask your doctor before using it.
Some components in rosehip oil might clash with certain drugs or health conditions. Always tell your healthcare provider about any supplements or herbal remedies you’re using.
In some cases, vitamin C in Rosehip might not be good for you. It’s unclear how much vitamin C is in rosehip oil or how much is absorbed by your skin. As a result, if you have any of the following conditions, do not use rosehip oil without your doctor’s approval:
Rosehips in any form may increase your bleeding risk. Stop using two weeks before surgery or if you take blood clotting medication.
True, rosehip oil is great for your skin. But other facial oils can offer unique benefits too. For example, jojoba oil closely mimics your skin’s natural oil. So, it’s a great moisturizer for all skin types. Argan oil, another popular skincare ingredient, is loaded with vitamin E and essential fatty acids known to maintain skin’s youthfulness.
Lots of facial oils offer different benefits. Yet, not all might suit every skin type. Some might even cause bad side effects. Like coconut oil, it can block pores and worsen acne-prone skin. It’s vital to choose oils based on your skin type and needs.
Here’s a handy table comparing Rosehip oil to other facial oils:
To sum it up, rosehip oil has many benefits for your skin, hair, and health in general. Its rich mix of essential fatty acids and vitamins makes it great for hydration, anti-ageing, and skin treatment. By using rosehip oil daily, you may keep your hair and skin healthy while enjoying its many benefits.
However, it’s vital to use oil with care and stick to the recommended dosage. Ask your healthcare provider if you have any queries or fears about safely using rosehip oil. With its many benefits and uses, rosehip oil might just be your new favourite skincare product!
Yes, you can generally put rosehip oil on your face up to two times a day. Start with a little and slowly increase as needed.
If you’re pregnant, nursing, or have a history of bleeding disorders, kidney stones, or heart problems, consult your healthcare provider before using rosehip oil.
Due to its collagen-boosting and skin-regenerating properties, rosehip oil can help reduce fine lines and wrinkles around the eyes, often referred to as “crow’s feet.”
They are the same thing and are harvested from the seeds of rose bushes. They are known for being rich in vitamins, antioxidants and essential fatty acids like omega-3 (linolenic acid) and omega-6 (linoleic acid).
When you’re shopping for one, make sure the rosehip oil is packaged in a dark, amber-coloured bottle. This protects it from UV rays, which can make it less effective.
If you buy unrefined or raw rose hip oil, be careful when applying it. These versions are less processed. So, while they’re rich in nutrients, they’re also rich in colour. And that colour can be quite noticeable on your hands, body — and clothes. If you don’t want that rosy-gold hue all over you, try an organic, cold-pressed option.
Store rosehip oil in a cool, dark spot away from sunlight and heat. You can also keep it in your fridge to prolong its life.
Generally, rosehip oil is suitable for all skin types, including sensitive ones. But before you use it, do a patch test to check for allergies. For personalized advice, consult your healthcare provider or dermatologist if you have sensitive skin.
Yes, they can. To help reduce the appearance of scars, wrinkles, blemishes, and skin pigmentation, rosehip oil is particularly efficient. Rosehip oil easily enters the skin and contains protective nutrients including Vitamins C and E, vital fatty acids, and other antioxidants that can lessen discolouration and encourage the synthesis of collagen.
Healthy hair results from the wonderful combination of a healthy diet, healthy lifestyle, good sleep, and the absence of illnesses that affect hair health. Sticking to your hair care routine is crucial for long-lasting shine.
In the pursuit of luscious and healthy locks, many individuals find themselves on prescribed treatment plans specifically designed to address various hair health conditions. Whether your hair fall is due to scalp disorders, hormonal issues, nutritional deficiencies, infections, or other concerns, adherence to the personalised treatment regimen is a key factor in achieving optimal results.
When it comes to hair health, you cannot expect results overnight. Hair growth occurs in a set pattern, and your treatment plan will need time to fix the underlying issues and improve hair health to its best possible state.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the significance of following prescribed treatment plans for hair health and how they contribute to unlocking the full potential of your tresses.
1. Optimising Treatment Efficacy
Prescribed treatment plans for hair health often encompass a combination of topical solutions, oral medications, and lifestyle adjustments tailored to address the root causes of specific conditions. Adherence to these plans is vital to ensure that the prescribed interventions work synergistically. Skipping doses, neglecting topical applications, or disregarding dietary recommendations may compromise the effectiveness of the treatment, hindering the journey to healthier and more vibrant hair.
2. Effective Hair Loss Management
For those navigating the challenges of hair loss, adherence to a prescribed treatment plan is crucial for effective management. Whether it involves medications promoting hair growth, scalp treatments, or dietary changes, consistent adherence contributes to minimising hair shedding and optimising regrowth. Deviating from the prescribed plan may impede progress and limit the desired outcomes in the battle against hair loss.
3. Preventing Complications and Promoting Scalp Health
Individuals dealing with scalp conditions such as dermatitis or psoriasis often receive treatment plans aimed at promoting scalp health. Adherence to prescribed shampoos, medicated treatments, and other recommendations is essential to prevent complications, reduce inflammation, and maintain a healthy scalp environment. Neglecting these guidelines may lead to persistent issues, hindering progress in achieving a balanced and nourished scalp.
4. Accelerating Recovery After Hair Procedures
Following hair procedures such as transplants or other surgical interventions, adherence to a post-procedure treatment plan is critical for a smooth and successful recovery. Whether it involves specialised shampoos, post-operative care instructions, or prescribed medications, consistent adherence helps reduce the risk of complications, promote healing, and enhance overall recovery outcomes.
5. Building Trust in the Patient-Provider Relationship
The relationship between individuals seeking hair health interventions and their healthcare providers is built on trust. Adhering to prescribed treatment plans demonstrates a commitment to the process, fostering trust and collaboration between patients and their healthcare teams. Open communication and active participation in the treatment plan create a foundation for a strong and supportive relationship, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the care provided.
6. Cost-effective Haircare
Adherence to prescribed treatment plans in the realm of hair health can have cost-saving implications. By preventing complications, minimising the need for additional interventions, and promoting long-term hair health, consistent adherence contributes to a more cost-effective approach to haircare. This proactive stance can alleviate the financial burden associated with prolonged or recurrent hair health issues.
7. Enhancing Confidence and Quality of Life
Ultimately, the goal of any hair health intervention is to enhance confidence and improve the quality of life for individuals. Adhering to a prescribed treatment plan contributes significantly to achieving this objective. Whether it’s promoting hair regrowth, maintaining a healthy scalp, or managing specific conditions, following the recommended course of action ensures that individuals can enjoy the full beauty and vitality of their hair.
In the intricate journey of hair health, adherence to prescribed treatment plans emerges as the guiding light that leads to the realisation of healthier and more vibrant locks. From optimising treatment efficacy and managing hair loss to preventing complications and building trust in the patient-provider relationship, the importance of adherence cannot be overstated. As active participants in the quest for beautiful and healthy hair, embracing the prescribed treatment plan is a powerful step toward unlocking the full potential of your tresses.
Also Read: Is Hair Transplant Safe? Unveiling the Research and Efficacy Behind the Procedure
Disclaimer: The information included on this site is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional. Because of unique individual needs, the reader should consult their physician to determine the appropriateness of the information for the reader’s situation.
Ref
Maintaining a consistent medication routine, known as medication adherence, is a critical aspect of managing your health. It involves taking your prescribed medications as directed – the right dose, at the right time, in the right way, and frequency. The consequences of not adhering to your medication plan can be severe, potentially worsening your condition, leading to hospitalisation, or, in extreme cases, even resulting in serious complications.
Numerous factors contribute to patients not following healthcare provider instructions. These include –
To optimise the benefits of your medications, adhering to your prescribed treatment plan is crucial. Establishing a personal connection with your healthcare provider or pharmacist is essential, as they can offer valuable guidance. Here are eight practical tips to help you maintain medication adherence:
1. Consistent Timing: Take your medication at the same time every day to establish a routine.
2. Tie it to Daily Habits: Associate medication with a daily routine, like brushing your teeth or getting ready for bed.
3. Medicine Calendar: Keep a “medicine calendar” with your pill bottles, noting each dose.
4. Pill Containers: Utilize pill containers with sections for different doses and refill them at the same time each week.
5. Set Timers: Invest in timer caps for pill bottles or pill boxes with timer functions to remind you when your next dose is due.
6. Travel Preparation: When travelling, bring sufficient medication and a few extra days’ supply in case of delays.
7. Flying Safely: Carry your medication in your carry-on to avoid potential damage due to temperature fluctuations in cargo holds.
8. Consult with Your Pharmacist: Leverage the expertise of your pharmacist to optimise your medication routine.
Medication adherence is the linchpin of successful healthcare management, ensuring that the benefits of prescribed treatments are fully realised. By implementing these tips and maintaining a strong connection with your healthcare provider, you can take charge of your health, effectively manage chronic conditions, and promote long-term well-being. Remember, your commitment to adhering to your prescribed treatment plan plays a pivotal role in achieving the best possible outcomes for your health.
Disclaimer: The information included on this site is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional. Because of unique individual needs, the reader should consult their physician to determine the appropriateness of the information for the reader’s situation.
Ref
Doctors often stress the importance of a night of uninterrupted sleep. We have all experienced the effects of quality sleep. We wake up the next morning feeling refreshed, focused and ready for the day’s work. We have also heard how sound sleep is crucial for our brain health, as well as immunity.
But now, new studies have discovered yet another benefit of sleep. It can help to manage diabetes more effectively!
What is the link between sound sleep and diabetes control? Let’s find out!
It has been found that irregularities in your sleep routine increase the chances of developing diabetes or affect your body’s ability to use glucose, which will lead to an increase in blood sugar levels. Similarly, if a person has diabetes, insufficient sleep can upset diabetes management steps such as your portion control medication (your body may not respond as well to the medicines) and it will also have a negative impact on your psychological health, which will make diabetes management more challenging.
There is ongoing scientific investigation into why poor quality sleep leads to a likelihood of diabetes and why diabetes management becomes difficult if one doesn’t get enough sleep. It is believed that not enough good sleep increases cortisol levels and oxidative stress and decreases insulin. Together, these factors make high blood sugar levels quite likely.
When you are not getting enough sleep, a few problems will crop up, which may make diabetes likely and its management very challenging.
The duration of sleep that one needs to stay healthy depends on a person’s age. The American Academy of Sleep Medicine and Sleep Research Society advises adults to get between 7-9 hours of sleep daily. Teenagers should get 8-10 hours of sleep. Senior citizens are recommended 7-8 hours or more of daily sleep.
Our hectic lifestyles, anxiety, responsibilities and the pervasive presence of social media and streaming services make it difficult to get the right amount of sleep every day.
Sleep problems not only increase the chances of developing diabetes but it has been found that people already diagnosed with diabetes have a hard time getting enough sleep and this makes the situation worse.
However, a few tips can help you optimise your sleep.
If you are diabetic
Diabetes is a condition that must be managed rigorously. As per reports, 10.1 crore people in India live with diabetes and the number is increasing. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to severe health complications that may even become fatal. But with proper management strategies, one can live a healthy life. A healthy sleep routine can help a person with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels better. It can also help a person with normal blood sugar levels lower the likelihood of developing diabetes at a later stage.
Disclaimer: The information included on this site is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional. Because of unique individual needs, the reader should consult their physician to determine the appropriateness of the information for the reader’s situation.
Ref-
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4674464/
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1944600#:~:text=As%20per%20Indian%20Council%20of,of%20diabetes%20is%2010.1%20crores

Recent talks about gut health have become more frequent. In these talks, Leaky Gut Syndrome often becomes a hot topic of debate. It leaves many people puzzled and eager for answers. This blog goes into detail on Leaky Gut Syndrome. It aims to tell fact from fiction and offer info that might help you better your gut health.
This article covers the description of Leaky Gut Syndrome, the doubts around it, its possible causes, how it relates to different diseases and how to perhaps better overall gut health. Won’t you join us on this info-filled path?
Did you know?
Everyone’s guts are semi-permeable. The mucous lining of our intestines is designed to absorb water and nutrients from our food into our bloodstream. But some people have increased intestinal permeability or hyperpermeability. That means their guts let more than water and nutrients through — they “leak”. Leaky Gut Syndrome, or higher gut porosity, is when the gut walls become more porous. This happens when tight links in the gut lining slacken. Harmful things like bacteria, food bits and toxins then seep through the gut walls and into the blood.
Several myths and misbeliefs about Leaky Gut Syndrome exist. Let’s debunk a few:
Whether Leaky Gut Syndrome is real and how important it is remain unsettled in the medical world. Many health experts do not accept it as diagnosable. Instead, they think it could be an effect of many different gut diseases.
Even though doubts over Leaky Gut Syndrome’s truth persist, some science-based facts suggest that high gut porosity is real. It seems to play a part in various health states like obesity, autoimmune problems and an inflammatory bowel syndrome (IBS).
Supporters of Leaky Gut Syndrome often link it to various health problems. These may include autism, worry, sadness, eczema and cancer. But there’s not enough research linking these claims to leaky gut. We need more studies to set a clear cause-effect relationship.
Leaky Gut Syndrome can be brought about by many things. Here are some:
An unbalanced gut tiny creature mix can badly affect total gut health. This includes its barrier work. The tiny creatures in our gut are key for proper digestion, immune system work and protecting the gut wall. When the balance between good and bad bacteria in the gut is upset, it could lead to lingering swollen changes in gut cells. This, in the end, causes Leaky Gut Syndrome.
Some diseases have been linked to Leaky Gut Syndrome. These include:
Celiac disease is an autoimmune (self-attack) disease caused by not tolerating gluten. Leaky Gut Syndrome has been noted in people with celiac disease. Studies show that eating gluten heavily boosts gut porosity in these patients.
Type 1 diabetes, an autoimmune (self-attack) disease, has been tied to higher gut porosity. Studies suggest that the immune reaction that wipes out insulin-making beta cells in the pancreas might be sparked off by outside things “leaking” through the gut.
High gut porosity is a major factor in Crohn’s disease, a lasting digestive problem marked by lingering swelling of the gut tract.
People with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) might have higher gut porosity. IBS is a digestive problem defined by diarrhea, constipation, or both.
People with food allergies might have a weak gut barrier. This suggests that a leaky gut might play a part in developing food allergies.
Even though there’s no complete proof, some studies have shown that some kids with autism have high gut porosity. We need more studies to clarify the link between leaky gut and autism.
Other diseases that may be a cause of leaky gut include:
There’s a fight over whether Leaky Gut Syndrome is a root or just a sign of lasting diseases. Some think that high gut porosity is a sign of a lasting disease and not a cause. But, some animal studies show that high gut porosity happens before certain diseases. This means leaky gut plays a part in these diseases starting.
In all, we do not have enough evidence to say for sure if leaky gut is the true cause of lasting diseases. We need more research to better understand the link between leaky gut and various health problems.
Many other diseases have been suggested as possible consequences of leaky gut syndrome. The idea is that “toxins” from your intestines may leak into your bloodstream and cause an inflammatory response. Chronic low-grade inflammation may, indeed, be a factor in many of these diseases, including metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes, arthritis, chronic fatigue syndrome, asthma and fibromyalgia. But the rest remains unclear.
In my opinion, your gut can be strengthened by eating a balanced diet that contains all the essential macronutrients and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals). Your gut lining may in particular benefit from the use of vitamin D and the amino acid L-glutamine.
Dr. Rajeev Singh, BAMS
Those with Leaky Gut Syndrome may show a range of signs. Here are some common ones:
Time to break down these points into simpler terms.
| Type | Symptoms |
| Gut | Diarrhea, constipation, bloating, gas, belly pain |
| Skin | Eczema, acne |
| Mental Health | Worry, sadness, brain fog, hard time focusing |
| Immune System | often getting sick, issues in the body’s defence mechanisms, food allergies |
In my knowledge, the erosion of the gut lining is one of the known causes of a leaky gut. This could be due to a long-term illness, drug or alcohol abuse, or radiation therapy. I strongly recommend one should consult their gastroenterologist for management of a leaky gut.
Dr. Siddharth Gupta, MD
Also Read: What is Kefir? A Comprehensive Guide to Its Health Benefits
Given that Leaky Gut Syndrome isn’t a diagnosed medical state, it’s hard for health experts to spot it. Plus, its symptoms are vague; therefore it’s hard to locate the exact cause of gut troubles.
Right now, there are no standard tests for spoting leaky gut. Depending on the symptoms and medical past, health experts might carry out tests to judge the work of the gut system, like blood tests, urine tests, stool tests, tissue biopsy, or imaging studies like confocal endomicroscopy. Finding and treating any veteran states can help deal with and maybe relieve symptoms linked to leaky gut.
While there’s no special treatment for Leaky Gut Syndrome, some things might help better gut health and lessen symptoms linked to leaky gut:
Dodging Trigger Foods
Dodging foods that can make gut symptoms worse or cause swelling is key. Common trigger foods are factory-made foods, refined carbs, fake sweeteners and too much sugar.
Focusing on Nutrient-packed Foods
Focusing on a nutrient-packed diet filled with whole foods, like fruits, veggies, lean proteins and healthy fats, can support gut health and lessen swelling.
Including foods high in probiotics, like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut and kimchi, or taking probiotic extras, can help restore the balance of good bacteria in the gut. This makes for a better gut system.
Low FODMAP Diet
This specific diet is often suggested for people who have IBS and certain food sensitivities because it systematically eliminates most of the common food triggers. Using it briefly may give your gut the rest it needs to repair, while also clueing you in to which food triggers you are sensitive to.
Some extras and natural remedies, like L-glutamine, collagen, or curcumin, might help support gut lining repair and manage symptoms linked to leaky gut.
Handling stress through techniques like focus, meditation, or yoga and following a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and sleep can help better gut health and lessen symptoms linked to leaky gut.
Time to unfold these aspects into simpler terms.
| Way of dealing | Action |
| Dietary changes | Dodge trigger foods; focus on nutrient-packed, whole foods |
| Probiotics | Include food or supplements high in probiotics |
| Extras and natural remedies | Think about extras like L-glutamine, collagen, or curcumin |
| Stress handling and changing lifestyle habits | Deal with stress, exercise often and get good sleep |
Leaky Gut Syndrome continues to be a hot topic of debate, with ongoing research striving to uncover its causes, implications and potential treatments. While some things remain controversial, it’s clear that gut health plays a crucial role in overall wellness. By prioritizing a nutrient-dense diet, managing stress and living a healthy lifestyle, you may positively affect your gut health and reduce symptoms related to leaky gut. Engaging in these habits can only help you move towards a healthier, happier life.
As the field of medicine continues to expand its knowledge, more research may shed a brighter light on the complex world of gut health and unveil new ways of treating and preventing states linked to Leaky Gut Syndrome.
Signs of Leaky Gut Syndrome might include lasting diarrhea or constipation, bloating, gas, belly pain, eczema, acne, worry, sadness, brain fog, hard time focusing, often getting sick and food allergies or sensitivities.
Three kinds of food that might lead to leaky gut are factory-made foods, refined carbs and too much sugar. It is good to limit these in your diet and focus on nutrient-packed, whole foods to support gut health.
To naturally heal your leaky gut, think about making dietary changes (focusing on nutrient-packed, whole foods), including probiotics, dealing with stress and living a healthy lifestyle – including regular exercise and enough sleep.
If you leave leaky gut untreated, the higher gut porosity might lead to lingering swelling. This can cause many health problems, including autoimmune disorders, gut diseases and potentially other conditions.
While there’s no direct evidence that leaky gut itself causes weight gain, factors linked to leaky gut (like a bad diet, swelling, or stress) may also play a part in weight gain or hard time losing weight.
The time it takes to heal leaky gut syndrome might vary depending on the person, depth of the harm and how well the treatment works. Changes in diet and lifestyle, as well as extras, may take several weeks or months to show clear improvements in gut health. Being constant and sticking to a healthy lifestyle are key for long-term success in healing leaky gut.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information and before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
Links and product recommendations in the information provided here are advertisements of third-party products available on the website. PharmEasy does not make any representation on the accuracy or suitability of such products/services. Advertisements do not influence the editorial decisions or content. The information in this blog is subject to change without notice. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. It is your responsibility to review this disclaimer regularly for any changes.
Next Page »« Previous Page